前言
数组是 JavaScript 最常见的一种数据结构,本文整理了几乎所有与 Array 操作相关的 Api , 很基础也很重要,希望本文对你有所帮助。
Array 的原型方法
添加元素
push
将一个或者多个元素添加至数组末尾处,并返回数组长度。
let arr = [1,2,3,4]
let length = arr.push(5,6)
console.log(length,arr) // => 6 [1,2,3,4,5,6]
unshift
将一个或多个元素添加到数组到开头,并返回数组长度。
let arr = [1,2,3,4]
let length = arr.unshift(0)
console.log(length, arr); //=> 5 [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 ]
删除元素
pop
从数组中删除最后一个元素,若对空数组调用 pop 则返回 undefined ,会更改源数组。
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
let delValue = arr.pop();
console.log(delValue, arr); //=> 4 [ 1, 2, 3 ]
shift
删除数组中第一个元素,若空数组返回 undefined ,会更改源数组。
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4];
let delValue = arr.shift();
console.log(delValue, arr); //=> 1 [ 2, 3, 4 ]
delete
删除数组元素,会让数组中出现 undefined , 很少使用。
let temp = [123, 456, 789];
delete temp[1];
console.log(temp.length, temp[1]); // 3, undefined
替换、删除、指定位置添加
splice
一个功能强大的函数,它可以通过删除/替换/添加,的方式修改数组,并返回修改的内容(以数组的格式)
//替换
let temp = [123, 456, 789];
temp.splice(1,1,'th') // [456]
console.log(temp) //[123,'th',789]
//删除
let temp = [123, 456, 789];
temp.splice(0,1) //[123]
console.log(temp) //[456,789]
//添加
let temp = [123, 456, 789];
temp.splice(2,0,'tj')
console.log(temp) //[123,456,'tj',789]
拷贝数组
slice
浅拷贝了愿数组,返回一个新的数组对象。
//元素是基本类型数据
const animals = ['ant', 'bison', 'camel', 'duck', 'elephant'];
console.log(animals.slice(2)); // ["camel", "duck", "elephant"]
console.log(animals.slice(2, 4)); // ["camel", "duck"]
console.log(animals.slice()); // ['ant', 'bison', 'camel', 'duck', 'elephant']
//元素是引用类型数据
let arr = [{a: 1}, {a: 2}];
let newArr = arr.slice(0, 1);
console.log(arr, newArr); //=> [ { a: 1 }, { a: 2 } ] [ { a: 1 } ]
newArr[0].a = 20;
console.log(arr, newArr); //=> [ { a: 20 }, { a: 2 } ] [ { a: 20 } ]
数组合并
concat
用于合并两个或多个数组,不会更改现有数组,会返回一个新的数组。
const array1 = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
const array2 = ['d', 'e', 'f'];
const array3 = array1.concat(array2);
console.log(array3);// ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"]
拓展运算符
不会更改源数组,拓展运算符也可以把 Set 转为数组。
let temp1 = [1,2,3];
let temp2 = [4,5,6];
let arr = [...temp1, ...temp2];
console.log(arr); //[1,2,3,4,5,6]
flat
多维数组合并,返回一个新的数组。
// 合并一维数组
let ary = [1,2,[3,4],5]
let newAry = ary.flat()
console.log(newAry) //=> [1,2,3,4,5]
//合并多维数组
[1,2,[3,[4,[5,6]]]].flat('Infinity'); //=> [1,2,3,4,5,6]
//移除数组空项
let arr = [1, 2, , 5];
let newArr = arr.flat();
console.log(arr, newArr); //=> [1, 2,, 5] [1, 2, 5]
数组迭代(循环)
forEach
遍历数组,对每个元素执行一次函数,不会更改源数组,也不会创建新数组。
let temp = [1,3,5];
temp.forEach(function(value, index, array){
console.log(value, index, array);
});
/****
1 0 [1,3,5]
3 1 [1,3,5]
5 2 [1,3,5]
***/
map
遍历数组,对每个元素执行一次函数,不会更改源数组,会创建一个新数组。
const array1 = [1, 4, 9, 16];
const map1 = array1.map(x => x * 2);
console.log(map1); //=> [2, 8, 18, 32]
filter
遍历数组,对每个元素执行一次函数,返回满足规则的元素。
const words = ['spray', 'limit', 'elite', 'exuberant', 'destruction', 'present'];
const result = words.filter(word => word.length > 6);
console.log(result); //=> ["exuberant", "destruction", "present"]
every
遍历数组,对每个元素执行一次函数,用于测试组内元素,是否全部满足指定规则。
const isBelowThreshold = (currentValue) => currentValue < 40;
const array1 = [1, 30, 39, 29, 10, 13];
console.log(array1.every(isBelowThreshold)); //=> true
some
遍历数组,对每个元素执行一次函数,用于判断组内元素至少有一个元素通过了指定规则。
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const even = (element) => element % 2 === 0;
console.log(array.some(even)); //=> true
reduce
const array1 = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const reducer = (accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue;
// 1 + 2 + 3 + 4
console.log(array1.reduce(reducer)); //=> 10
// 5 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4
console.log(array1.reduce(reducer, 5)); //=> 15
