Koa 简介
Koa (koajs) 是一个新的 web 框架,由 Express 幕后的原班人马打造,致力于成为 web 应用和 API 开发领域中的一个更小、更富有表现力、更健壮的基石。
第一个 Koa 应用
- 首先创建一个空目录,然后在终端执行
npm init -y快速生成一个npm项目。 - 安装
Koa,执行yarn add koa -S。 - 创建
src目录并编写index.js。
|-- koa
|-- node_modules
|-- src
|-- index.js
|-- package-lock.json
|-- package.json
// index.js
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async ctx => {
ctx.body = 'Hello world';
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('server is running at http://localhost:3000');
});
执行 node src/index.js,打开浏览器访问 http://localhost:3000,就可以看到 Hello world 了。
Request 属性、路由、app.use()链式处理
上一节写的一点代码是远远达不到需求的,有一下几个问题需要解决。
- request、response 是什么?method 的什么类型?
- 特定的 api url 要执行特定的方法。(router)
- ctx、中间件
request、response 是什么?method 的什么类型
request、response、method 都保存在 ctx 上下文当中,ctx 中包含了许多请求与响应的信息,需要用到什么只需要在 ctx 中直接获取就可以了。
特定的 api url 要执行特定的方法。(router)
这里我们使用一个 Koa 的中间件 koa-router。
执行 yarn add koa-router -S 安装 koa-router。
修改 index.js 代码
// index.js
const Koa = require('koa');
const Router = require('koa-router');
const app = new Koa();
const router = new Router();
router.get('/', async ctx => {
ctx.body = 'Home';
});
router.get('/api', async ctx => {
ctx.body = 'API';
});
app.use(router.routes()).use(router.allowedMethods());
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('server is running at http://localhost:3000');
});
这里就是 koa-router 的简单用法。
用浏览访问 http://localhost:3000 和 http://localhost:3000/api,就能看到不同的响应。
ctx、中间件
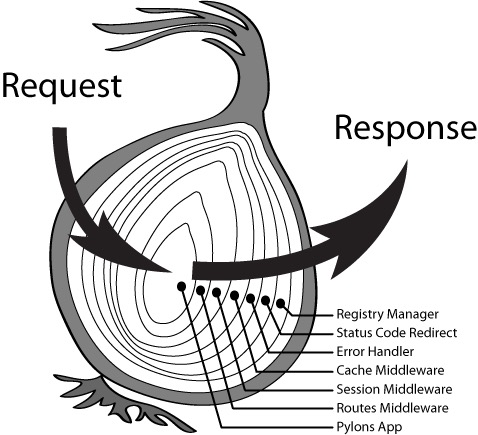
const Koa = require("koa");
const app = new Koa();
app.use(asycn (ctx, next) => {
console.log(1);
await next();
console.log(2);
});
app.use(asycn (ctx, next) => {
console.log(3);
await next();
console.log(4);
});
app.use(asycn (ctx, next) => {
console.log(5);
await next();
console.log(6);
});
app.listen(3000);
// 1
// 3
// 5
// 6
// 4
// 2
上面的写法我们按照官方推荐,使用了 async/await,但如果是同步代码不使用也没有关系,这里简单的分析一下执行机制,第一个中间件函数中如果执行了 next ,则下一个中间件会被执行,依次类推,就有了我们上面的结果。
Koa 开发 RESTful 接口,GET&POST 获取数据及数据格式化方法
首先需要安装几个中间件
- koa-router
- koa-body(功能齐全的 koa body 解析器中间件。支持 multipart、urlencoded 和 json 请求报文)
- @koa/cors(koa 跨域处理中间件)
yarn add koa-router koa-body @koa/cors -S
获取 POST 请求体内容
const Koa = require('koa');
const Router = require('koa-router');
const cors = require('@koa/cors');
const koaBody = require('koa-body');
const app = new Koa();
const router = new Router();
router.get('/', async ctx => {
ctx.body = 'Home';
});
router.get('/api', async ctx => {
ctx.body = 'API';
});
router.post('/post', async ctx => {
const { body } = ctx.request;
ctx.body = {
...body,
};
});
app.use(koaBody());
app.use(cors());
app.use(router.routes()).use(router.allowedMethods());
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('server is running at http://localhost:3000');
});
使用 postman 工具向 http://localhost:3000/post 发送 JSON 数据,可以被原样返回。
获取 GET 请求参数
更新 api 接口
router.get('/api', async ctx => {
const params = ctx.request.query;
ctx.body = {
name: params.name,
age: params.age,
};
});
请求接口 http://localhost:3000/api?name=huiazir&age=22,就会将name和age返回。
Koa 进阶配置
如果把接口全都写在index.js,那么index.js将会变得异常冗余,这节就来优化一下。
开发目录结构
先把 index.js 清空,并更新目录接口
|-- koa
|-- node_modules
|-- src
|-- api (所有接口)
|-- routes (路由路径)
|-- routes.js
|-- index.js (入口)
|-- package-lock.json
|-- package.json
添加两个接口
// scr/api/a.js
module.exports = ctx => {
ctx.body = {
message: 'From A',
};
};
// scr/api/b.js
module.exports = ctx => {
ctx.body = {
message: 'From B',
