图的存储
- 邻接矩阵
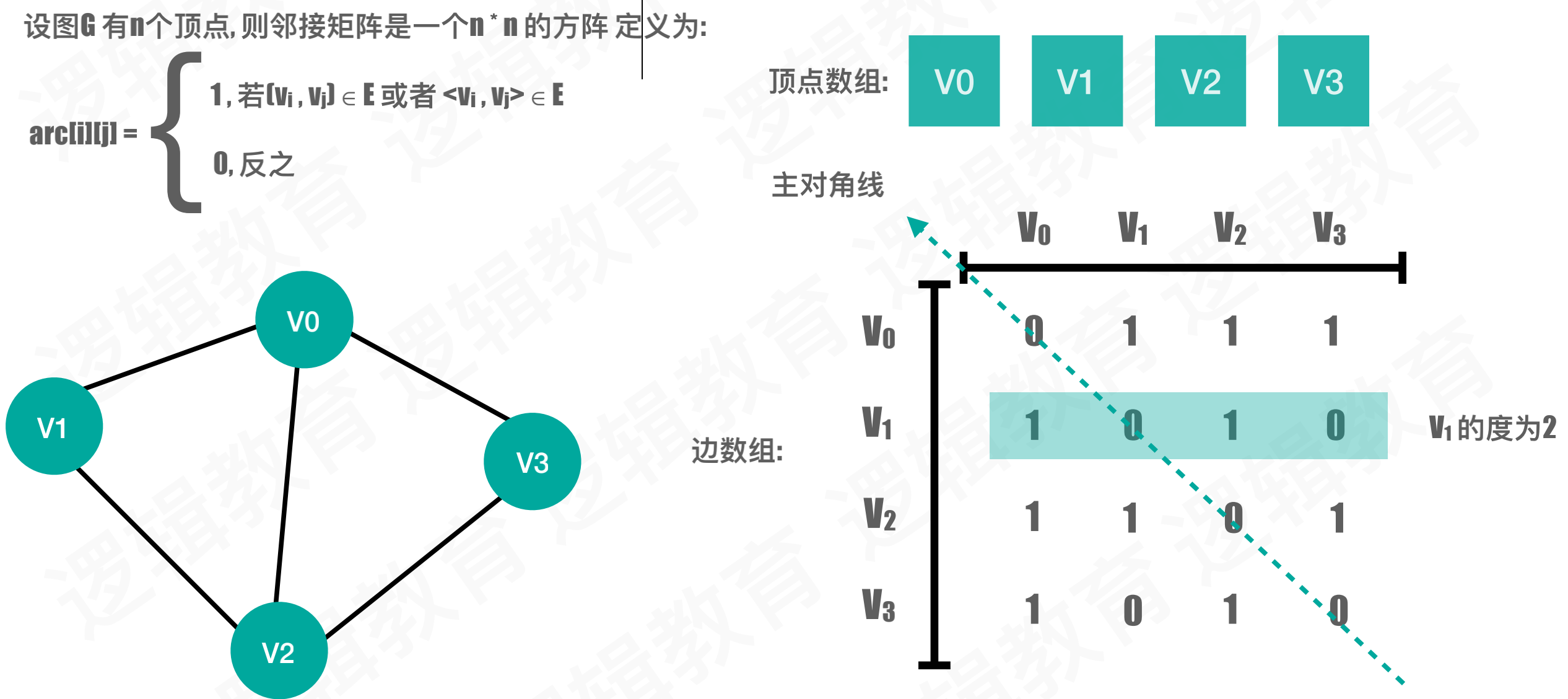
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAXVEX 100 /* 最大顶点数,应由用户定义 */
#define INFINITYC 0
typedef int Status; /* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */
typedef char VertexType; /* 顶点类型应由用户定义 */
typedef int EdgeType; /* 边上的权值类型应由用户定义 */
typedef struct
{
VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; /* 顶点表 */
EdgeType arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];/* 邻接矩阵,可看作边表 */
int numNodes, numEdges; /* 图中当前的顶点数和边数 */
}MGraph;
void CreateMGraph(MGraph *G){
int i,j,k,w;
printf("输入顶点数和边数:\n");
//1. 输入顶点数/边数
scanf("%d,%d",&G->numNodes,&G->numEdges);
printf("顶点数:%d,边数:%d\n",G->numNodes,G->numEdges);
//2.输入顶点信息/顶点表
for(i = 0; i<= G->numNodes;i++)
scanf("%c",&G->vexs[i]);
//3.初始化邻接矩阵
