树的概念
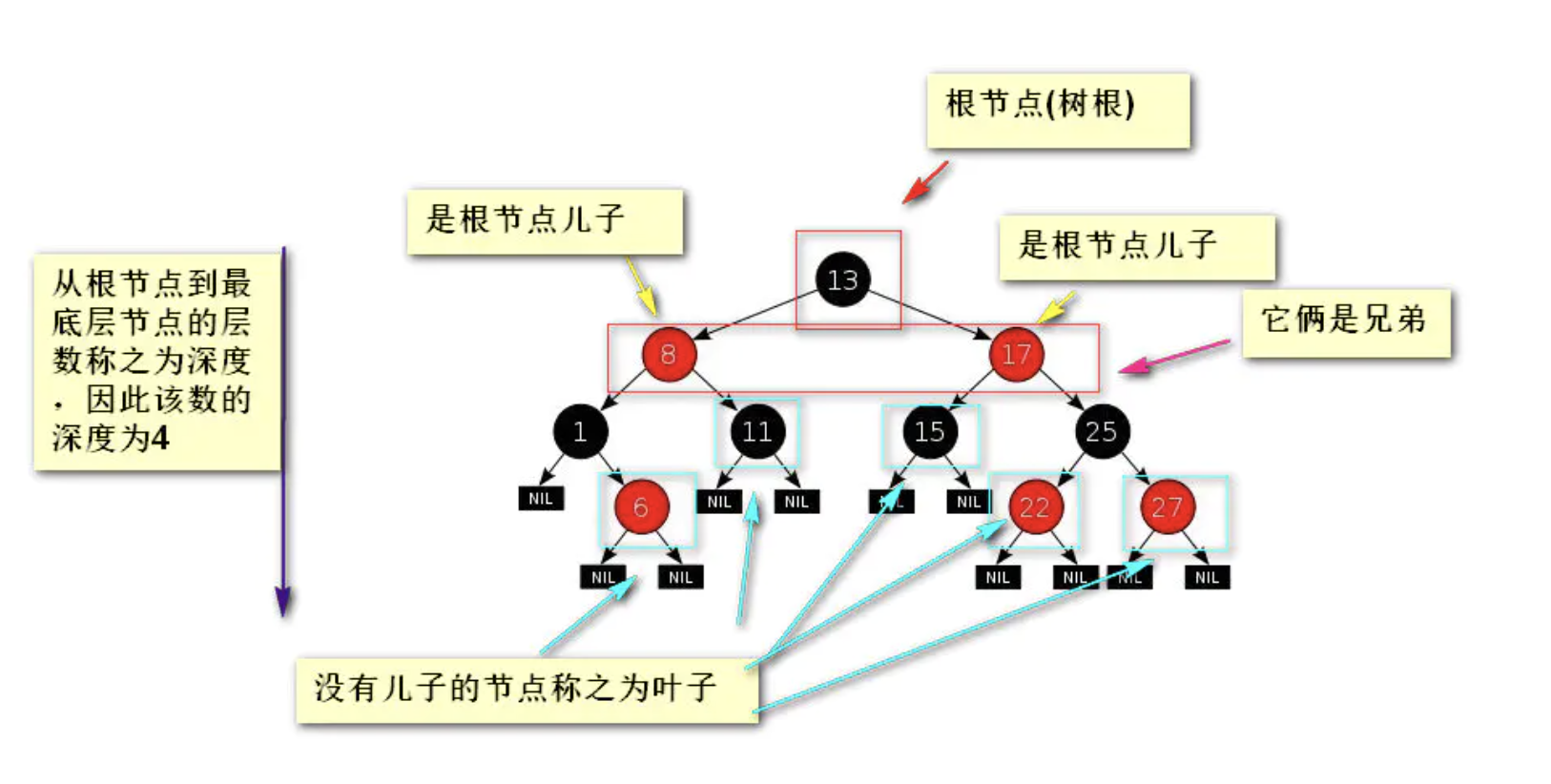
- 度:节点拥有子树的个数
二叉树
- 如果一棵树每个节点的度小于等于2,那就是二叉树。其子树分为左子树和右子树。
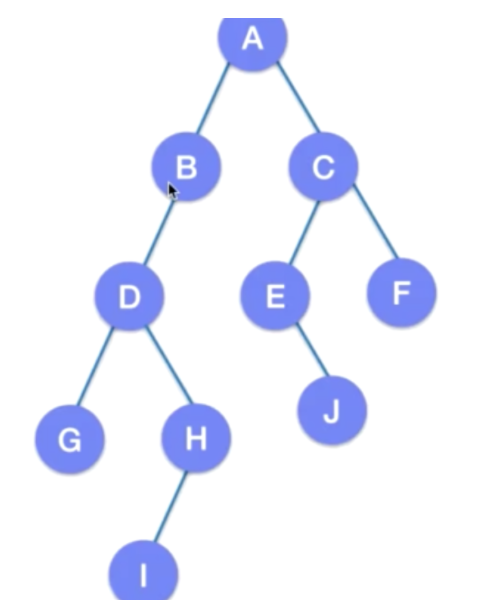
特殊的二叉树
-
斜树
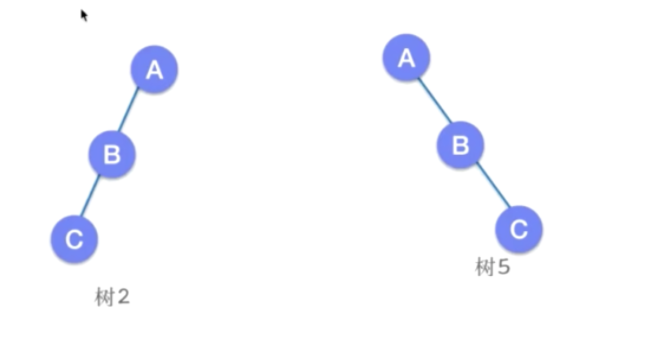
-
满二叉树 每一个节点都有两个节点,而叶子节点都在处于同一层
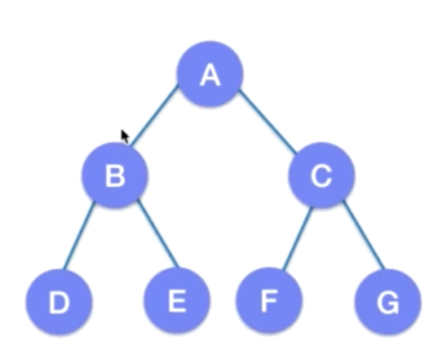
-
完全二叉树
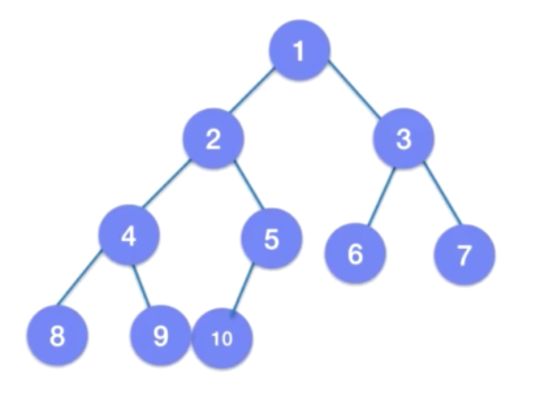
二叉树的存储
这里以链式存储为例
#include <stdio.h>
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "math.h"
#include "time.h"
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
/* 存储空间初始分配量 */
#define MAXSIZE 100
/* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK ERROR等 */
typedef int Status;
#pragma mark 二叉树的构造
int indexs = 1;
typedef char String[24];//0号单元存放的长度
String str;
Status StrAssign(String T,char *chars) {
int i;
if (strlen(chars) > MAXSIZE) {
return ERROR;
} else {
T[0] = strlen(chars);//0号单元存放串的长度
for (i = 1; i <= T[0]; i++) {
T[i] = *(chars+i-1);
}
return OK;
}
}
typedef char Element;
Element Nil = ' ';//字符型以空格符为空
typedef struct BiNode {//节点结构
Element data;//数据节点
struct BiNode *lchild,*rchild;//左右孩子指针
} BiNode,*BiTree;
//创建二叉树
//按前序输入二叉树的中节点值(字符),#表示空树
void BiTree_Create(BiTree *T) {
Element ele;
//获取字符串
ele = str[indexs++];
//判断当前字符是否为“#”
if (ele == '#') {
*T = NULL;
} else {
//创建新节点
*T = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiNode));
//是否创建成功
if (!*T) {
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
//生成根节点
(*T)->data = ele;
BiTree_Create(&(*T)->lchild);/* 构造左子树 */
BiTree_Create(&(*T)->rchild);/* 构造右子树 */
}
}
//构建空树T
Status BiTree_InitEmpty(BiTree *T) {
*T = NULL;
return OK;
}
//是否为空树
Status BiTree_IsEmpty(BiTree T) {
if (T) {
return FALSE;
} else {
return TRUE;
}
}
//销毁二叉树
void BiTree_Destroy(BiTree *T) {
if (*T) {
if ((*T)->lchild) {
BiTree_Destroy(&(*T)->lchild);/* 销毁左孩子子树 */
}
if ((*T)->rchild) {
BiTree_Destroy(&(*T)->rchild);/* 销毁左孩子子树 */
}
free(*T);//释放根节点
*T = NULL;//空指针赋值0
}
}
//树的深度
int BiTree_Deep(BiTree T) {
int i,j;
if (!T) {
return 0;
}
//计算左孩子的深度
if (T->lchild) {
i = BiTree_Deep(T->lchild);
} else {
i = 0;
}
//计算右孩子的深度
if (T->rchild) {
j = BiTree_Deep(T->rchild);
} else {
j = 0;
}
//比较深度
return i > j ? i +1 : j +1;
}
//二叉树的根data
Element BiTree_Root(BiTree T) {
if (T) {
return T->data;
} else {
return Nil;
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
// insert code here...
