一 Mock
01 方式一 使用serve
npm i serve -g
- 创建mock文件,mock/api/data.json
yarn global add server- 在mock目录下运行
serve启用mock服务 localhost:5000 yarn global add createProxyMiddleware- 在src目录下新建setupProxy.js
const { createProxyMiddleware } = require('http-proxy-middleware');
module.exports = function(app) {
app.use(createProxyMiddleware('/api', {target: 'http://localhost:5000/'}))
}
工程下所有/api都会被代理到localhost:5000
02 方式二 public目录
- public目录下创建mock/data.json
- 浏览器访问http://localhost:3000/mock/data.json
03 方式三 Charles
04 方式四 json-server
db.json
{
"posts": [
{"id":1, "title":"json-server", "author": "typicode"}
],
"comments": [
{"id":1, "body":"some comment", "postId": 1}
],
"profile": {"name": "typicode"}
}
package.json
{
"scripts": {
"mock": "json-server --watch db.json"
}
}
05 方式五 Postman 测试API接口
二 注释
在function上键入 /** ,展开
注释规则参看
三 React思维方式
01 组件划分
- 解耦:降低单一模块/组件的复杂度
- 复用:保证组件一致性,提升开发效率
- 组件颗粒度需要避免过大或过小
02 什么是State
- 代表UI的
完整且最小状态集合(可变的)
this.setState((prevState)=>({
list: [...prevState.list, prevState.inputValue],
inputValue: ''
}))
001 如何判断
- 是否通过分组件props传入?
- 是否不会随着时间、交互等操作变化?
- 是否可通过其他state或props计算得到?
002 State的双层含义
- 代表应用UI的所有状态的集合
- 状态集合中的每一部分(待办事项列表、新增输入框文本、筛选条件)
003 分析State保存位置
- 确定依赖state的每一个组件
- 如果某个state被多个组件依赖,寻找共同的父组件(状态上移)
四 PropTypes & DefaultProps
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
TodoItem.propTypes = {
content: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
deleteItem: propTypes.func
}
TodoItem.defaultProps = {
test: 'hello world'
}
- PropTypes: react.docschina.org/docs/typech…
- Flow: flow.org/
- Flow 入门: zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/26204569
- Flow 指北:www.tinymind.net.cn/articles/3f…
五 生命周期
在某一时刻会自动执行的函数
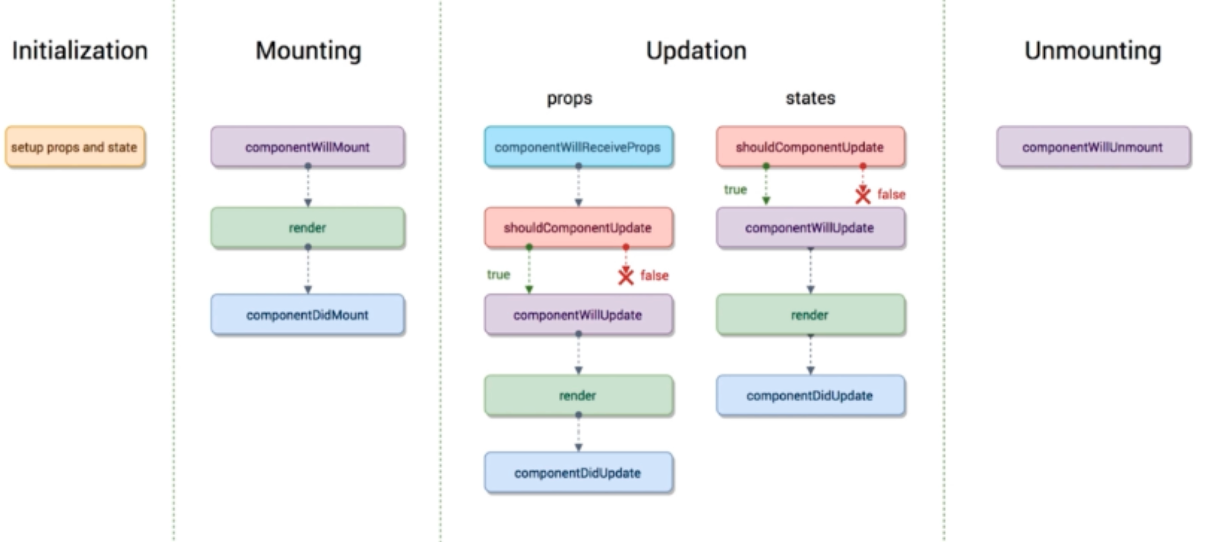
01 调用API时机componentDidMount
- UI渲染完成后调用
- 只执行一次
- 典型场景:获取外部资源
componentWillMount看起来是合适的时机,但是当RN或深层次同构时可能会产生冲突。更安全的是componentDidMount
componentDidMount(){
axios.get('/api/todoList').then((res)=>{
this.setState(()=>({
