二叉树新建
function Node(data, left, right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
Node.prototype = {
show: function () {
console.log(this.data);
}
}
function Tree() {
this.root = null;
}
Tree.prototype = {
insert: function (data) {
var node = new Node(data, null, null);
if (!this.root) {
this.root = node;
return;
}
var current = this.root;
var parent = null;
while (current) {
parent = current;
if (data < parent.data) {
current = current.left;
if (!current) {
parent.left = node;
return;
}
} else {
current = current.right;
if (!current) {
parent.right = node;
return;
}
}
}
},
preOrder: function (node) {
if (node) {
node.show();
this.preOrder(node.left);
this.preOrder(node.right);
}
},
middleOrder: function (node) {
if (node) {
this.middleOrder(node.left);
node.show();
this.middleOrder(node.right);
}
},
laterOrder: function (node) {
if (node) {
this.laterOrder(node.left);
this.laterOrder(node.right);
node.show();
}
},
getMin: function () {
var current = this.root;
while(current){
if(!current.left){
return current;
}
current = current.left;
}
},
getMax: function () {
var current = this.root;
while(current){
if(!current.right){
return current;
}
current = current.right;
}
},
getDeep: function (node,deep) {
deep = deep || 0;
if(node == null){
return deep;
}
deep++;
var dleft = this.getDeep(node.left,deep);
var dright = this.getDeep(node.right,deep);
return Math.max(dleft,dright);
}
}
var t = new Tree();
t.insert(3);
t.insert(8);
t.insert(1);
t.insert(2);
t.insert(5);
t.insert(7);
t.insert(6);
t.insert(0);
console.log(t);
// t.middleOrder(t.root);
console.log(t.getMin(), t.getMax());
console.log(t.getDeep(t.root, 0));
console.log(t.getNode(5,t.root));
二叉树查找
递归法查找
- 先从根节点查找
- 如果目标值等于根节点的值,返回
- 如果目标值小于根节点的值,则去左子树找
- 如果目标值大于根节点的值,则去右子树找
- 依次把左子树和右子树当作根节点递归查找
/**
* data 目标值
* node 树
**/
function getNode(data,node){
if(node){
if(data == node.data){
return node;
}else if(data < node.data){
return getNode(data,node.left)
}else if(data > node.data){
return getNode(data,node.right)
}
}else{
return null;
}
}
二分查找
- 二分查找的条件是必须是有序的线性表。
- 和线性表的中点值进行比较,如果小就继续在小的序列中查找,如此递归直到找到相同的值
/**
* data 目标值
* arr 有序线性表
* start 开始的index
* end 结束的index
**/
function binarySearch(data, arr, start, end) {
if (start > end) {
return -1;
}
var mid = Math.floor((end + start) / 2);
if (data == arr[mid]) {
return mid;
} else if (data < arr[mid]) {
return binarySearch(data, arr, start, mid - 1);
} else {
return binarySearch(data, arr, mid + 1, end);
}
}
var arr = [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4, 6, 7, 8]
console.log(binarySearch(1, arr, 0, arr.length-1));
二叉树遍历
先序(根->左->右),中序(左->根->右),后序(左->右->根)。如果访问有孩子的节点,先处理孩子的,随后返回
无论先中后遍历,每个节点的遍历如果访问有孩子的节点,先处理孩子的
以下边的二叉树为例
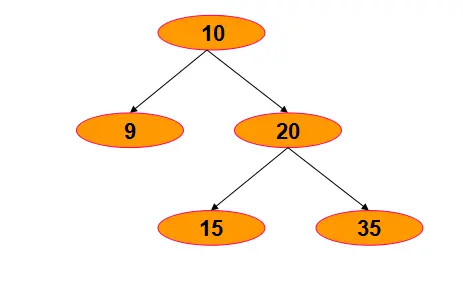
前序遍历
根节点——左子树——右子树
图上的输出顺序为 10-9-20-15-35
递归实现
function preOrder(root,array=[]){
if(root){
array.push(root.val);
preOrder(root.left,array);
preOrder(root.right,array)
}
return arrag;
}
非递归实现
- 取跟节点为目标节点,开始遍历
- 1.访问目标节点
- 2.左孩子入栈 -> 直至左孩子为空的节点
- 3.节点出栈,以右孩子为目标节点,再依次执行1、2、3
var preorderTraversal = function (root) {
const result = [];
const stack = [];
let current = root;
while (current || stack.length > 0) {
while (current) {
result.push(current.val);
stack.push(current);
current = current.left;
}
current = stack.pop();
current = current.right;
}
return result;
};
中序遍历
左子树——根节点——右子树 图上的输出顺序为 9-10-15-20-35
访问完10节点过后,去找的是20节点,但20下还有子节点,因此先访问的是20的左儿子15节点。由于15节点没有儿子了。所以就返回20节点,访问20节点。最后访问35节点
递归实现
function inOrder(root,array=[]){
if(root){
inOrder(root.left,array)
array.push(root.val)
inOrder(root.right,array)
}
return array;
}
非递归实现
- 取跟节点为目标节点,开始遍历
- 1.左孩子入栈 -> 直至左孩子为空的节点
- 2.节点出栈 -> 访问该节点
- 3.以右孩子为目标节点,再依次执行1、2、3
var inorderTraversal = function (root) {
const result = [];
const stack = [];
let current = root;
while (current || stack.length > 0) {
while (current) {
stack.push(current);
current = current.left;
}
current = stack.pop();
result.push(current.val);
current = current.right;
}
return result;
};
后序遍历
左子树——右子树——根节点 图上的输出顺序为 9-35-15-20-10
先访问9节点,随后应该访问的是20节点,但20下还有子节点,因此先访问的是20的左儿子15节点。由于15节点没有儿子了。所以就去访问35节点,由于35节点也没有儿子了,所以返回20节点,最终返回10节点
递归实现
var postorderTraversal = function (root, array = []) {
if (root) {
postorderTraversal(root.left, array);
postorderTraversal(root.right, array);
array.push(root.val);
}
return array;
};
非递归实现
- 取跟节点为目标节点,开始遍历
- 1.左孩子入栈 -> 直至左孩子为空的节点
- 2.栈顶节点的右节点为空或右节点被访问过 -> 节点出栈并访问他,将节点标记为已访问
- 3.栈顶节点的右节点不为空且未被访问,以右孩子为目标节点,再依次执行1、2、3
var postorderTraversal = function (root) {
const result = [];
const stack = [];
let last = null; // 标记上一个访问的节点
let current = root;
while (current || stack.length > 0) {
while (current) {
stack.push(current);
current = current.left;
}
current = stack[stack.length - 1];
if (!current.right || current.right == last) {
current = stack.pop();
result.push(current.val);
last = current;
current = null; // 继续弹栈
} else {
current = current.right;
}
}
return result;
}