};
};
添加 A、B 两个路由模块
// src/routes/aRouter.js
const KoaRouter = require('koa-router');
const a = require('../api/a');
const router = new KoaRouter();
router.get('/a', a);
module.exports = router;
// src/routes/bRouter.js
const KoaRouter = require('koa-router');
const b = require('../api/b');
const router = new KoaRouter();
router.get('/b', b);
module.exports = router;
路由压缩合并
将两个路由模块压缩合并并导出,这里要安装一个包 koa-combine-routers ,执行 yarn add koa-combine-routers -S 安装。然后编写 src/routes/routes.js文件。
// src/routes/routes.js
const combine = require('koa-combine-routers');
const aRouters = require('./aRouter');
const bRouters = require('./bRouter');
module.exports = combine(aRouters, bRouters);
这样就完成了两个路由的拼装。接下来我们更新入口文件 src/index.js
// src/index.js
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
const router = require('./routes/routes');
app.use(router());
app.listen(3000);
到此路由合并就完成了。
Koa 安全 header 处理
这里需要使用 koa-helmet 就可以实现安全的 header。
使用 yarn add koa-helmet -S 命令安装、并添加这个中间件。
// src/index.js
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
const helmet = require('koa-helmet');
const router = require('./routes/routes');
app.use(helmet());
app.use(router());
app.listen(3000);
Koa 静态资源处理
使用 koa-static 中间件来实现静态资源处理。
使用 yarn add koa-static -S 命令安装、并添加配置这个中间件。
我们在根目录下创建 public 目录,并放入一张图片,然后修改入口代码。
// src/index.js
const path = require('path');
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
const helmet = require('koa-helmet');
const static = require('koa-static');
const router = require('./routes/routes');
app.use(helmet());
app.use(static(path.resolve(__dirname, '../public')));
app.use(router());
app.listen(3000);
访问 http://localhost:3000/koa.png 就可以看到图片啦!
Koa 配置开发热加载、ES6 语法支持及 Webpack 配置
热加载
首先安装 nodemon 来监听文件的变化。
yarn add nodemon -D
在 package.json 中添加一句脚本
{
// ...
"scripts": {
"start": "nodemon src/index.js"
}
// ...
}
然后执行 yarn start 命令就可以监控文件的变化啦!
ES6 语法支持
首先我们来安装 Webpack
yarn add webpack webpack-cli -D
然后再安装一些插件
- clean-webpack-plugin
- webpack-node-externals
- @babel/core
- @babel/node (后续做调试用到)
- @babel/preset-env
- @babel/plugin-transform-runtime
- @babel/runtime
- babel-loader
- cross-env (设置环境变量的)
yarn add clean-webpack-plugin webpack-node-externals @babel/core @babel/node @babel/preset-env @babel/plugin-transform-runtime @babel/runtime babel-loader cross-env -D
配置 webpack
// webpack.config.js
const path = require('path');
const nodeExternals = require('webpack-node-externals');
const { CleanWebpackPlugin } = require('clean-webpack-plugin');
const config = {
target: 'node',
mode: 'development',
entry: {
server: path.resolve(__dirname, './src/index.js'),
},
output: {
filename: '[name].js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, './dist'),
},
devtool: 'eval-source-map',
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.(js|jsx)$/,
use: ['babel-loader'],
exclude: [path.resolve(__dirname, './node_modules')],
},
],
},
externals: [nodeExternals()],
plugins: [new CleanWebpackPlugin()],
node: {
console: true,
global: true,
process: true,
Buffer: true,
path: true,
setImmediate: true,
__filename: true,
__dirname: true,
},
};
module.exports = config;
配置 babel
// .babelrc
{
"presets": [
[
"@babel/preset-env",
{
"targets": {
"node": "current"
}
}
]
],
"plugins": ["@babel/plugin-transform-runtime"]
}
这样之后我们可以改用 ES Module 来引入模块,将修改代码成 ES6 语法之后执行 npx babel-node scr/index.js 来验证 babel 配置是否生效。
如果生效了就可以重新配置我们的 package.json 了
{
// ...