for(i = 0; i < G->numNodes;i++)
for(j = 0; j < G->numNodes;j++)
G->arc[i][j] = INFINITYC;
//4.输入边表信息
for(k = 0; k < G->numEdges;k++){
printf("输入边(vi,vj)上的下标i,下标j,权w\n");
scanf("%d,%d,%d",&i,&j,&w);
G->arc[i][j] = w;
//如果无向图,矩阵对称;
G->arc[j][i] = G->arc[i][j];
}
/*5.打印邻接矩阵*/
for (int i = 0; i < G->numNodes; i++) {
printf("\n");
for (int j = 0; j < G->numNodes; j++) {
printf("%d ",G->arc[i][j]);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
- 邻接表
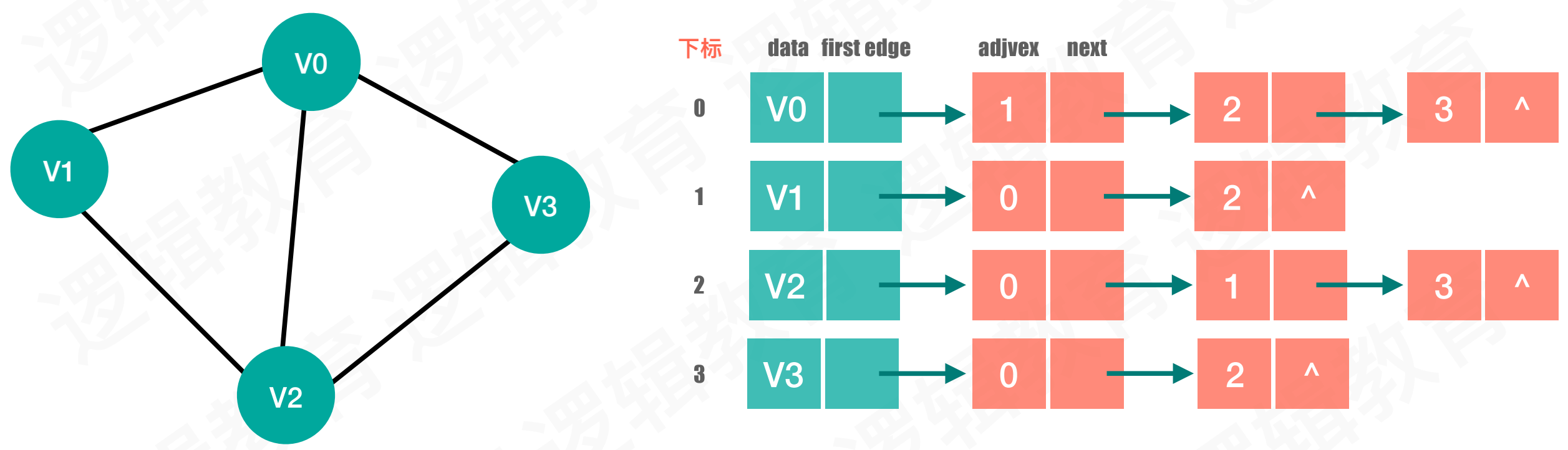
#define M 100
#define true 1
#define false 0
typedef char Element;
typedef int BOOL;
//邻接表的节点
typedef struct Node{
int adj_vex_index; //弧头的下标,也就是被指向的下标
Element data; //权重值
struct Node * next; //边指针
}EdgeNode;
//顶点节点表
typedef struct vNode{
Element data; //顶点的权值
EdgeNode * firstedge; //顶点下一个是谁?