printf("二叉树链式存储结构实现!\n");
int i;
BiTree T;
BiTree_InitEmpty(&T);
StrAssign(str,"ABDH#K###E##CFI###G#J##");
Element rootData = BiTree_Root(T);
printf("二叉树的根为: %c\n",rootData);
printf("\n前序遍历二叉树:");
BiTree_TraversePre(T);
printf("\n中序遍历二叉树:");
BiTree_TraverseMid(T);
printf("\n后序遍历二叉树:");
BiTree_TraverseSuf(T);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
打印
二叉树链式存储结构实现!
二叉树是否为空0(1:是 0:否),树的深度=5
二叉树的根为: A
后序遍历二叉树:KHDEBIFJGCA
二叉树的遍历
遍历顺序有下面几种
- 前序:父节点->左子树->右子树,父节点在前
//遍历-前序 父节点->左子树->右子树
void BiTree_TraversePre(BiTree T) {
if (T == NULL) {
return;
}
printf("%c",T->data);//打印当前节点值-父节点
BiTree_TraversePre(T->lchild);//先遍历左子树
BiTree_TraversePre(T->rchild);//先遍历右子树
}
前序遍历二叉树:ABDHKECFIGJ
- 中序:左子树->父节点->右子树,父节点在中
//遍历-中序 左子树->父节点->右子树
void BiTree_TraverseMid(BiTree T) {
if (T == NULL) {
return;
}
BiTree_TraverseMid(T->lchild);//先遍历左子树
printf("%c",T->data);//打印当前节点值-父节点
BiTree_TraverseMid(T->rchild);//先遍历右子树
}
中序遍历二叉树:HKDBEAIFCGJ
- 后序:左子树 -> 右子树 ->父节点,父节点在后
//遍历-后序 左子树->右子树->父节点
void BiTree_TraverseSuf(BiTree T) {
if (T == NULL) {
return;
}
BiTree_TraverseSuf(T->lchild);//先遍历左子树
BiTree_TraverseSuf(T->rchild);//后遍历右子树
printf("%c",T->data);//打印当前节点值-父节点
}
- 层序遍历:一层层遍历,一般需要用到队列
- 遍历总结:
- 前序:父节点->左子树->右子树,父节点在前
- 中序:左子树->父节点->右子树,父节点在中
- 后序:左子树 -> 右子树 ->父节点,父节点在后
- 层序遍历:一层层遍历,一般需要用到队列