todoList: [...res.todoList]
}))
}).catch((error)=>{
console.error(error)
})
}
02 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
- 在页面render之前调用,state已更新
- 典型场景:获取render之前的DOM状态
03 shouldComponentUpdate
- 决定Virtual DOM是否需要重绘
- 一般可由PureComponent自动实现
- 典型场景:性能优化
为避免子组件render无意义的刷新,产生性能损耗。借用shouldComponentUpdate拦截
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextSatate){
if(nextProps.content !== this.porps.content){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
04 getDerivedStateFromProps
- 当state需要从props初始化时使用
- 尽量不要使用:维护两者状态一致性会增加复杂度
- 每次render都会调用
- 典型场景:表单控件获取默认值
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState) {
const {type} = nextProps;
// 当传入的type发生变化的时候,更新state
if (type !== prevState.type) {
return {
type,
};
}
// 否则,对于state不进行任何操作
return null;
}
05 componentDidUpdate
- 每次UI更新时被调用
- 典型场景:页面需要根据props变化重新获取数据
比如切换detail,通过url里的id更新数据
六 react-transition-group 动画插件
七 Context API
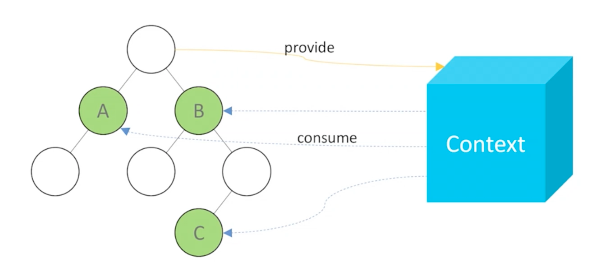
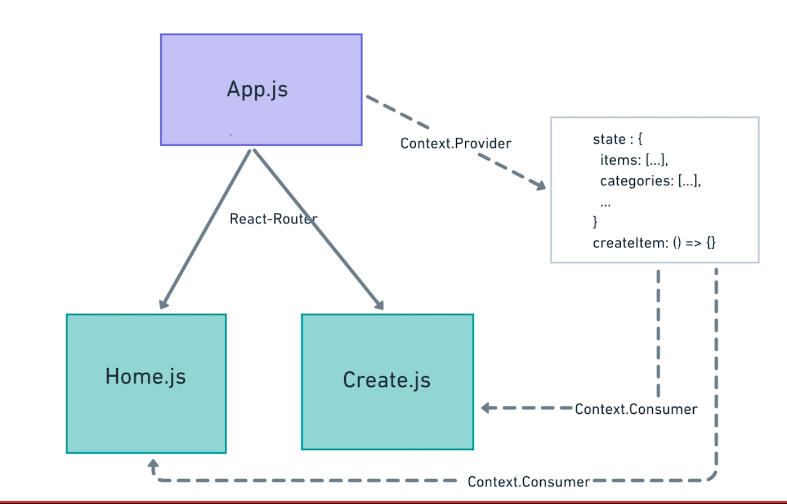
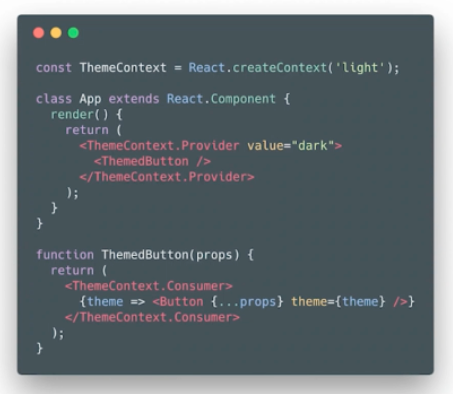
const en = {submit: "Submit", cancel: "Cancel"}
const cn = {submit: "提交", cancel: "取消"}
const LocaleContext = React.createContext(en)
class LocaleProvider extends React.Component {
state = {locale: cn}
render(){
return(
<LocaleContext.Provider value={this.state.locale}>
<button onClick={this.toggle}> 切换语言 </button>
{this.props.children}
</LocaleContext.Provider>
)
}
}
class LocaleButtons extends React.component {
render(){
return (
<LocaleContext.Consumer>
{locale => (
<div>
<button>{locale.cancel}</button>
<button>{locale.submit}</button>
</div>
)}
</LocaleContext.Consumer>
)
}
}
export defalut () => {
<div>
<LocaleProvider>
<>
<br/>
<LocaleButtons />
</>
</LocaleProvider>
</div>
}
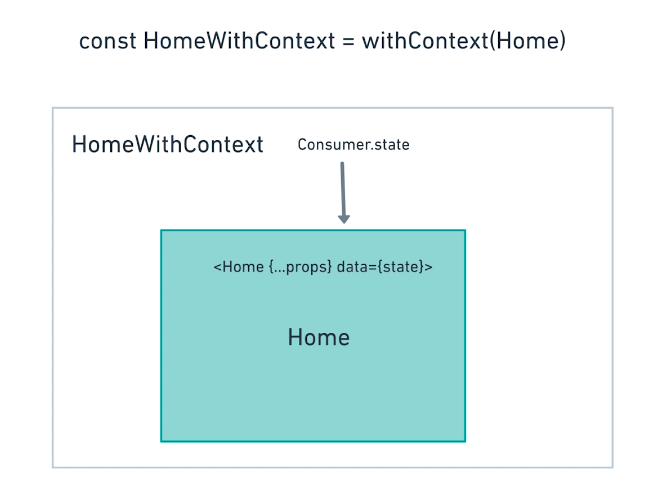
使用高阶组件实现Context重用
export const AppContext = React.createContext()
class App extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {
items: flatternArr(testItems),
//...
