Java 内置了很多数据结构,阻塞队列也有。最近在看 Java 中的并发包:Lock&Condition。然后看到了有人说可以用他们实现阻塞队列,然后我想着,那我是不是也可以写一个阻塞队列?
想着就想着先写一个,阻塞队列的特点:
- 一个有限的存数据的队列;
- 入队的时候要判断队列是否已满;已满的时候,入队的线程要阻塞等待,直到队列有空位,被唤醒继续入队;
- 出队的时候要判断队列是否为空;为空的时候,获取队列数据的线程阻塞等待,直到队列有新数据的时候被唤醒继续执行;
也就是说我们在对队列操作的时候有两个操作,一个入队,一个出队:
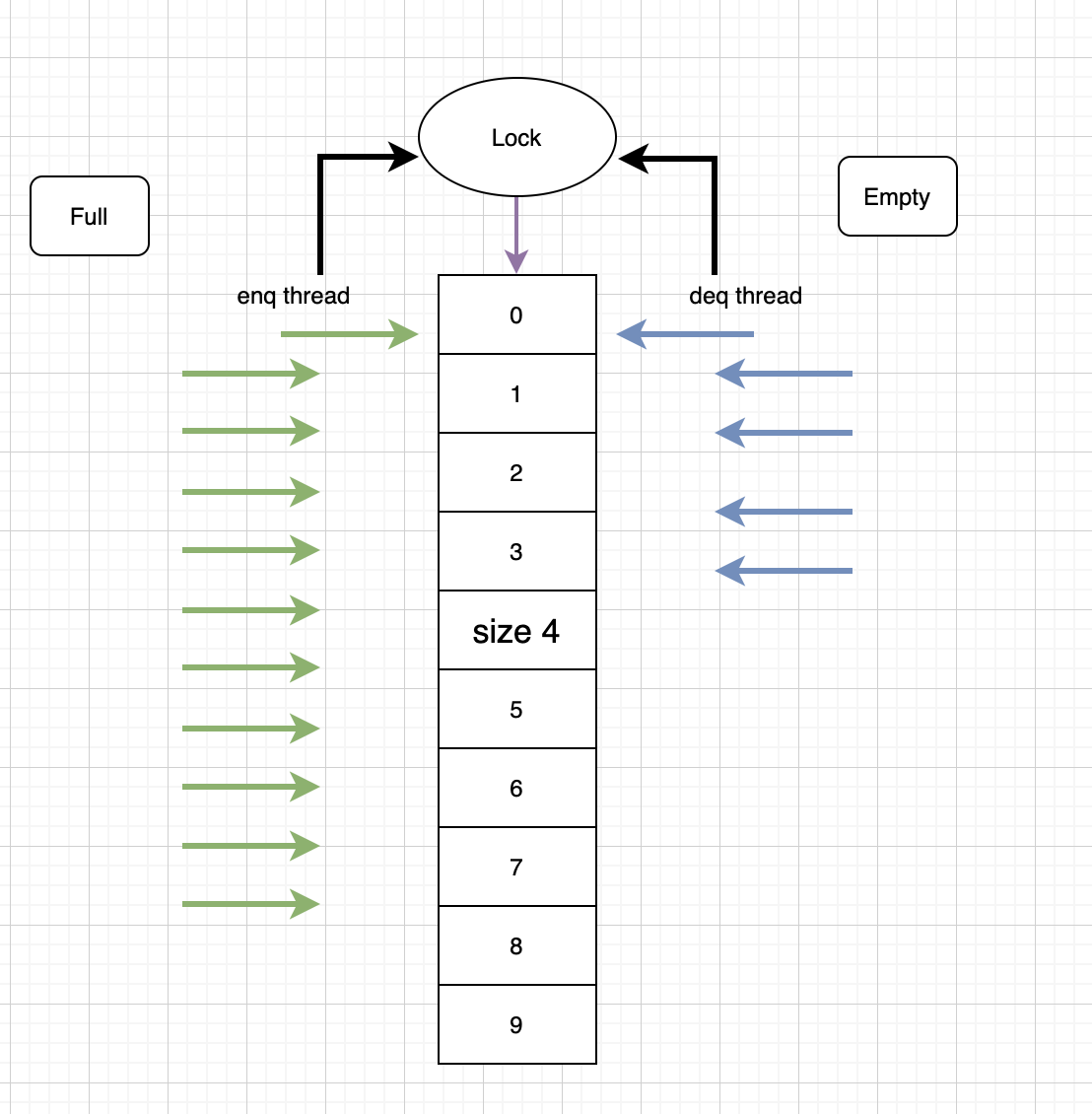
入队线程:enq thread; 出队线程 deq thread。两者在进行入队和出队的时候都会要先获取全局 lock。默认我们使用的是 size 来存储 list 的容量,入队的时候:size+1;出队的时候 size-1;然后我们用了两个 condition 来告诉当前入队线程和出队线程当前是应该等待,还是可以继续执行。当队列容量不够的时候,入队线程进入 await,否则就入队,并且唤醒出队的线程。出队的线程进入之后先判断队列是否为空,为空的时候就await,然后等地啊被唤醒。大致流程就是这样:
然后就写了下面的比较初级的代码。
v1 版本:
class BlockedQueue<T> {
final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>(10);
int size = 0;
//判断是否满了
Condition full = lock.newCondition();
//判断是否空的
Condition empty = lock.newCondition();
//入队
T enq(T t) {
lock.lock();
try {
//判断队列是否已满
while (size >= 10) {
System.out.println("不好意思,满了!!!");
full.await();
}
list.add(size, t);
size++;
empty.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return t;
}
//出队
T deq() {
lock.lock();
T t = null;
try {
while (size <= 0) {
System.out.println("不好意思,空了~~");
empty.await();
}
t = list.get(size);
size--;
full.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return t;
}
}
然后写了个main测试方法:
public class MyBlockQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockedQueue<Integer> blockedQueue = new BlockedQueue<>();
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i++ < 30) {
Thread thread = new Thread("producer-" + i) {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println(this.getName() + ",生产数字:" + blockedQueue.enq(new Random().nextInt(10)));
try {
Thread.sleep(1000 * new Random().nextInt(10));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
thread.start();
}
while (j++ < 30) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread("consumer-" + j) {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println(this.getName() + ",消费数字:" + blockedQueue.deq());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000 * new Random().nextInt(10));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
thread1.start();
}
while (true) {
Thread.sleep(1000 * 60 * 60);
//System.out.println(blockedQueue.size);
}
}
}
然后就会发现一个报错:
Exception in thread "consumer-4" java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: Index: 10, Size: 10
