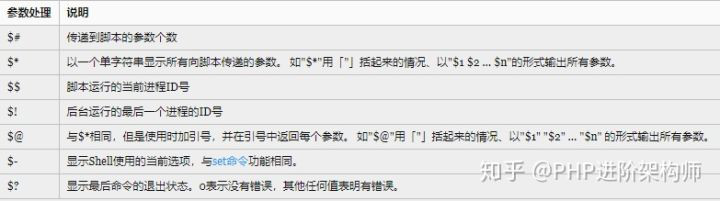
简介
除了基本的获取脚本执行时的传入参数外, 还有更便捷的语法糖:参数默认值,自动赋值。
基本传参
先来一个示例:
#!/bin/sh
echo 参数0: $0;
echo 参数1: $1;
echo 参数2: $2;
echo 参数3: $3;
echo 参数4: $4;执行测试脚本
[root@yjx214 tmp]# sh testParam.sh a b c d
所有参数: a b c d
参数0: testParam.sh
参数1: a
参数2: b
参数3: c
参数4: d$* 与 $@ 区别
相同点:都是引用所有参数。
不同点:只有在双引号中体现出来。
假设在脚本运行时写了三个参数 1、2、3,,则 " * " 等价于 "1 2 3"(传递了一个参数),而 "@" 等价于 "1" "2" "3"(传递了三个参数)。
#!/bin/bash
# author:PHP编程
# url:www.PHPXS.com
echo "-- \$* 演示 ---"
for i in "$*"; do
echo $i
done
echo "-- \$@ 演示 ---"
for i in "$@"; do
echo $i
done执行脚本,输出结果如下所示:
$ chmod +x test.sh
$ ./test.sh 1 2 3
-- $* 演示 ---
1 2 3
-- $@ 演示 ---
1
2
3默认参数(变量默认值)
if繁琐方式
if [ ! $1 ]; then
$1='default'
fi- 变量为null
取默认值
- 变量 为 null
${vari-defaultValue}实践
[root@yjx214 /]# unset name
[root@yjx214 /]# echo ${name}
[root@yjx214 /]# echo ${name-yjx}
yjx
[root@yjx214 /]# name=
[root@yjx214 /]# echo ${name-yjx}
[root@yjx214 /]# echo ${name}
[root@yjx214 /]#= 变量为null时, 同时改变变量值
[root@yjx214 /]# unset name
[root@yjx214 /]# echo ${name=yjx}
yjx
[root@yjx214 /]# echo $name
yjx
[root@yjx214 /]# name=""
[root@yjx214 /]# echo ${name=yjx}
[root@yjx214 /]#:- 变量为null 或 空字符串
取默认值
- 变量为null
- 变量为空字符串
${vari:-defaultValue}:= 变量为null 或 空字符串, 同时改变变量值
{$vari:=defaultValue}测试 null
[root@yjx214 /]# unset name
[root@yjx214 /]# echo ${name:=yjx}
yjx
[root@yjx214 /]# echo ${name}
yjx
[root@yjx214 /]#测试 空字符串
[root@yjx214 /]# name=""
[root@yjx214 /]# echo ${name:=yjx}
yjx
[root@yjx214 /]# echo $name
yjx:? 变量为null 或 空字符串时报错并退出
[root@yjx214 /]# unset name
[root@yjx214 /]# echo ${name:?yjx}
-bash: name: yjx
[root@yjx214 /]# name=""
[root@yjx214 /]# echo ${name:?yjx}
-bash: name: yjx
[root@yjx214 /]# name="guest"
[root@yjx214 /]# echo ${name:?yjx}
guest:+ 变量不为空时使用默认值
与 :- 相反
[root@yjx214 /]# name="guest"
[root@yjx214 /]# echo ${name:+yjx}
yjx
[root@yjx214 /]# echo $name
guest