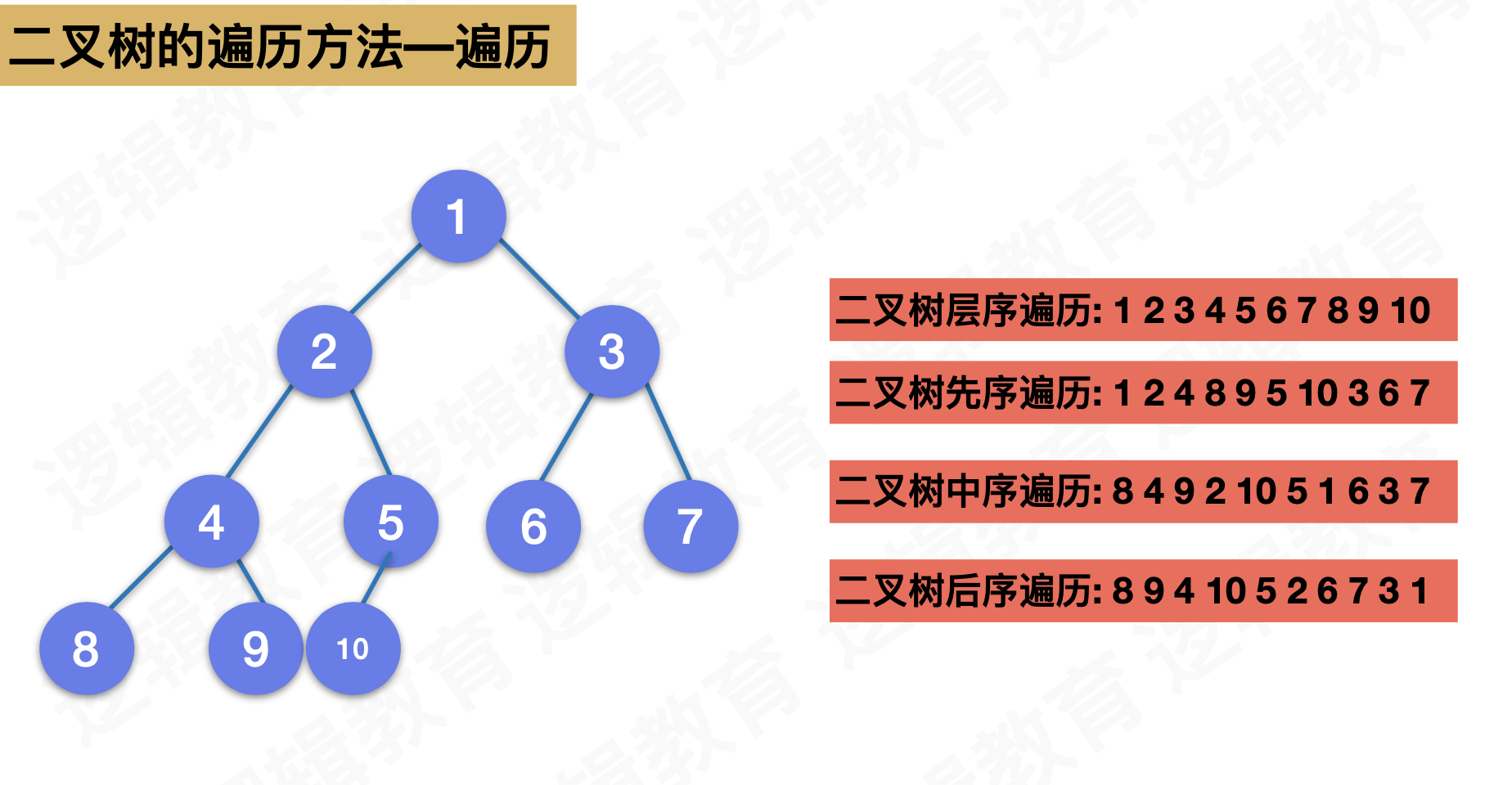
线索二叉树
在二叉树的结点上加上线索的二叉树称为线索二叉树,对二叉树以某种遍历方式(如先序、中序、后序或层次等)进行遍历,使其变为线索二叉树的过程称为对二叉树进行线索化
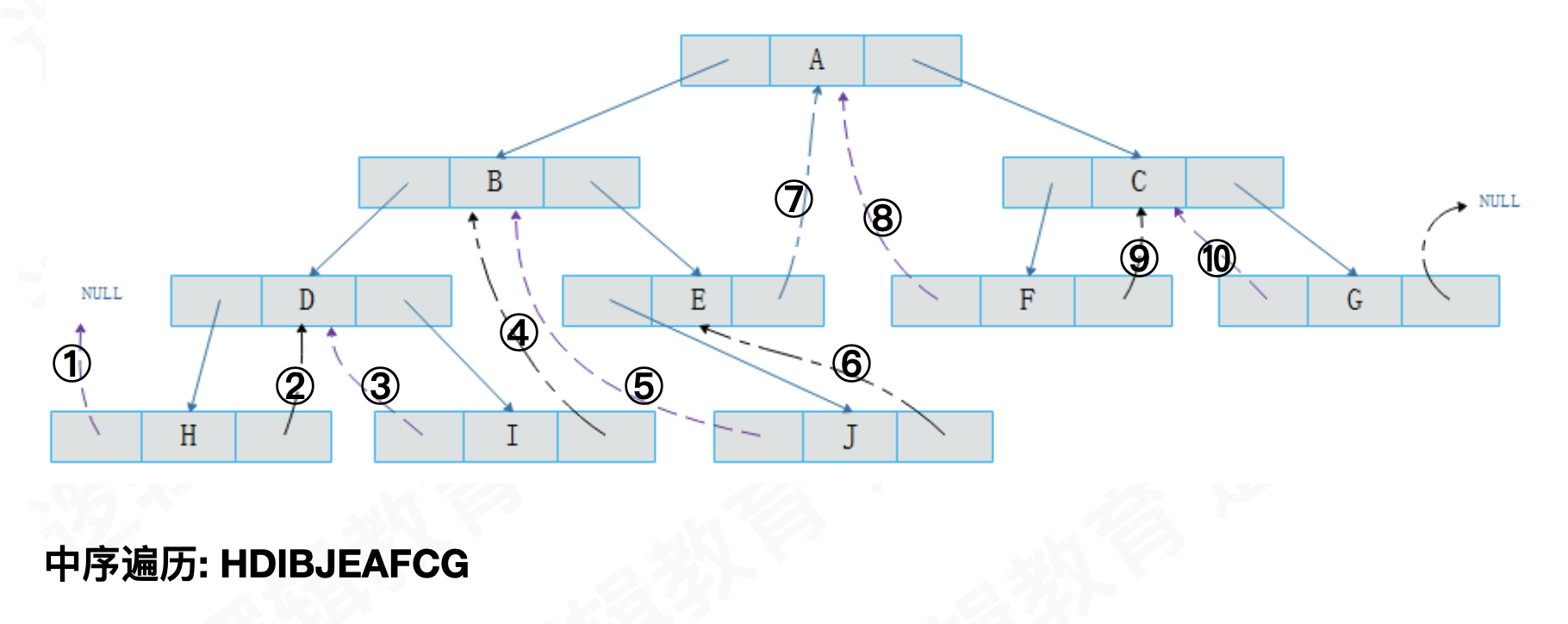
- 线索二叉树结构
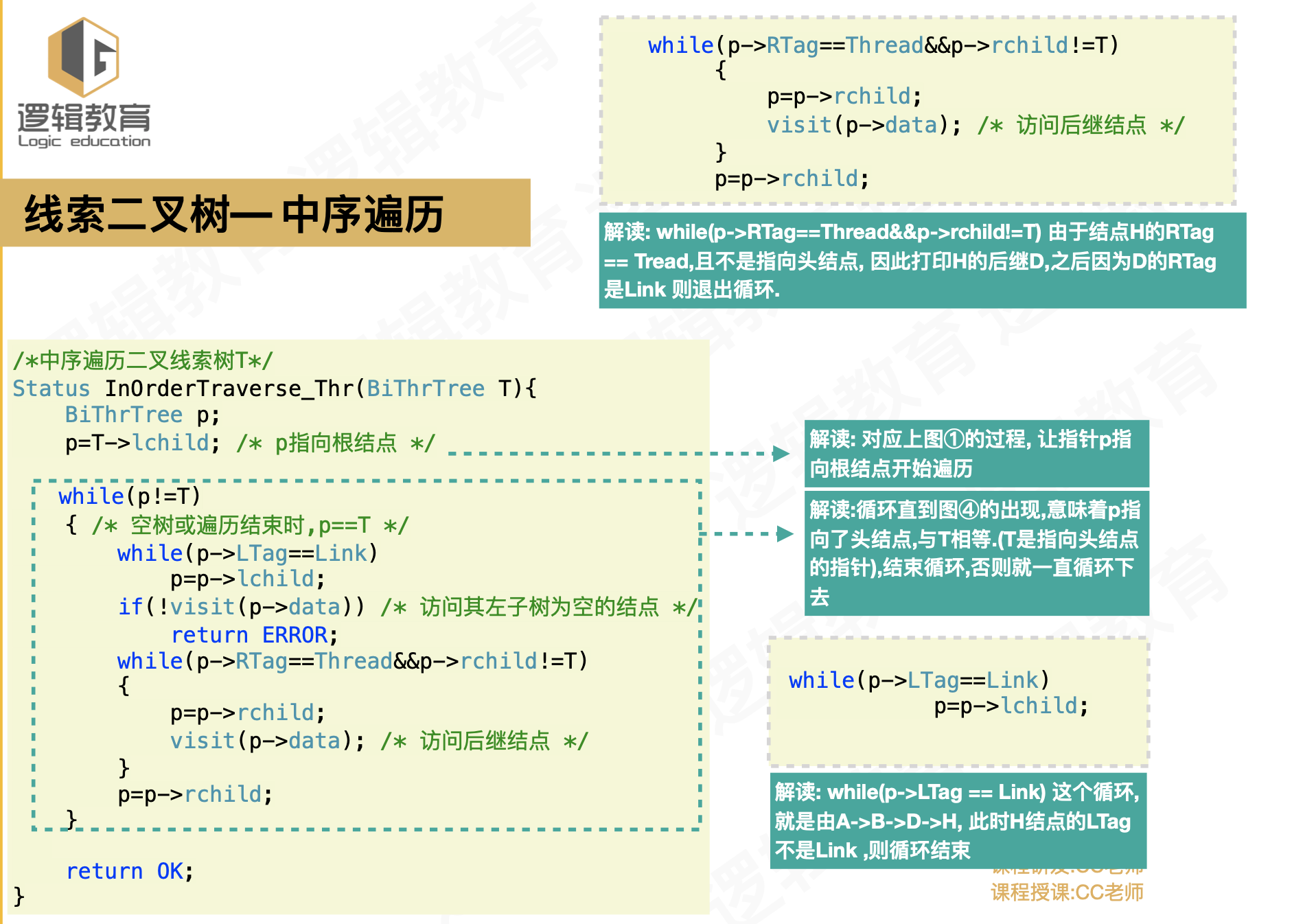
- 完整代码
#include "string.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "math.h"
#include "time.h"
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAXSIZE 100 /* 存储空间初始分配量 */
/* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */
typedef int Status;
typedef char CElemType;
/* 字符型以空格符为空 */
CElemType Nil='#';
#pragma mark--二叉树构造
int indexs = 1;
typedef char String[24]; /* 0号单元存放串的长度 */
String str;
Status StrAssign(String T,char *chars)
{
int i;
if(strlen(chars)>MAXSIZE)
return ERROR;
else
{
T[0]=strlen(chars);
for(i=1;i<=T[0];i++)
T[i]=*(chars+i-1);
return OK;
}
}
/* Link==0表示指向左右孩子指针, */
/* Thread==1表示指向前驱或后继的线索 */
typedef enum {Link,Thread} PointerTag;
/* 线索二叉树存储结点结构*/
typedef struct BiThrNode{
//数据
CElemType data;
//左右孩子指针
struct BiThrNode *lchild,*rchild;
//左右标记
PointerTag LTag;
PointerTag RTag;
}BiThrNode,*BiThrTree;
/*
8.1 打印
*/
Status visit(CElemType e)
{
printf("%c ",e);
return OK;
}
/*
8.3 构造二叉树
按照前序输入线索二叉树结点的值,构造二叉树T
*/
Status CreateBiThrTree(BiThrTree *T){
CElemType h;
//scanf("%c",&h);
//获取字符
h = str[indexs++];
if (h == Nil) {