at java.util.ArrayList.rangeCheck(ArrayList.java:657)
at java.util.ArrayList.get(ArrayList.java:433)
at me.chenzhijun.gk_multithread.BlockedQueue.deq(Item15_Lock_Condition.java:105)
at me.chenzhijun.gk_multithread.Item15_Lock_Condition$2.run(Item15_Lock_Condition.java:46)
java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: Index: 10, Size: 10
at java.util.ArrayList.rangeCheck(ArrayList.java:657)
at java.util.ArrayList.get(ArrayList.java:433)
at me.chenzhijun.gk_multithread.BlockedQueue.deq(Item15_Lock_Condition.java:105)
at me.chenzhijun.gk_multithread.Item15_Lock_Condition$2.run(Item15_Lock_Condition.java:46)
Exception in thread "consumer-6" java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: Index: 10, Size: 10
at java.util.ArrayList.rangeCheck(ArrayList.java:657)
at java.util.ArrayList.get(ArrayList.java:433)
at me.chenzhijun.gk_multithread.BlockedQueue.deq(Item15_Lock_Condition.java:105)
at me.chenzhijun.gk_multithread.Item15_Lock_Condition$2.run(Item15_Lock_Condition.java:46)
当时看到这个报错,真的是一脸懵逼,我代码看起来好像没有错误啊。那是哪里的原因,顺着代码一行行读,主要是发现数组越界:10。是不是因为我们size++比如第 10 个 Thread 将 size 加到了 10,但是我们的 arrayList 最大也就为 9。那好像是会出现是问题哦,代码越界判断的习惯真的要注意。然后改了下代码v2版本:
class BlockedQueue<T> {
final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>(10);
//改为了 -1 然后在入队的时候先加1
int size = -1;
//判断是否满了
Condition full = lock.newCondition();
//判断是否空的
Condition empty = lock.newCondition();
//入队
T enq(T t) {
lock.lock();
try {
//判断队列是否已满
while (size >= 10) {
System.out.println("不好意思,满了!!!");
full.await();
}
//先加一,再往队列加数据。
size++;
list.add(size, t);
empty.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return t;
}
//出队
T deq() {
lock.lock();
T t = null;
try {
while (size <= 0) {
System.out.println("不好意思,空了~~");
empty.await();
}
t = list.get(size);
size--;
full.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return t;
}
}
然后再运行 main 方法就发现正常了。
producer-1,生产数字:8
producer-14,生产数字:7
producer-14,生产数字:6
consumer-7,消费数字:6
consumer-7,消费数字:7
producer-16,生产数字:1
producer-25,生产数字:6
consumer-24,消费数字:6
producer-11,生产数字:5
producer-7,生产数字:6
consumer-17,消费数字:6
consumer-17,消费数字:5
consumer-16,消费数字:1
consumer-21,消费数字:8
不好意思,空了~~
不好意思,空了~~
这样改了之后看起来好像是可以了。但总觉得哪里不对,可又说不出哪里的问题。你觉得了?欢迎评论留言讨论。谢谢!