}VertexNode, Adjlist[M];
//总图的一些信息
typedef struct Graph{
Adjlist adjlist; //顶点表
int arc_num; //边的个数
int node_num; //节点个数
BOOL is_directed; //是不是有向图
}Graph, *GraphLink;
void creatGraph(GraphLink *g){
int i,j,k;
EdgeNode *p;
//1. 顶点,边,是否有向
printf("输入顶点数目,边数和有向?:\n");
scanf("%d %d %d", &(*g)->node_num, &(*g)->arc_num, &(*g)->is_directed);
//2.顶点表
printf("输入顶点信息:\n");
for (i = 0; i < (*g)->node_num; i++) {
getchar();
scanf("%c", &(*g)->adjlist[i].data);
(*g)->adjlist[i].firstedge = NULL;
}
//3.
printf("输入边信息:\n");
for (k = 0; k < (*g)->arc_num; k++){
getchar();
scanf("%d %d", &i, &j);
//①新建一个节点
p = (EdgeNode *)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
//②弧头的下标
p->adj_vex_index = j;
//③头插法插进去,插的时候要找到弧尾,那就是顶点数组的下标i
p->next = (*g)->adjlist[i].firstedge;
//④将顶点数组[i].firstedge 设置为p
(*g)->adjlist[i].firstedge = p;
//j->i
if(!(*g)->is_directed)
{
// j -----> i
//①新建一个节点
p = (EdgeNode *)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
//②弧头的下标i
p->adj_vex_index = i;
//③头插法插进去,插的时候要找到弧尾,那就是顶点数组的下标i
p->next = (*g)->adjlist[j].firstedge;
//④将顶点数组[i].firstedge 设置为p
(*g)->adjlist[j].firstedge = p;
}
}
}
void putGraph(GraphLink g){
int i;
printf("邻接表中存储信息:\n");
//遍历一遍顶点坐标,每个再进去走一次
for (i = 0; i < g->node_num; i++) {
EdgeNode * p = g->adjlist[i].firstedge;
while (p) {
printf("%c->%c ", g->adjlist[i].data, g->adjlist[p->adj_vex_index].data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
图的遍历
-
深度优先遍历
邻接矩阵思路:
1. 将图的顶点和边信息输⼊到图结构中; 2. 创建⼀个visited 数组,⽤来标识顶点是否已经被遍历过. 3. 初始化visited 数组,将数组中元素置为FALSE 4. 选择顶点开始遍历.(注意⾮连通图的情况) 5. 进⼊递归; 打印i 对应的顶点信息. 并将该顶点标识为已遍历. 6. 循环遍历边表,判断当前arc[i][j]是否等于1,并且当前该顶点没有被遍历过,则继续递归DFS;#define OK 1 #define ERROR 0 #define TRUE 1 #define FALSE 0 typedef int Status; /* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */ typedef int Boolean; /* Boolean是布尔类型,其值是TRUE或FALSE */ typedef char VertexType; /* 顶点类型应由用户定义 */ typedef int EdgeType; /* 边上的权值类型应由用户定义 */ #define MAXSIZE 9 /* 存储空间初始分配量 */ #define MAXEDGE 15 #define MAXVEX 9 #define INFINITYC 65535 typedef struct { VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; /* 顶点表 */ EdgeType arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];/* 邻接矩阵,可看作边表 */ int numVertexes, numEdges; /* 图中当前的顶点数和边数 */ } MGraph; /*4.1 构建一个邻接矩阵*/ void CreateMGraph(MGraph *G) { int i, j; //1. 确定图的顶点数以及边数 G->numEdges=15; G->numVertexes=9; /*2.读入顶点信息,建立顶点表 */ G->vexs[0]='A'; G->vexs[1]='B'; G->vexs[2]='C'; G->vexs[3]='D'; G->vexs[4]='E'; G->vexs[5]='F'; G->vexs[6]='G'; G->vexs[7]='H'; G->vexs[8]='I'; /*3. 初始化图中的边表*/ for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++) { for ( j = 0; j < G->numVertexes; j++) { G->arc[i][j]=0; } } /*4.