}
this.actions = {
deleteItem: (item)=>{/*...*/}
}
}
render(){
return (
<AppContext.Provider value={{
state: this.state,
actions: this.actions
}}>
<Router>
<Route path="/" exact compoonent ={Home}/>
//...
</Router>
</AppContext.Provider>
)
}
}
WithContext.js
import React from 'react';
import {AppConext} from '.App';
const withContext = (Component) =>{
return (props) => {
<AppConext.Consumer>
{({state})=>{
return <Component {...props} data={state} actions={actions}/>
}}
</AppConext.Consumer>
}
}
export default withContext;
Home.js
import {withContext} frim '../withContext';
//...
render(){
const {data, actions} this.props;
}
//...
export default withContext(Home)
八 router
01 三种实现方式
- URL路径
import { BrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom'; - hash路由 (兼容底版本浏览器)
import { HashRouter } from 'react-router-dom'; - 内存路由 (多用于SSR,存于内存中,跟DOM无关,所以从react-router引入)
import { Memory } from 'react-router';
import { BrowserRouter, Route } from 'react-router-dom';
<Provider store={store}>
<BrowserRouter>
<>
<Route path ='/' exact component={Home} />
<Route path ='/detail' exact component={Detail} />
</>
</BrowserRouter>
</Provider>
02 React Router API
- : 普通链接,不会触发浏览器刷新
- : 类似Link但是会添加CSS class
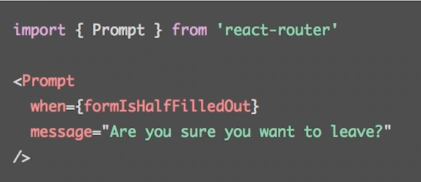
- : 满足条件时提示用户是否离开当前页面
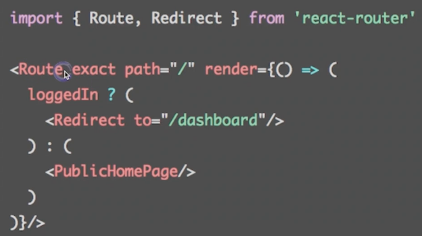
- : 重定向当前页面,例如登录判断
- : 路由配置的核心标记,路径匹配时显示对应组件, (多条匹配时都显示)
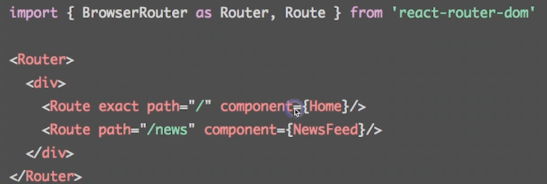
- : 只显示第一个匹配的路由(多条匹配时只显示第一个)
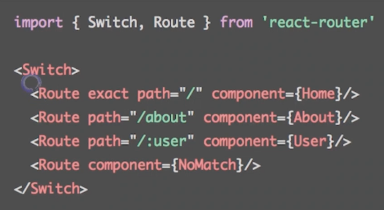
03 通过URL传参
- 如何通过URL传递参数:<Route path="/topic/:id" ... />
- 如何获取参数: this.props.match.params
- github.com/pillarjs/pa…
index.js
<Route path ='/detail:id' exact component={Detail} />
list.js
<Link to={`/detail/${id}`}> detail </Link>
detail.js
componentDidMount(){
const id = this.porps.match.params.id;
// cocalhost:3000/detail?id=2 ?传递的参数通过下面获取, 需要手动拆分
const location = this.props.location.search // ?id=2
}
通过withRouter跳转
import {withRouter} from 'react-router-dom'
//...
this.props.history.push(`./edit/${item.id}`)
//...
export default withRouter(Home);
何时需要URL参数?
页面状态尽量通过URL参数定义
如日历当前月份,内部不必维护月份信息
04 嵌套路由
04 react-loadable 异步组件
app.js
import Detail from './pages/detail/loabable.js'
loadable.js
import Ladable from 'react-loadable';
const LoableComponent = Loadable({
loader: ()=> import('./'), // 同目录下的index.js
loading(){
return <div>加载中...<.div>
}
})
export default (props) => <LoableComponent {...props}/>
detail/index.js
import { withRouter } from 'react-router-dom';
//...
export defaut connect(mapState, mapDispatch)(withRouter(Detail))
九 常用开发调试工具
01 ESLint
- 使用 .eslintrc 进行规则的配置
- 使用 airbnb的JS代码风格
02 Prettier
代码格式化
03 classnames
import classnames from 'classnames';
//...
return (<div className={
classnames(
'name',
isOpen ? 'name--open': 'name-close'
)
}> ... </div>)