"scripts": {
"start": "nodemon --exec babel-node src/index.js"
}
// ...
}
如何调试 webpack、如何配置 VSCode 调试
调试 webpack
我们如何调试才能知道 Webpack 配置是否正确呢?console.log()是一种方式,我们也可以使用 node 来进行调试。
npx node --inspect-brk ./node_modules/.bin/webpack --inline --progress
$ npx node --inspect-brk ./node_modules/.bin/webpack --inline --progress
Debugger listening on ws://127.0.0.1:9229/3f3ff823-f71f-490d-bdb3-d8ecb8c90a9a
For help, see: https://nodejs.org/en/docs/inspector
执行这条命令就可以在 Chrome 中调试了,我们在浏览器中输入 chrome://inspect/#devices 就可以进入 DevTools 界面,然后选择要调试的 Remote Target,点击 inspect 就可以看到我们熟悉的 Chrome 调试工具了。
我们也可以将这段脚本添加到 package.json 中
{
// ...
"scripts": {
"start": "nodemon --exec babel-node src/index.js",
"webpack:debug": "npx node --inspect-brk ./node_modules/.bin/webpack --inline --progress"
}
// ...
}
配置 VSCode 调试
-
我们点开 VSCode 的 debugger(小虫子),点考之后默认情况下是没有配置的,我们需要自行配置,点击创建 launch.json 文件,选择 node.js 环境。
-
点及右下角的添加配置,然后输入 nodemon,回车确定
-
配置参数
// .vscode/launch.json
{
// 使用 IntelliSense 了解相关属性。
// 悬停以查看现有属性的描述。
// 欲了解更多信息,请访问: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"type": "node",
"request": "launch",
"name": "nodemon",
"runtimeExecutable": "${workspaceFolder}/node_modules/.bin/nodemon",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/src/index.js",
"restart": true,
"console": "integratedTerminal",
"internalConsoleOptions": "neverOpen",
"skipFiles": ["<node_internals>/**"],
"runtimeArgs": ["--exec", "babel-node"]
}
]
}
配置好之后点的 debugger 就可以调试了。
优化 Webpack 配置、npm 构建脚本
通过上几节的代码我们了解 Koa 的基本使用,但是还不能达到生产环境的要求,还存在以下几个问题。
- 没有使用 Koa-body 来解析 post 请求过来的数据
- 只配置了开发环境的 webpack 没有配置生产环境的
解决问题之前先介绍两个个依赖包
npm-check-updates,它用来检查npm依赖包有没有新的版本。全局安装yarn global add npm-check-updates,在项目中执行ncm来检查更新项目koa-compose整合 koa 中间件,在项目中安装yarn add koa-compose -S
导入 koa-body、@koa/cors 等中间件
// src/index.js
import path from 'path';
import Koa from 'koa';
import helmet from 'koa-helmet';
import kosStatic from 'koa-static';
import router from './routes/routes';
import koaBody from 'koa-body';
import koaCors from '@koa/cors';
import compose from 'koa-compose';
const app = new Koa();
const middleware = compose([
koaCors(),
koaBody(),
helmet(),
kosStatic(path.resolve(__dirname, '../public')),
router(),
]);
app.use(middleware);
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('server is running at http://localhost:3000/');
});
配置生产环境的 Webpack
首先在工程目录下创建 config 文件夹并创建配置文件如下:
|-- koa
|-- config
|-- utils.js (工具函数)
|-- webpack.config.base.js (公共配置)
|-- webpack.config.dev.js (开发环境配置)
|-- webpack.config.prod.js (生产环境配置)
// config/utils.js
const path = require('path');
exports.resolve = function (_path) {
return path.join(__dirname, '..', _path);
};
exports.APP_PATH = exports.resolve('');
exports.SRC_PATH = exports.resolve('src');
exports.DIST_PATH = exports.resolve('dist');
先书写一下 webpack.config.base.js
// webpack.config.base.js
const webpack = require('webpack');
const path = require('path');
const nodeExternals = require('webpack-node-externals');
const { CleanWebpackPlugin } = require('clean-webpack-plugin');
const { APP_PATH, DIST_PATH, SRC_PATH } = require('./utils');
const config = {
target: 'node',
entry: {
server: path.resolve(SRC_PATH, './index.js'),
},
output: {
