ServletContainerInitializer
Shared libraries(共享库) and runtimes pluggability(运行时插件)的原理,在后面的框架整合里,用得比较多,来分析下它
ServletContainerInitializer在web容器启动时为提供给第三方组件机会做一些初始化的工作,例如注册servlet或者filters等,servlet规范(JSR356)中通过ServletContainerInitializer实现此功能。
每个框架要使用ServletContainerInitializer就必须在对应的jar包的META-INF/services 目录创建一个名为javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer的文件,文件内容指定具体的ServletContainerInitializer实现类,那么,当web容器启动时就会运行这个初始化器做一些组件内的初始化工作。
如下:
@HandlesTypes(value = SamService.class)//感兴趣的类
public class SamServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> set, ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("感兴趣的类型");
for (Class<?> clazz : set) {
System.out.println(clazz);// 反射
}
ServletRegistration.Dynamic orderServlet = servletContext.addServlet("orderServlet", new OrderServlet());
orderServlet.addMapping("/order");
servletContext.addListener(OrderListener.class);
FilterRegistration.Dynamic orderFilter = servletContext.addFilter("orderFilter", OrderFilter.class);
orderFilter.addMappingForUrlPatterns(EnumSet.of(DispatcherType.REQUEST), true, "/*");
}
}
在springMVC中的使用:
我们可以通过依赖发现SpringMvc也使用了这么一种方式,

我们打开可以看到里买呢额内容是:
org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer
所以在我我们的容器启动的时候就会执行者们一个类
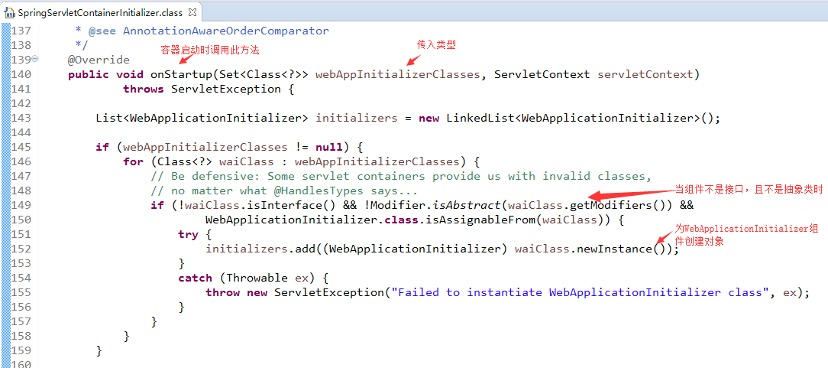
打开WebApplicationInitializer源码看看组件及实现
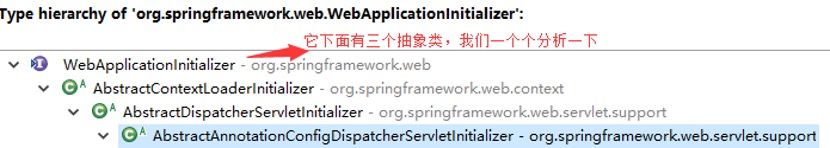
子类AbstractContextLoaderInitializer作用:
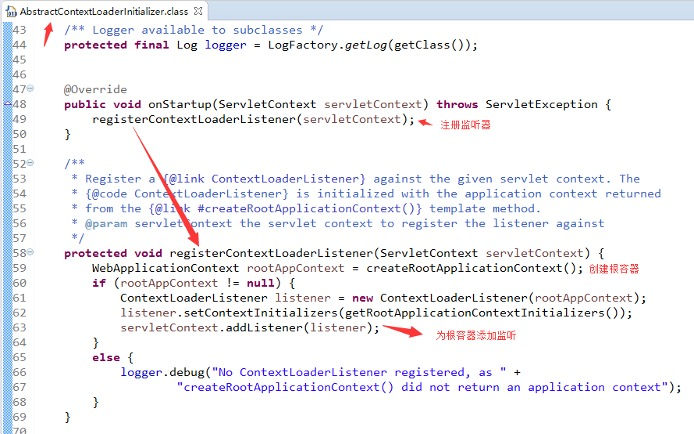
子类AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer的作用:从名字来看可知是DispatcherServlet初始化
子类AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer:注解方式配置的dispatcherServlet初始化器
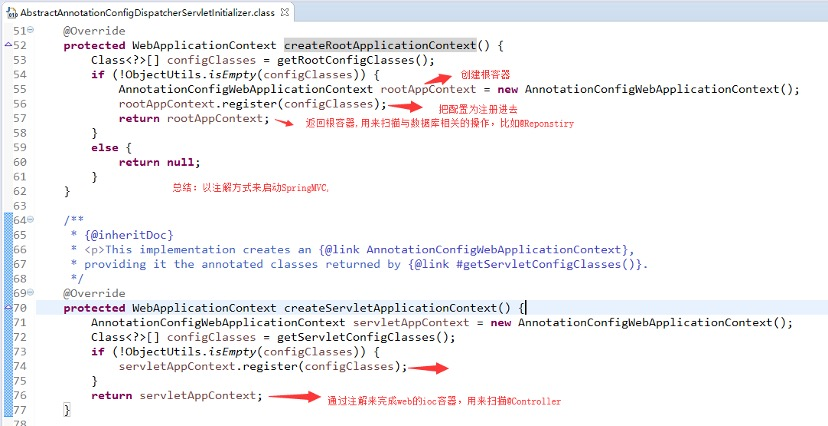
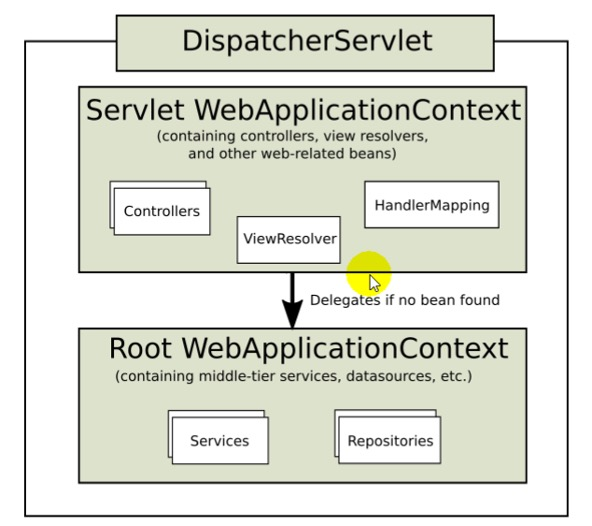
很明显,servlet的容器用来处理@Controller,视图解析,和web相关组件
而root根容器主要针对服务层,和数据源DAO层及事务控制相关处理(图源自spring官网)
SpringMVC流程整合
新建类继承AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer类
public class SamWebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
//获取根容器的配置类;(Spring的配置文件) 父容器;
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SamRootConfig.class};
}
//获取web容器的配置类(SpringMVC配置文件) 子容器;
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SamApplicationConfig.class};
}
//获取DispatcherServlet的映射信息