*T = NULL;
}else{
*T = (BiThrTree)malloc(sizeof(BiThrNode));
if (!*T) {
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
//生成根结点(前序)
(*T)->data = h;
//递归构造左子树
CreateBiThrTree(&(*T)->lchild);
//存在左孩子->将标记LTag设置为Link
if ((*T)->lchild) (*T)->LTag = Link;
//递归构造右子树
CreateBiThrTree(&(*T)->rchild);
//存在右孩子->将标记RTag设置为Link
if ((*T)->rchild) (*T)->RTag = Link;
}
return OK;
}
/*
8.3 中序遍历二叉树T, 将其中序线索化,Thrt指向头结点
*/
BiThrTree pre; /* 全局变量,始终指向刚刚访问过的结点 */
/* 中序遍历进行中序线索化*/
void InThreading(BiThrTree p){
/*
InThreading(p->lchild);
.....
InThreading(p->rchild);
*/
if (p) {
//递归左子树线索化
InThreading(p->lchild);
//无左孩子
if (!p->lchild) {
//前驱线索
p->LTag = Thread;
//左孩子指针指向前驱
p->lchild = pre;
}else
{
p->LTag = Link;
}
//前驱没有右孩子
if (!pre->rchild) {
//后继线索
pre->RTag = Thread;
//前驱右孩子指针指向后继(当前结点p)
pre->rchild = p;
}else
{
pre->RTag = Link;
}
//保持pre指向p的前驱
pre = p;
//递归右子树线索化
InThreading(p->rchild);
}
}
/* 中序遍历二叉树T,并将其中序线索化,Thrt指向头结点 */
Status InOrderThreading(BiThrTree *Thrt , BiThrTree T){
*Thrt=(BiThrTree)malloc(sizeof(BiThrNode));
if (! *Thrt) {
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
//建立头结点;
(*Thrt)->LTag = Link;
(*Thrt)->RTag = Thread;
//右指针回指向
(*Thrt)->rchild = (*Thrt);
/* 若二叉树空,则左指针回指 */
if (!T) {
(*Thrt)->lchild=*Thrt;
}else{
(*Thrt)->lchild=T;
pre=(*Thrt);