filename: '[name].js',
path: path.resolve(DIST_PATH),
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.(js|jsx)$/,
use: ['babel-loader'],
exclude: [path.resolve(APP_PATH, './node_modules')],
},
],
},
externals: [nodeExternals()],
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(),
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': {
NODE_ENV:
process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ||
process.env.NODE_ENV === 'prod'
? "'production'"
: "'development'",
},
}),
],
node: {
console: true,
global: true,
process: true,
Buffer: true,
path: true,
setImmediate: true,
__filename: true,
__dirname: true,
},
};
module.exports = config;
这里我们用到了 DefinePlugin``,DefinePlugin 允许创建一个在编译时可以配置的全局常量。这可能会对开发模式和生产模式的构建允许不同的行为非常有用。
接下来写 webpack.config.dev.js 。我们需要合并两个配置文件,所以需要 webpack-merge 来帮助我们合并配置,现在安装它 yarn add webpack-merge -D,然后编写 webpack.config.dev.js。
// webpack.config.dev.js
const merge = require('webpack-merge');
const baseConfig = require('./webpack.config.base');
const config = merge(baseConfig, {
mode: 'development',
devtool: 'eval-source-map',
stats: { children: false }, // 屏蔽一些统计信息
});
module.exports = config;
接下来我们需要配置生产环境下的 webpack 配置,通常在生产环境下,我们需要给 js 代码做一些打包压缩的处理。
这里要使用一个 webpack 插件 TerserWebpackPlugin,先来安装一下 yarn add terser-webpack-plugin -D。
// webpack.config.prod.js
const webpackMerge = require('webpack-merge');
const TerserPlugin = require('terser-webpack-plugin');
const baseConfig = require('./webpack.config.base');
const webpackConfig = webpackMerge(baseConfig, {
mode: 'production',
optimization: {
minimize: true,
minimizer: [
new TerserPlugin({
terserOptions: {
warnings: false,
compress: {
warnings: false,
drop_console: false,
drop_debugger: true,
},
output: { comments: false, beautify: false },
mangle: true,
},
sourceMap: false,
parallel: true,
}),
],
},
stats: { children: false, warnings: false },
});
module.exports = webpackConfig;
Koa 应用打包优化
代码分割
我们可以先对 webpack 进行一个打包优化,使用代码分割来提取公共模块。修改一下 webpack.config.prod.js
// webpack.config.prod.js
const webpackMerge = require('webpack-merge');
const TerserPlugin = require('terser-webpack-plugin');
const baseConfig = require('./webpack.config.base');
const webpackConfig = webpackMerge(baseConfig, {
mode: 'production',
optimization: {
minimize: true,
minimizer: [
new TerserPlugin({
terserOptions: {
warnings: false,
compress: {
warnings: false,
drop_console: false,
drop_debugger: true,
},
output: { comments: false, beautify: false },
mangle: true,
},
sourceMap: false,
parallel: true,
}),
],
splitChunks: {
cacheGroups: {
commons: {
name: 'commons',
chunks: 'initial',
minChunks: 2,
enforce: true,
},
},
},
},
stats: { children: false, warnings: false },
});
module.exports = webpackConfig;
使用 splitChunks 来提取公共代码,实现代码分割。
构建脚本
在这之前,我们先安装一个依赖包 cross-env,它能保证跨平台下环境变量能够正确设置。
yarn add cross-env -D
然后我们在 package.json 中添加构建脚本
{
// ...
"scripts": {
"start": "nodemon --exec babel-node src/index.js",
"webpack:debug": "npx node --inspect-brk ./node_modules/.bin/webpack --inline --progress",
"build": "cross-env NODE_ENV=prod webpack --config config/webpack.config.prod.js",
"dev": "cross-env NODE_ENV=dev nodemon --exec babel-node --inspect src/index.js",
"clean": "rimraf dist"
}
// ...
}