// /:拦截所有请求(包括静态资源(xx.js,xx.png)),但是不包括*.jsp;
// /*:拦截所有请求;连*.jsp页面都拦截;jsp页面是tomcat的jsp引擎解析的;
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
}
新建两个配置类模拟根容器和web容器
@ComponentScan(value = "com.enjoy", excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, classes = {Controller.class})
}, useDefaultFilters = true)
public class SamRootConfig {
}
@ComponentScan(value = "com.enjoy",includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,value = {Controller.class})
},useDefaultFilters = false)
@EnableWebMvc
public class SamApplicationConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//实现webMvcConfigurer可以自定义一些SpringMVC功能
public void configureViewResolvers(ViewResolverRegistry registry) {
registry.jsp("/WEB-INF/pages/",".jsp");
}
public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.enable();
}
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new SamInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/*");
}
}
新建Controller与Service
@Service
public class OrderService {
public String goBuy(String orderId) {
return "orderId====" + orderId;
}
}
@Controller
public class OrderController {
@Autowired
OrderService orderService;
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/buy")
public String buy() {
return orderService.goBuy("12345678");
}
//相当于会找 /WEB-INF/pages/ok.jsp
@RequestMapping("/ok")
public String ok() {
return "ok";
}
}
Servlet异步请求
同步请求
同步请求的原理
从tomcat中获取连接线程进行处理,但tomcat的线程数有限,会造成线程资源的紧张。
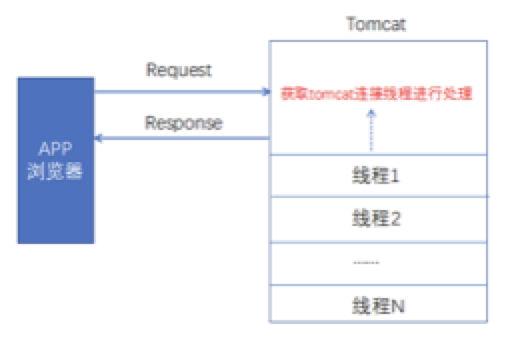
异步请求
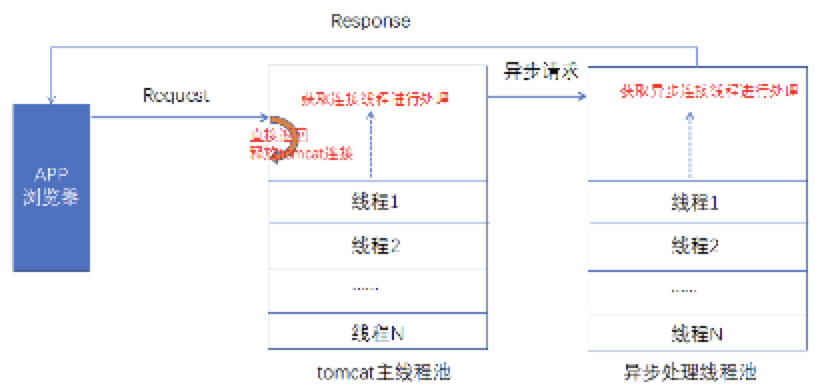
Servlet实现异步请求的方式
@WebServlet(value = "/asyncOrder", asyncSupported = true)
public class OrderAsyncServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("主线程开始……" + Thread.currentThread() + "start....." + System.currentTimeMillis());
AsyncContext asyncContext = req.startAsync();
asyncContext.start(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("副线程开始……" + Thread.currentThread() + "start....." + System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
buyCards();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
asyncContext.complete();
ServletResponse response = asyncContext.getResponse();
try {