//中序遍历进行中序线索化
InThreading(T);
//最后一个结点rchil 孩子
pre->rchild = *Thrt;
//最后一个结点线索化
pre->RTag = Thread;
(*Thrt)->rchild = pre;
}
return OK;
}
/*中序遍历二叉线索树T*/
Status InOrderTraverse_Thr(BiThrTree T){
BiThrTree p;
p=T->lchild; /* p指向根结点 */
while(p!=T)
{ /* 空树或遍历结束时,p==T */
while(p->LTag==Link)
p=p->lchild;
if(!visit(p->data)) /* 访问其左子树为空的结点 */
return ERROR;
while(p->RTag==Thread&&p->rchild!=T)
{
p=p->rchild;
visit(p->data); /* 访问后继结点 */
}
p=p->rchild;
}
return OK;
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
// insert code here...
printf("Hello, 线索化二叉树!\n");
BiThrTree H,T;
//StrAssign(str,"ABDH#K###E##CFI###G#J##");
StrAssign(str,"ABDH##I##EJ###CF##G##");
CreateBiThrTree(&T); /* 按前序产生二叉树 */
InOrderThreading(&H,T); /* 中序遍历,并中序线索化二叉树 */
InOrderTraverse_Thr(H);
printf("\n\n");
return 0;
}
哈夫曼树
基本术语
- 路径和路径长度
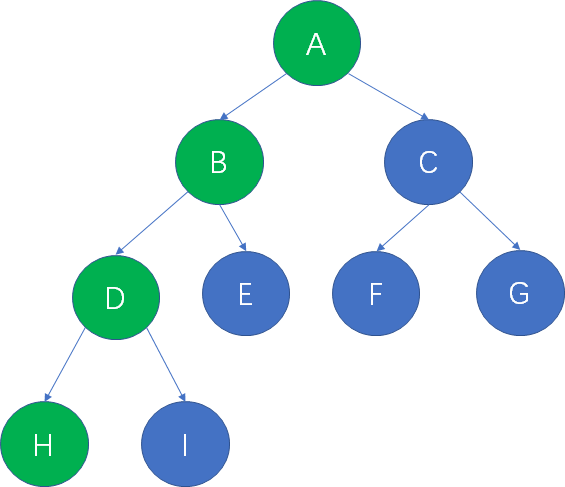
- 在一棵树中,从一个结点往下可以达到的孩子或孙子结点之间的通路,称为路径。eg:下图从根结点A到叶子结点H的路径,就是A,B,D,H
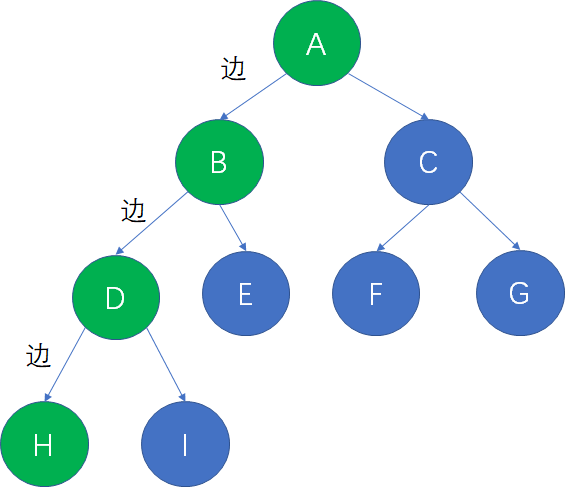
- 通路中分支的数目称为路径长度。eg:下图从根结点A到叶子结点H,共经过了3条边,因此路径长度是3
-
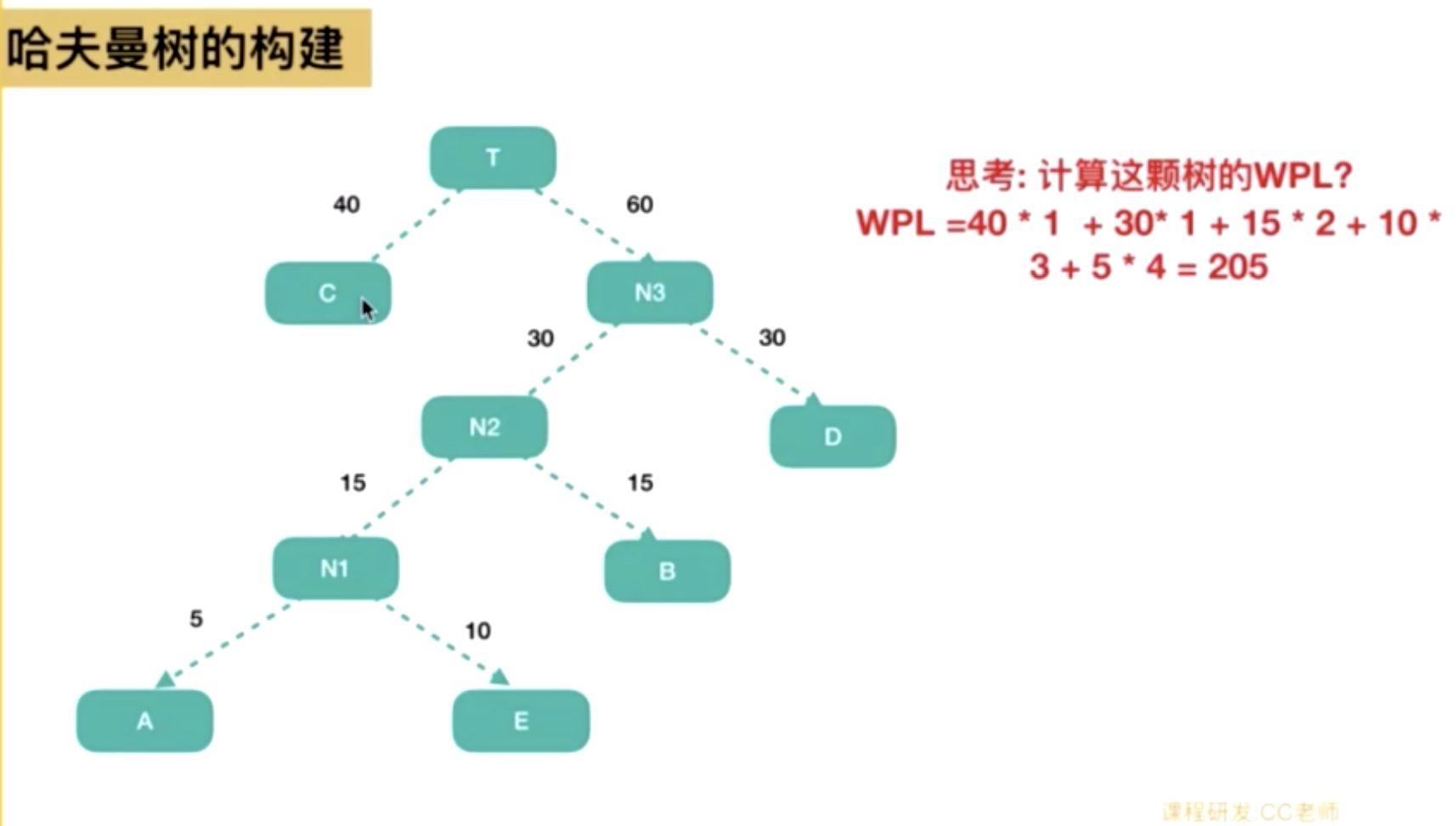
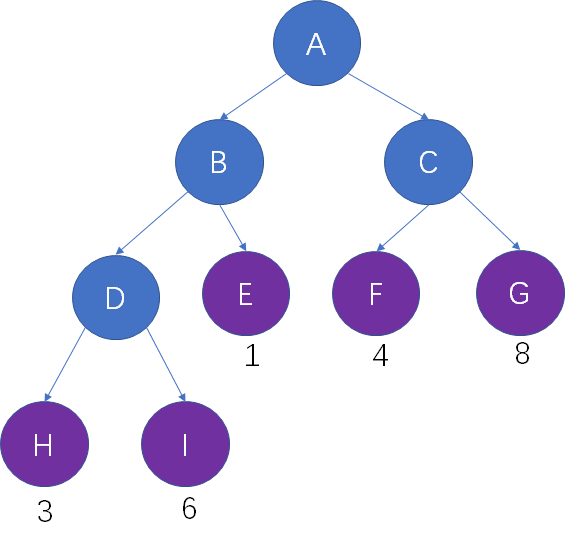
结点的权及带权路径长度 在一棵树中,所有叶子结点的带权路径长度之和,被称为树的带权路径长度,也被简称为WPL。
-
哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree)是在叶子结点和权重确定的情况下,带权路径长度最小的二叉树,也被称为最优二叉树。
哈夫曼树的构建