将图中的连接信息输入到边表中*/ G->arc[0][1]=1; G->arc[0][5]=1; G->arc[1][2]=1; G->arc[1][8]=1; G->arc[1][6]=1; G->arc[2][3]=1; G->arc[2][8]=1; G->arc[3][4]=1; G->arc[3][7]=1; G->arc[3][6]=1; G->arc[3][8]=1; G->arc[4][5]=1; G->arc[4][7]=1; G->arc[5][6]=1; G->arc[6][7]=1; /*5.无向图是对称矩阵.构成对称*/ for(i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++) { for(j = i; j < G->numVertexes; j++) { G->arc[j][i] =G->arc[i][j]; } } } /*4.2 DFS遍历*/ Boolean visited[MAXVEX]; /* 访问标志的数组 */ //1. 标识顶点是否被标记过; //2. 选择从某一个顶点开始(注意:非连通图的情况) //3. 进入递归,打印i点信息,标识; 边表 //4. [i][j] 是否等于1,没有变遍历过visted void DFS(MGraph G,int i){ //1. visited[i] = TRUE; printf("%c",G.vexs[i]); //2.0~numVertexes for(int j = 0; j < G.numVertexes;j++){ if(G.arc[i][j] == 1 && !visited[j]) DFS(G, j); } } void DFSTravese(MGraph G){ //1.初始化 for(int i=0;i<G.numVertexes;i++){ visited[i] = FALSE; } //2.某一个顶点 for(int i = 0;i<G.numVertexes;i++){ if(!visited[i]){ DFS(G, i); } } }邻接表思路:
1. 利⽤邻接矩阵将信息存储到邻接表中 2. 创建⼀个visited 数组,⽤来标识顶点是否已经被遍历过. 3. 初始化visited 数组,将数组中元素置为FALSE 4. 选择顶点开始遍历.(注意⾮连通图的情况) 5. 进⼊递归; 打印i 对应的顶点信息. 并将该顶点标识为已遍历. 6. 循环遍历边表,判断当前顶点是否等于1,并且当前该顶点没有被遍历过,则继续递归DFS;#define OK 1 #define ERROR 0 #define TRUE 1 #define FALSE 0 #define MAXSIZE 9 /* 存储空间初始分配量 */ #define MAXEDGE 15 #define MAXVEX 9 #define INFINITYC 65535 typedef int Status; /* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */ typedef int Boolean; /* Boolean是布尔类型,其值是TRUE或FALSE */ typedef char VertexType; /* 顶点类型应由用户定义 */ typedef int EdgeType; /* 边上的权值类型应由用户定义 */ /* 邻接矩阵结构 */ typedef struct { VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; /* 顶点表 */ EdgeType arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];/* 邻接矩阵,可看作边表 */ int numVertexes, numEdges; /* 图中当前的顶点数和边数 */ } MGraph; /* 邻接表结构****************** */ typedef struct EdgeNode {/* 边表结点 */ int adjvex; /* 邻接点域,存储该顶点对应的下标 */ int weight; /* 用于存储权值,对于非网图可以不需要 */ struct EdgeNode *next; /* 链域,指向下一个邻接点 */ } EdgeNode; typedef struct VertexNode {/* 顶点表结点 */ int in; /* 顶点入度 */ char data; /* 顶点域,存储顶点信息 */ EdgeNode *firstedge;/* 边表头指针 */ } VertexNode, AdjList[MAXVEX]; typedef struct { AdjList adjList; int numVertexes,numEdges; /* 图中当前顶点数和边数 */ }graphAdjList,*GraphAdjList; /*4.1 构建一个邻接矩阵*/ void CreateMGraph(MGraph *G) { int i, j; //1. 确定图的顶点数以及边数 G->numEdges=15; G->numVertexes=9; /*2.读入顶点信息,建立顶点表 */ G->vexs[0]='A'; G->vexs[1]='B'; G->vexs[2]='C'; G->vexs[3]='D'; G->vexs[4]='E'; G->vexs[5]='F'; G->vexs[6]='G'; G->vexs[7]='H'; G->vexs[8]='I'; /*3. 初始化图中的边表*/ for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++) { for ( j = 0; j < G->numVertexes; j++) { G->arc[i][j]=0; } } /*4.将图中的连接信息输入到边表中*/ G->arc[0][1]=1; G->arc[0][5]=1; G->arc[1][2]=1; G->arc[1][8]=1; G->arc[1][6]=1; G->arc[2][3]=1; G->arc[2][8]=1; G->arc[3][4]=1; G->arc[3][7]=1; G->arc[3][6]=1; G->arc[3][8]=1; G->arc[4][5]=1; G->arc[4][7]=1; G->arc[5][6]=1; G->arc[6][7]=1; /*5.