response.getWriter().write("order successful");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("副线程结束……" + Thread.currentThread() + "end....." + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
});
System.out.println("主线程结束……" + Thread.currentThread() + "end....." + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
public void buyCards() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + ".............");
Thread.sleep(5000);//模拟业务操作
}
}
SpringMvc中的异步请求
- Callable
@Controller
public class AsyncOrderController {
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/orderCallable")
public Callable<String> callOrder() {
System.out.println("主线程开始..." + Thread.currentThread() + "==>" + System.currentTimeMillis());
Callable<String> callable = new Callable<String>() {
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("副线程开始..." + Thread.currentThread() + "==>" + System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("副线程开始..." + Thread.currentThread() + "==>" + System.currentTimeMillis());
return "order buy successful........";
}
};
System.out.println("主线程结束..." + Thread.currentThread() + "==>" + System.currentTimeMillis());
return callable;
}
}
- DeferredResult
@Controller
public class AsyncUserController {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
private static final int CPU_COUNT = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(20);
private ExecutorService threadPool;
@PostConstruct
public void startThreadPool() {
threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(CPU_COUNT * 2, CPU_COUNT * 2, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, queue);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/login")
@ResponseBody
public DeferredResult<String> login(final String name) {
System.out.println("主线程开始..." + Thread.currentThread() + "==>" + System.currentTimeMillis());
final DeferredResult<String> deferredResult = new DeferredResult<String>(10000L, "----failed-------");
threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
Random r = new Random();
userService.login(name, r.nextInt(5000), deferredResult);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
System.out.println("主线程结束..." + Thread.currentThread() + "==>" + System.currentTimeMillis());
return deferredResult;
}
}