假设有6个叶子结点,权重依次是2,3,7,9,18,25,如何构建一颗哈夫曼树,也就是带权路径长度最小的树呢?
- 1.构建一个队列,由小至大排列。找到最小的两个树作为叶子节点,构成一颗二叉树,其根节点的权值为两者相加
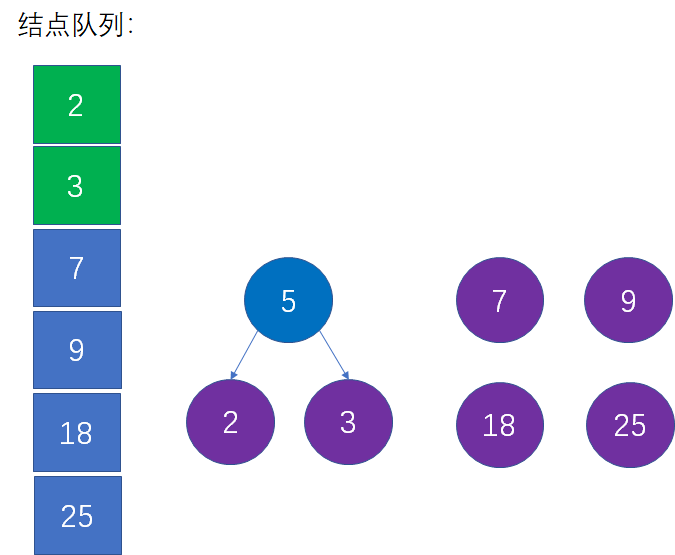
-
- 从队列中移除上一步选择的两个最小结点,把新的父节点加入队列
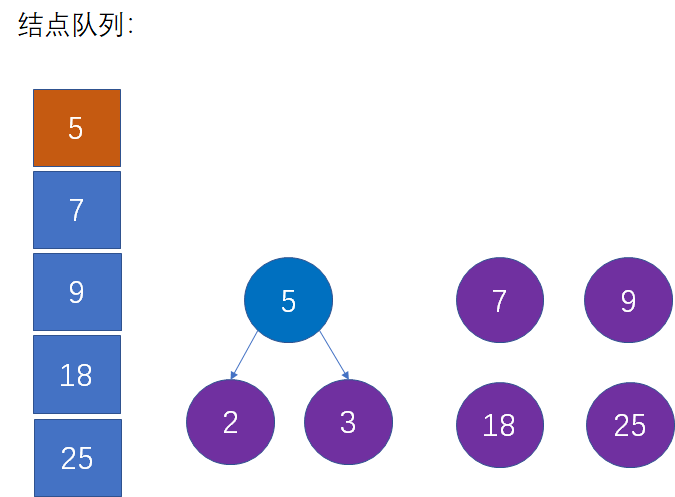
- 从队列中移除上一步选择的两个最小结点,把新的父节点加入队列
-
- 选择当前权值最小的两个结点,生成新的父结点,即重复第一步
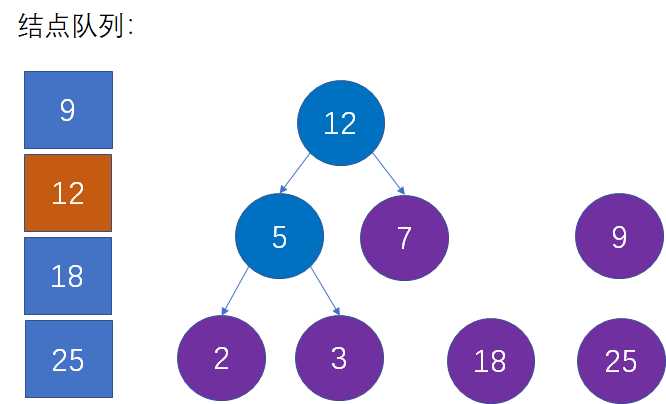
- 选择当前权值最小的两个结点,生成新的父结点,即重复第一步
-
- 根据上述逻辑,不断重复,最终构建成一个树
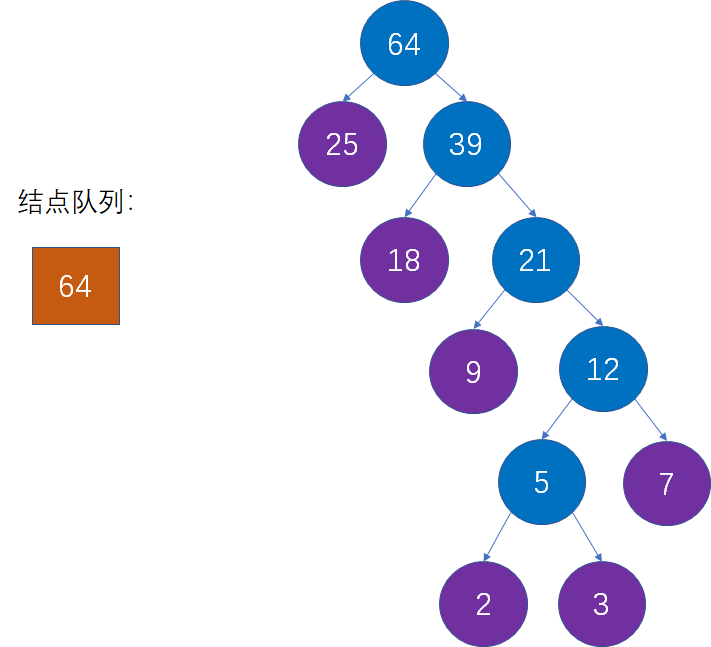
- 根据上述逻辑,不断重复,最终构建成一个树
哈夫曼树和哈夫曼编码算法实现
哈夫曼树
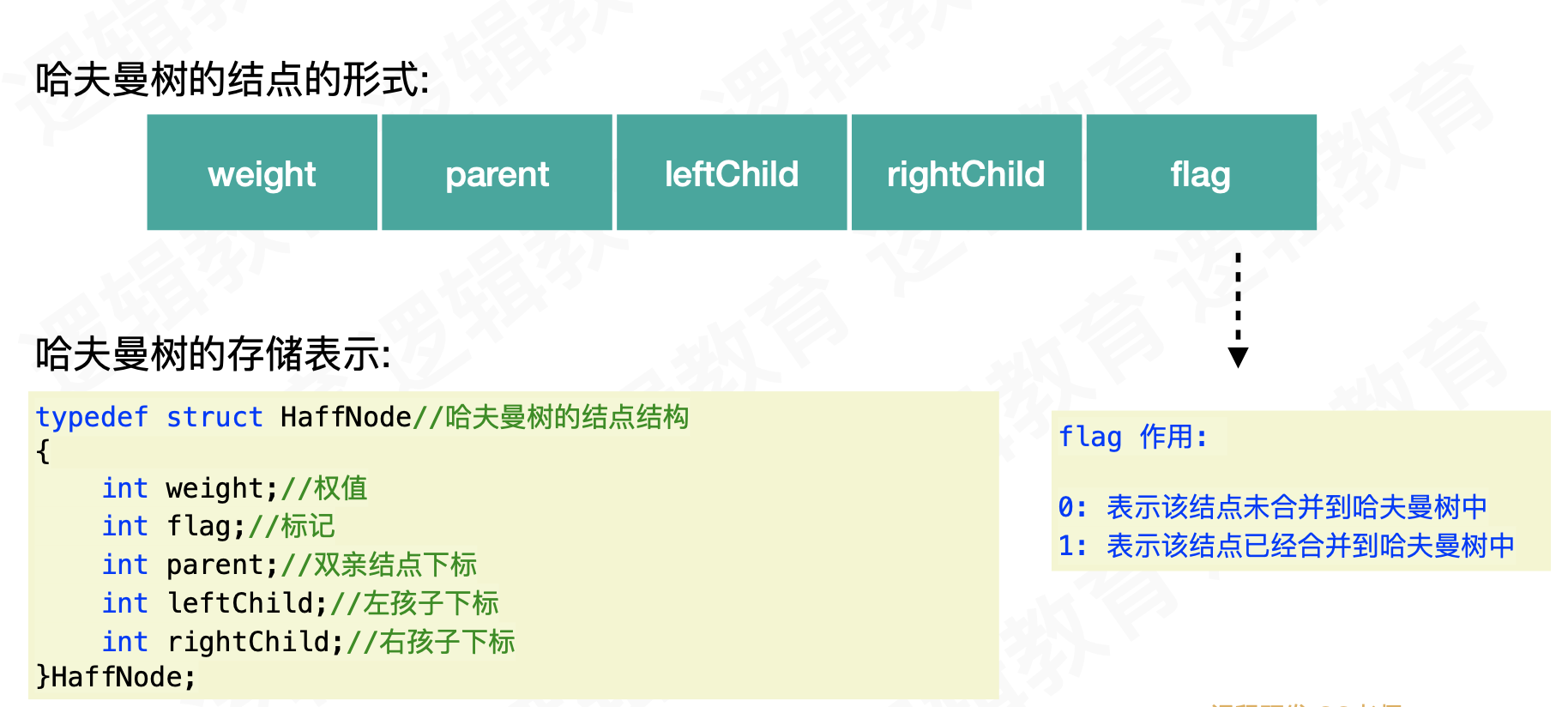
- 初始化哈法曼二叉树
- 循环不断找到节点中,最小的两个节点值,加入到哈夫曼树中
哈夫曼编码
哈夫曼编码是可变字长编码(VLC)的一种。Huffman于1952年提出一种编码方法,该方法完全依据字符出现概率来构造异字头的平均长度最短的码字。

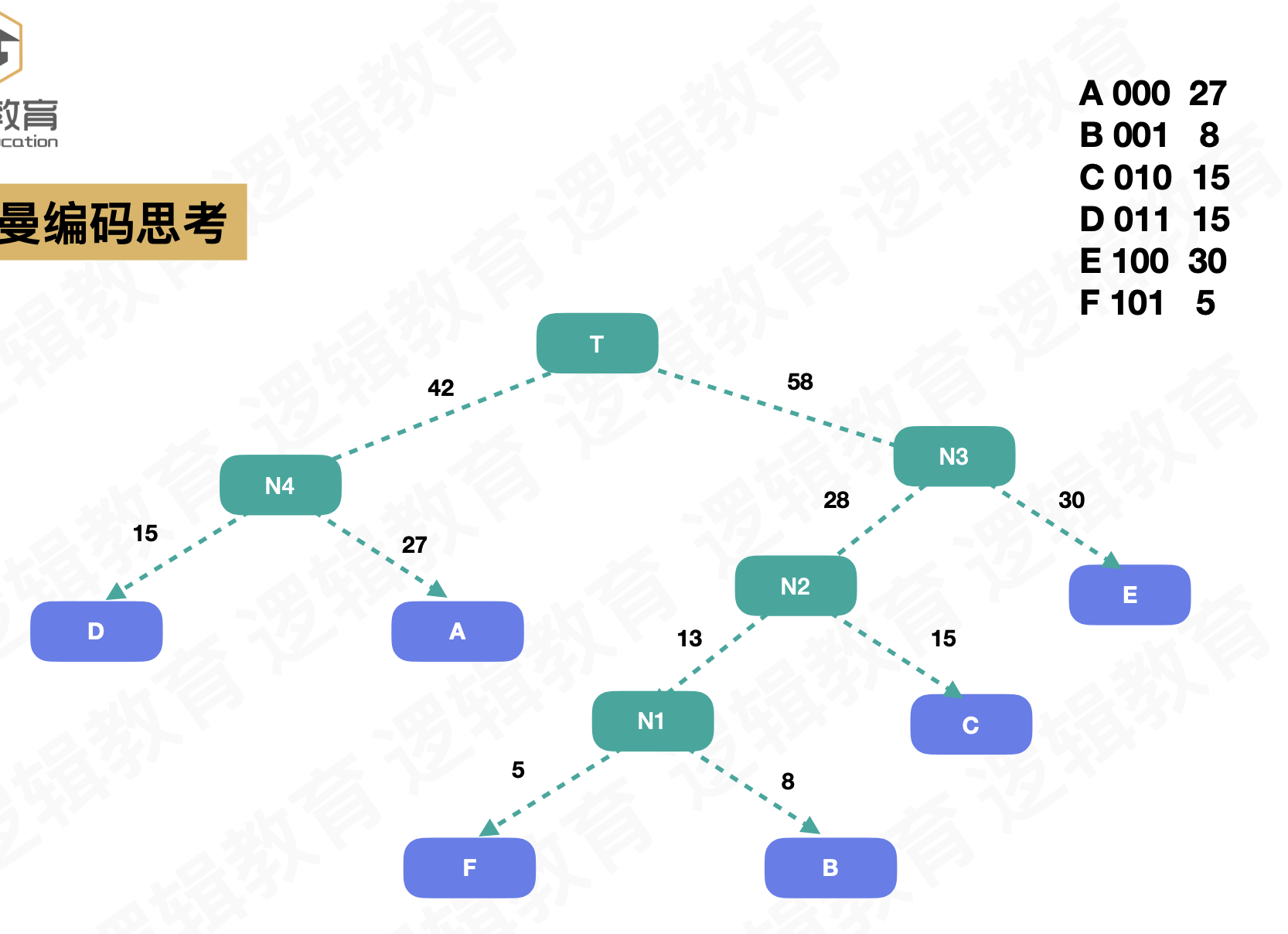
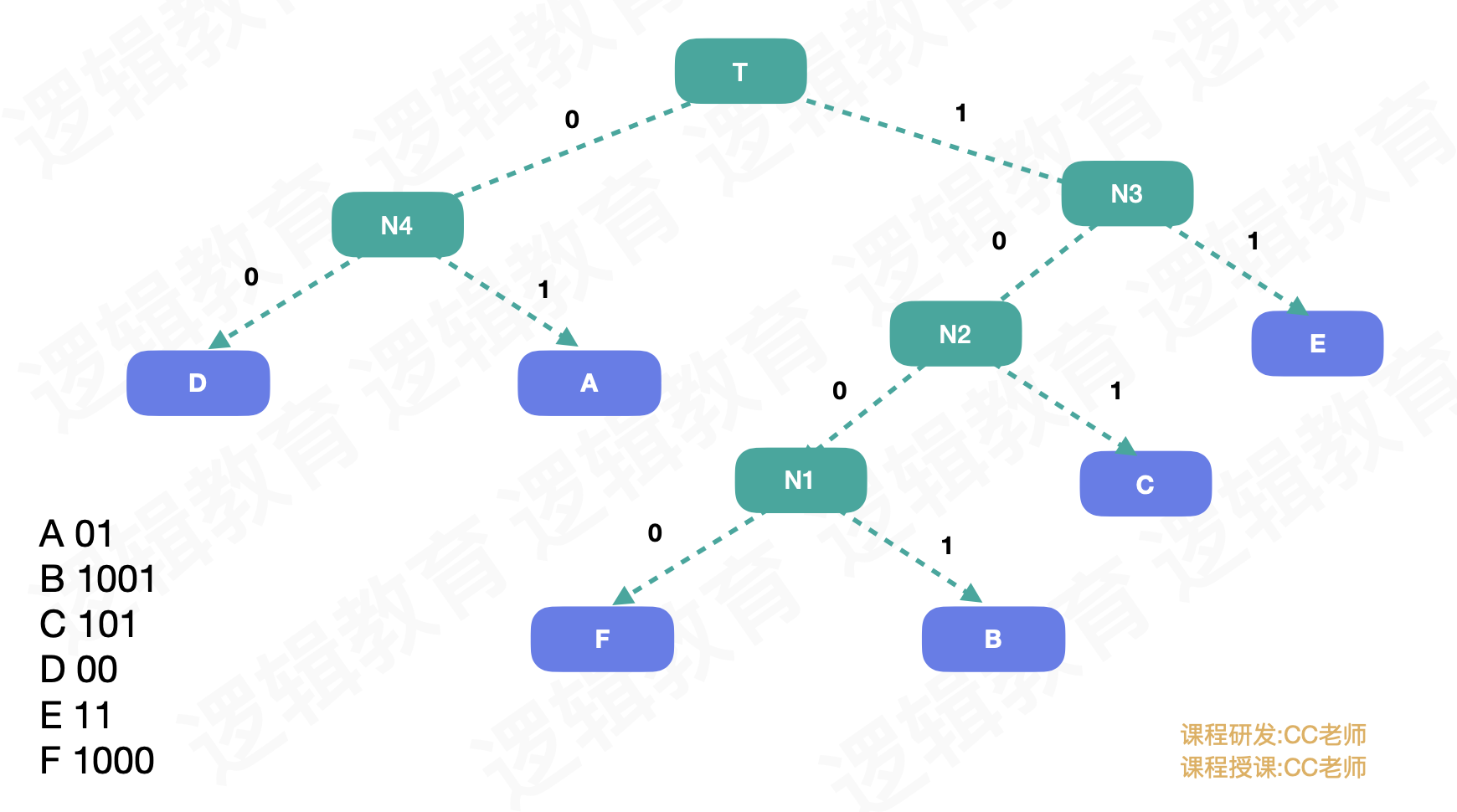
- 获取根据全职构建的哈夫曼树
- 循环遍历[0,n]个节点
- 创建临时节点cd,从根节点开始对齐进行编码,左孩子为0,右孩子为1
- 将编码后的节点存储haffCode[i]
- 设置haffCode[i]的开始位置以及权值
代码实现
#include "string.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
const int MaxValue = 10000;//初始设定的权值最大值
const int MaxBit = 4;//初始设定的最大编码位数
const int MaxN = 10;//初始设定的最大结点个数
typedef struct HaffNode{
int weight;
int flag;
int parent;
int leftChild;
int rightChild;
}HaffNode;
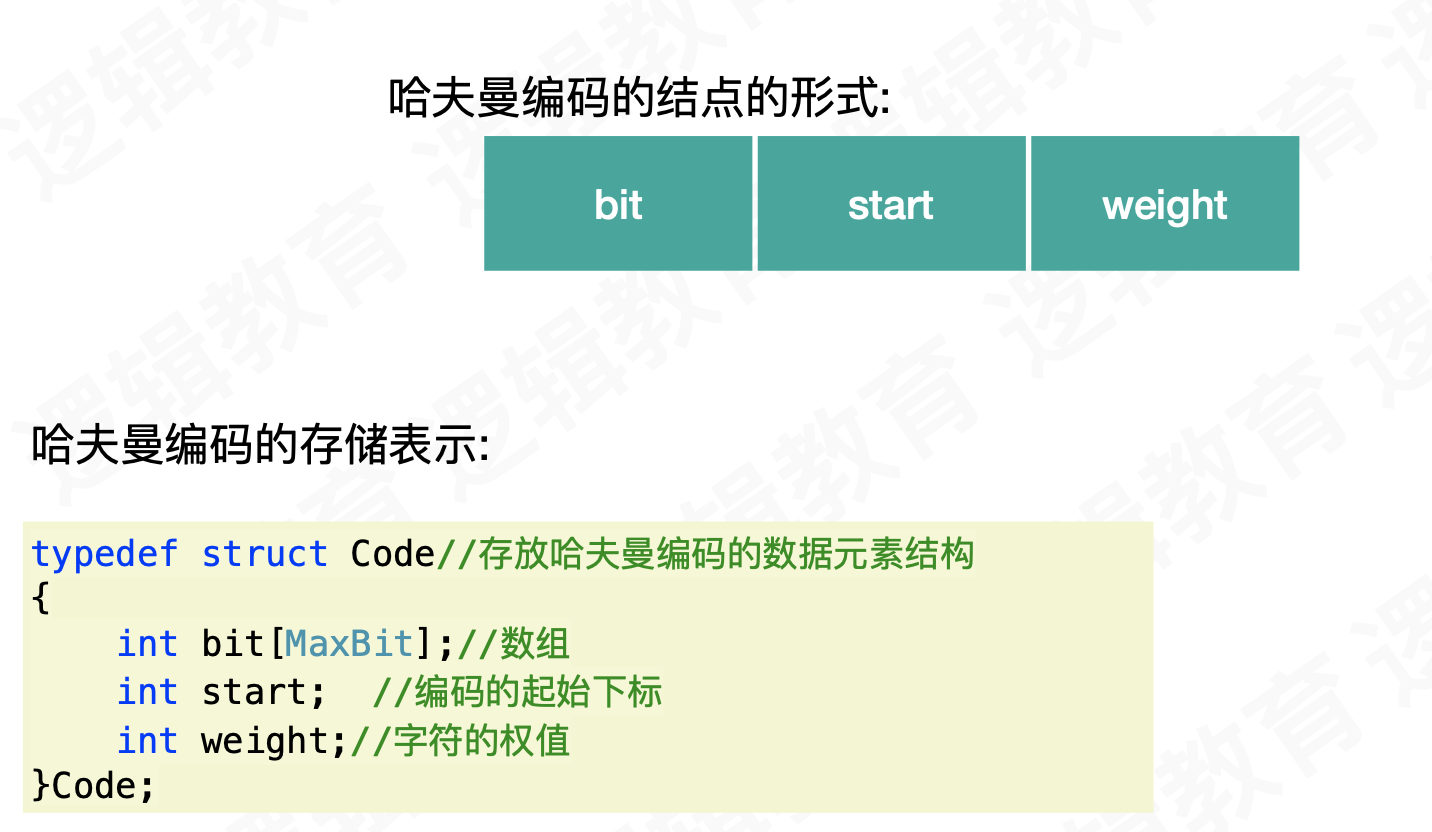
typedef struct Code//存放哈夫曼编码的数据元素结构
{
int bit[MaxBit];//数组
int start; //编码的起始下标
int weight;//字符的权值
}Code;
//1.
//根据权重值,构建哈夫曼树;
//{2,4,5,7}
//n = 4;