for...in
const array1 = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
for(const element in array1){
console.log(element) //0,1,2
}
for...of
const array1 = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
for (const element of array1) {
console.log(element); //a,b,c
}
跳出迭代汇总
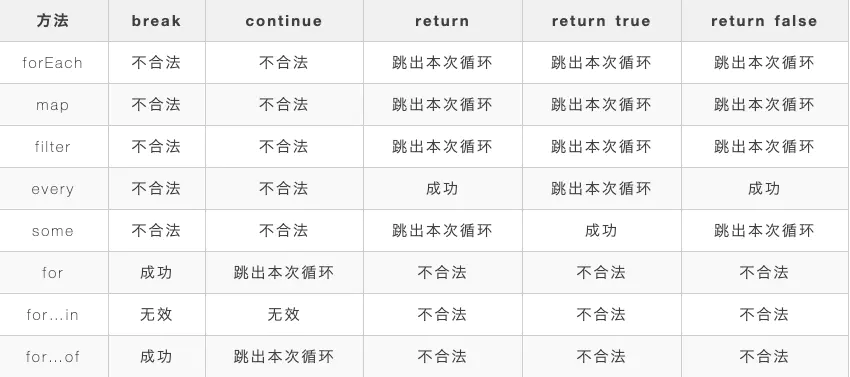
查找定位
indexOf
获取数组元素的索引。
const beasts = ['ant', 'bison', 'camel', 'duck', 'bison'];
console.log(beasts.indexOf('duck')) // 3
console.log(beasts.indexOf('gogo')) // -1
lastIndexOf
获取数组元素最后一个索引。
const animals = ['Dodo', 'Tiger', 'Penguin', 'Dodo'];
console.log(animals.lastIndexOf('Dodo')) // 3
findIndex
循环数组,返回第一个满足条件的索引。
const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];
const where = (value) => value > 13;
console.log(array1.findIndex(where)) // 3
find
循环数组,返回第一个满足条件的元素值。
const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];
const where = (value) => value > 13;
console.log(array1.find(where)) // 130
数组排序
sort
数组排序,直接修改原数组,如果不带参数,默认按照数组元素的字母排序,如果是数字则按照大小顺序排列。
let array1 = ['bi','ci','di','ai']
console.log(array1.sort()) // ai bi ci di
let array2 = [1,2,3,4]
array2.sort((a,b)=>{
//retrun a - b // 生序
return b - a // 降序
})
console.log(array2) // [4,3,2,1]
reverse
数组倒序,不更改源数组,返回一个新的数组。
const array1 = ['one', 'two', 'three'];
const array2 = array1.reverse()
console.log(array2) // ["three", "two", "one"]
数组转换
toString
将数组元素转为字符串,并以逗号分割,不更改源数组。
const array1 = [1, 2, 'a', '1a'];
console.log(array1.toString()) // "1,2,a,1a"
join
将数组所有元素连接成一个字符串返回,可以指定连接符。
const elements = ['Fire', 'Air', 'Water'];
console.log(elements.join()) // Fire,Air,Water
console.log(elements.join('-')) // Fire-Air-Water
填充/包含
fill
用一个固定的值,替换掉数组中指定起始位置到结束位置的全部元素。
const array1 = [1, 2, 3, 4];
console.log(array1.fill(0,2,4)) //
console.log(array1.fill(5, 1)) // [1, 5, 5, 5]
console.log(array1.fill(6)); // [6, 6, 6, 6]
includes
判断数组中是否包含一个指定的值。
const array1 = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(array1.includes(2)) //true
Array 的类方法
isArray
类型判断
console.log(Array.isArray([1,2,3])) // true
console.log(Array.isArray({num:123})) // false
from
字符串转数组
Array.from('foo') // ['f','o','o']
set转数组
const set = new Set(['foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'foo']);
Array.from(set); // [ "foo", "bar", "baz" ]
map转数组
const map = new Map([['name','666'],['name','pp']])
Array.from(map) // ['name','pp']
循环数组
Array.from([1, 2, 3], x => x + x); // [2, 4, 6]
类数组转换为数组
function f() {
return Array.from(arguments);
}
f(1, 2, 3);
of
数值转换数组
Array.of(1,2,3) // [1,2,3]
其他常用操作
以下问题,希望大家可以借助上面的知识独立编写。
洗牌算法
将一个数组打乱,返回一个打乱的数组。
let array = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
array.sort(()=>{
return Math.random() - 0.5
})
数组去重
const arr = [1,2,2,4,6,7,8,6];
let arr2 = [];
//set 方式实现
const set = new Set(arr);
Array.from(set) //[1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8]
arr.forEach(value=>{
arr2.includes(value) ? false : arr2.push(value)
});
arr.forEach(value => {
arr2.indexOf(value) === -1 ? arr2.push(value) : false
})
数组交集
const array1 = [1,2,3,4,5]
const array2 = [2,5,1,6,9]
//filter + includes
array1.filter( value => array2.includes(value))
//filter + set
let set2 = new Set(array2)
array1.filter(value => set2.has(value))
//还有可以采用 filter + indexOf 的方式实现 - -.
数组差集
const array1 = [1,2,3,4,5]
const array2 = [2,5,1,6,9]
//filter + includes
const fil1 = array1.filter( value => !array2.includes(value))
const fil2 = array2.filter( value => !array1.includes(value))
fil1.concat(fil2)
//filter + indexOf && lastIndexOf
const array3 = array1.concat(array2)
array3.filter(value => array3.indexOf(value) === array3.lastIndexOf(value))
结尾
我一直认为模仿和借鉴是学习一个新东西最高效的方法,作为一名开发者,你需要时刻保持警惕,有危机意识,有持续学习的能力。
如果这篇文章帮助到了你,欢迎点赞和关注,搜索《海洋里的魔鬼鱼》加入我们的技术群一起学习讨论,共同探索前端的边界。