无向图是对称矩阵.构成对称*/ for(i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++) { for(j = i; j < G->numVertexes; j++) { G->arc[j][i] =G->arc[i][j]; } } } /*4.2 利用邻接矩阵构建邻接表*/ void CreateALGraph(MGraph G,GraphAdjList *GL) { //1.创建邻接表,并且设计邻接表的顶点数以及弧数 *GL = (GraphAdjList)malloc(sizeof(graphAdjList)); (*GL)->numVertexes = G.numVertexes; (*GL)->numEdges = G.numEdges; //2. 从邻接矩阵中将顶点信息输入 for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++) { //顶点入度为0 (*GL)->adjList[i].in = 0; //顶点信息 (*GL)->adjList[i].data = G.vexs[i]; //顶点边表置空 (*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge = NULL; } //3. 建立边表 EdgeNode *e; for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < G.numVertexes; j++) { if (G.arc[i][j] == 1) { //创建边表中的邻近结点 i->j e = (EdgeNode *)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode)); //邻接序号为j e->adjvex = j; //将当前结点的指向adjList[i]的顶点边表上 e->next = (*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge; (*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge = e; //顶点j 上的入度++; (*GL)->adjList[j].in++; // //创建边表中的邻近结点 j->i // e = (EdgeNode *)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode)); // //邻接序号为j // e->adjvex = i; // //将当前结点的指向adjList[i]的顶点边表上 // e->next = (*GL)->adjList[j].firstedge; // (*GL)->adjList[j].firstedge = e; // //顶点j 上的入度++; // (*GL)->adjList[i].in++; } } } } Boolean visited[MAXSIZE]; /* 访问标志的数组 */ /* 邻接表的深度优先递归算法 */ void DFS(GraphAdjList GL, int i) { EdgeNode *p; visited[i] = TRUE; //2.打印顶点 A printf("%c ",GL->adjList[i].data); p = GL->adjList[i].firstedge; //3. while (p) { if(!visited[p->adjvex]) DFS(GL,p->adjvex); p = p->next; } } /* 邻接表的深度遍历操作 */ void DFSTraverse(GraphAdjList GL) { //1. 将访问记录数组默认置为FALSE for (int i = 0; i < GL->numVertexes; i++) { /*初始化所有顶点状态都是未访问过的状态*/ visited[i] = FALSE; } //2. 选择一个顶点开始DFS遍历. 例如A for(int i = 0; i < GL->numVertexes; i++) //对未访问过的顶点调用DFS, 若是连通图则只会执行一次. if(!visited[i]) DFS(GL, i); } -
广度优先遍历
特点:
1、把根节点放到队列的末尾。 2、每次从队列的头部取出⼀个元素,查看这个元素所有的下⼀级元素,把它们放到队列的末尾。 并把这个元素记为它下⼀级元素的前驱。 3、找到所要找的元素时结束程序。 4、如果遍历整个树还没有找到,结束程序。邻接矩阵实现:
#define OK 1 #define ERROR 0 #define TRUE 1 #define FALSE 0 typedef int Status; /* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */ typedef int Boolean; /* Boolean是布尔类型,其值是TRUE或FALSE */ typedef char VertexType; /* 顶点类型应由用户定义 */ typedef int EdgeType; /* 边上的权值类型应由用户定义 */ #define MAXSIZE 9 /* 存储空间初始分配量 */ #define MAXEDGE 15 #define MAXVEX 9 #define INFINITYC 65535 typedef struct { VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; /* 顶点表 */ EdgeType arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];/* 邻接矩阵,可看作边表 */ int numVertexes, numEdges; /* 图中当前的顶点数和边数 */ }MGraph; /* 构建一个邻接矩阵*/ void CreateMGraph(MGraph *G) { int i, j; //1. 