void Haffman(int weight[],int n,HaffNode *haffTree){
int j,m1,m2,x1,x2;
//1.哈夫曼树初始化
//n个叶子结点. 2n-1
for(int i = 0; i < 2*n-1;i++){
if(i<n)
haffTree[i].weight = weight[i];
else
haffTree[i].weight = 0;
haffTree[i].parent = 0;
haffTree[i].flag = 0;
haffTree[i].leftChild = -1;
haffTree[i].rightChild = -1;
}
//2.构造哈夫曼树haffTree的n-1个非叶结点
for (int i = 0; i< n - 1; i++){
m1 = m2 = MaxValue;
x1 = x2 = 0;
//2,4,5,7
for (j = 0; j< n + i; j++)//循环找出所有权重中,最小的二个值--morgan
{
if (haffTree[j].weight < m1 && haffTree[j].flag == 0)
{
m2 = m1;
x2 = x1;
m1 = haffTree[j].weight;
x1 = j;
} else if(haffTree[j].weight<m2 && haffTree[j].flag == 0)
{
m2 = haffTree[j].weight;
x2 = j;
}
}
//3.将找出的两棵权值最小的子树合并为一棵子树
haffTree[x1].parent = n + i;
haffTree[x2].parent = n + i;
//将2个结点的flag 标记为1,表示已经加入到哈夫曼树中
haffTree[x1].flag = 1;
haffTree[x2].flag = 1;
//修改n+i结点的权值
haffTree[n + i].weight = haffTree[x1].weight + haffTree[x2].weight;
//修改n+i的左右孩子的值
haffTree[n + i].leftChild = x1;
haffTree[n + i].rightChild = x2;
}
}
/*
9.2 哈夫曼编码
由n个结点的哈夫曼树haffTree构造哈夫曼编码haffCode
//{2,4,5,7}
*/
void HaffmanCode(HaffNode haffTree[], int n, Code haffCode[])
{
//1.创建一个结点cd
Code *cd = (Code * )malloc(sizeof(Code));
int child, parent;
//2.求n个叶结点的哈夫曼编码
for (int i = 0; i<n; i++)
{
//从0开始计数
cd->start = 0;
//取得编码对应权值的字符
cd->weight = haffTree[i].weight;
