一.异常
1.异常的概述
- Java中,将异常封装成了一些异常类,当代码出现异常,创建异常对象,这个异常对象中有针对于这个异常发生位置,发生原因等信息。
- 处理异常方法:终止代码、解决异常、代码跳转
2.异常的体系结构
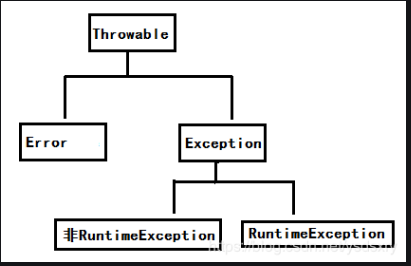
Throwable - Error 错误
- Exception 异常 - RunTimeException,代码在运行时期抛出的异常,在代码中不需要做任何处理。
- 编译异常,写代码过程中就会报错,要求代码必须声明异常或处理异常。
Error,表示代码发生了很严重的问题,无法进行代码的控制和处理,如果出现,只能修改代码。
Exception,表示代码发生了不正常的情况,不严重,甚至可以避免,在代码中适当的处理。Exception是所有异常的父类。
public class ErrorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.error,只能修改代码
/* int [] arr = new int[1024*1024*1024];
System.out.println(arr);//java.lang.OutOfMemoryError*/
//2.Exception
int [] arr = new int[5];
System.out.println(arr[10]);//java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 10 out of bounds for length 5
}
}
3.JVM对异常的默认的处理机制
public class JvmException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,3,5};
getEle(arr); //3.JVM先检测main方法是否对于异常有处理,没有处理
//4.JVM再将异常抛出,抛给了main方法的调用者,JVM虚拟机
//5.将异常信息以红色的字体展示在控制台上,停止代码运行
}
public static void getEle(int[] arr){
int count = arr[4];//系统检测arr数组没有4索引;
//1.JVM new了一个异常对象,new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(4),4作为参数传递
//2.JVM将异常的信息抛出给getEle方法的调用者,抛给了main方法
System.out.println(count);//java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 4 out of bounds for length 3
}
}
4.异常的手动处理
方法内部出现了异常,可以在方法上进行异常的声明,目的是让方法的调用者有一个提醒作用,对于方法可能会出现问题做一个提前的准备。
1.throw 关键字的使用场景:
程序员觉得这种情况不合理,可以通过throw关键字将不合理的情况进行抛出。
throw 格式:
throw new Exception 或者是Exception的子类
说明:
1.throw后面只能抛出一个异常;
2.代码中如果有多个错误,可以使用多个throw进行每一个异常的抛出;
3.throw关键字的异常,一旦执行,那么throw之后的代码不再执行。
public class ThrowDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
int[] a = null;
getArr(arr,5);
System.out.println("main方法结束了!");
}
public static void getArr(int[] arr,int index){
if(arr == null){//如果数组为null,异常
throw new NullPointerException("数组不能为null!");//java.lang.NullPointerException: 数组不能为null!
}
if(arr.length <= index){//数组没有index索引,不正常情况
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("数组中没有"+index+"索引!");//java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 数组中没有4索引!
}
System.out.println(arr[index]);
System.out.println("getArr方法结束了");
}
}
2.throws 关键字的使用场景:
当方法内部出现了异常
1.如果是运行时异常,就不需要进行异常的声明和处理
2.如果是编译异常,就需要在方法上进行 1.异常的声明(throws)、2.处理异常
throws 格式:
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数) throws 异常1,异常2{
}
throws特点:
1.throws只是作为异常的声明,作用:通知方法的调用者,方法内部可能会出现异常,提示方法调用者做一个提前的处理。
2.throws关键字后面可以写多个异常,异常之间","分隔。
3.方法中的运行异常,不需要声明;编译异常,需要声明或处理
public class ThrowsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
//main方法调用的方法getArr声明了一个Exception异常,因此需要main处理
//1.异常声明 2.异常处理
getArr(arr,4);
}
public static void getArr(int[] arr,int index) throws Exception{
if(arr == null){
throw new NullPointerException("数组不能为null!");
}
if(arr.length <= index){
//Exception异常是编译异常,因此需要声明异常或者处理异常
throw new Exception("数组中没有"+index+"索引!");
}
System.out.println(arr[index]);
}
}
3.throw和throws的区别
1.throw关键字写到方法内部;throws写到方法之上。
2.throw表示异常的抛出;throws表示异常的声明。
3.throw关键字每次只能抛出一个异常;throws关键字一次可以抛出多个异常。
1.try{
//可能会发生异常的代码
}catch(异常类型 异常名){
//异常的处理方式
}
说明:
1.try:检测的含义,检测卸载try大括号中的代码是否具有异常。
2.catch:捕获,捕获try代码块中发生的异常情况。
catch()中,是try可能会发生的异常类型举例,举例NullPointerException
catch(){}中,是针对于异常发生后,处理方式
try...catch的执行过程:
1.如果try代码块中没有异常,不执行catch中的内容,代码不停止,继续运行。
2.如果try代码块中出现了异常,让异常信息与catch()中的异常类型进行匹配。
匹配成功,catch捕获异常成功,执行catch{}中的代码,代码不停止,继续后面语句运行。
匹配失败,不执行catch{}中内容,使用JVM的默认处理异常机制,最终代码中止。
public class TryCatchDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = null;
try {//可能发生异常的代码写在try的代码块中
getLength(arr);
}catch(NullPointerException ex){
System.out.println("catch已经将异常捕获了");//catch已经将异常捕获了
}
System.out.println("main方法结束!");//main方法结束!
}
public static void getLength(int[] arr){
if(arr == null){
throw new NullPointerException("数组不能为空!");
}
System.out.println(arr.length);
}
}
2.try{
//可能会发生异常的代码
}catch(异常类型 异常名1){
//处理方法1
}catch(异常类型 异常名){
//处理方法2
}
多catch的执行过程:
1.如果try代码块中,没有异常,那么所有catch语句都不执行,代码继续运行
2.如果try代码块中,出现异常,try中的异常信息与catch中的异常类型依次从上到下匹配,
匹配哪个catch成功,执行对应catch代码块中的内容。
try中异常和所有catch的所有异常类型都不匹配,JVM默认处理异常,代码中止。
3.不论哪个catch执行,那么整个try...catch都结束了,然后代码接着try...catch之后继续运行。
public class MoreCatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = null;
try{
getArr(arr,5);
}catch (NullPointerException ex1){
System.out.println("catch捕获了空指针异常!");
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex2){
System.out.println("catch捕获了数组下标越界异常");
}
System.out.println("main方法完成!");
}
public static void getArr(int[] arr ,int index){
if(arr==null){
throw new NullPointerException("数组不能为空!");
}
if(arr.length<=index){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("没有"+index+"索引");
}
}
}
3.try{
//可能出现异常的代码
}catch(异常类型 名字){
//异常的处理方式
}finally{
//一定会执行的代码
}
说明: 一般finally中用于资源的关闭
执行过程:
1.try代码块中,没有异常,catch不执行,finally一定执行,执行try完毕,执行finally
2.try代码块中出现异常,匹配任意一个catch执行,执行完catch之后,执行finally
二.递归