//当叶子结点i 为孩子结点.
child = i;
//找到child 的双亲结点;
parent = haffTree[child].parent;
//由叶结点向上直到根结点
while (parent != 0)
{
if (haffTree[parent].leftChild == child)
cd->bit[cd->start] = 0;//左孩子结点编码0
else
cd->bit[cd->start] = 1;//右孩子结点编码1
//编码自增
cd->start++;
//当前双亲结点成为孩子结点
child = parent;
//找到双亲结点
parent = haffTree[child].parent;
}
int temp = 0;
for (int j = cd->start - 1; j >= 0; j--){
temp = cd->start-j-1;
haffCode[i].bit[temp] = cd->bit[j];
}
//把cd中的数据赋值到haffCode[i]中.
//保存好haffCode 的起始位以及权值;
haffCode[i].start = cd->start;
//保存编码对应的权值
haffCode[i].weight = cd->weight;
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
// insert code here...
printf("Hello, 哈夫曼编码!\n");
int i, j, n = 4, m = 0;
//权值
int weight[] = {2,4,5,7};
//初始化哈夫曼树, 哈夫曼编码
HaffNode *myHaffTree = malloc(sizeof(HaffNode)*2*n-1);
Code *myHaffCode = malloc(sizeof(Code)*n);
//当前n > MaxN,表示超界. 无法处理.
if (n>MaxN)
{
printf("定义的n越界,修改MaxN!");
exit(0);
}
//1. 构建哈夫曼树
Haffman(weight, n, myHaffTree);
//2.根据哈夫曼树得到哈夫曼编码
HaffmanCode(myHaffTree, n, myHaffCode);
//3.
for (i = 0; i<n; i++)
{
printf("Weight = %d\n",myHaffCode[i].weight);
for (j = 0; j<myHaffCode[i].start; j++)
printf("%d",myHaffCode[i].bit[j]);
m = m + myHaffCode[i].weight*myHaffCode[i].start;
printf("\n");
}
printf("Huffman's WPS is:%d\n",m);
return 0;
}