确定图的顶点数以及边数 G->numEdges=15; G->numVertexes=9; /*2.读入顶点信息,建立顶点表 */ G->vexs[0]='A'; G->vexs[1]='B'; G->vexs[2]='C'; G->vexs[3]='D'; G->vexs[4]='E'; G->vexs[5]='F'; G->vexs[6]='G'; G->vexs[7]='H'; G->vexs[8]='I'; /*3. 初始化图中的边表*/ for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++) { for ( j = 0; j < G->numVertexes; j++) { G->arc[i][j]=0; } } /*4.将图中的连接信息输入到边表中*/ G->arc[0][1]=1; G->arc[0][5]=1; G->arc[1][2]=1; G->arc[1][8]=1; G->arc[1][6]=1; G->arc[2][3]=1; G->arc[2][8]=1; G->arc[3][4]=1; G->arc[3][7]=1; G->arc[3][6]=1; G->arc[3][8]=1; G->arc[4][5]=1; G->arc[4][7]=1; G->arc[5][6]=1; G->arc[6][7]=1; /*5.无向图是对称矩阵.构成对称*/ for(i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++) { for(j = i; j < G->numVertexes; j++) { G->arc[j][i] =G->arc[i][j]; } } } /* 循环队列的顺序存储结构 */ typedef struct { int data[MAXSIZE]; int front; /* 头指针 */ int rear; /* 尾指针,若队列不空,指向队列尾元素的下一个位置 */ }Queue; /* 初始化一个空队列Q */ Status InitQueue(Queue *Q) { Q->front=0; Q->rear=0; return OK; } /* 若队列Q为空队列,则返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE */ Status QueueEmpty(Queue Q) { if(Q.front==Q.rear) /* 队列空的标志 */ return TRUE; else return FALSE; } /* 若队列未满,则插入元素e为Q新的队尾元素 */ Status EnQueue(Queue *Q,int e) { if ((Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE == Q->front) /* 队列满的判断 */ return ERROR; Q->data[Q->rear]=e; /* 将元素e赋值给队尾 */ Q->rear=(Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE;/* rear指针向后移一位置, */ /* 若到最后则转到数组头部 */ return OK; } /* 若队列不空,则删除Q中队头元素,用e返回其值 */ Status DeQueue(Queue *Q,int *e) { if (Q->front == Q->rear) /* 队列空的判断 */ return ERROR; *e=Q->data[Q->front]; /* 将队头元素赋值给e */ Q->front=(Q->front+1)%MAXSIZE; /* front指针向后移一位置, */ /* 若到最后则转到数组头部 */ return OK; } /* 邻接矩阵广度优先遍历-代码实现*/ Boolean visited[MAXVEX]; /* 访问标志的数组 */ void BFSTraverse(MGraph G) { int temp = 0; //1. Queue Q; InitQueue(&Q); //2.将访问标志数组全部置为"未访问状态FALSE" for (int i = 0 ; i < G.numVertexes; i++) { visited[i] = FALSE; } //3.对遍历邻接表中的每一个顶点(对于连通图只会执行1次,这个循环是针对非连通图) for (int i = 0 ; i < G.numVertexes; i++) { if(!visited[i]){ visited[i] = TRUE; printf("%c ",G.vexs[i]); //4. 入队 EnQueue(&Q, i); while (!QueueEmpty(Q)) { //出队 DeQueue(&Q, &i); for (int j = 0; j < G.numVertexes; j++) { if(G.arc[i][j] == 1 && !visited[j]) { visited[j] = TRUE; printf("%c ",G.vexs[j]); EnQueue(&Q, j); } } } } } }邻接表实现:
#define OK 1 #define ERROR 0 #define TRUE 1 #define FALSE 0 #define MAXSIZE 9 /* 存储空间初始分配量 */ #define MAXEDGE 15 #define MAXVEX 9 #define INFINITYC 65535 typedef int Status; /* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */ typedef int Boolean; /* Boolean是布尔类型,其值是TRUE或FALSE */ typedef char VertexType; /* 顶点类型应由用户定义 */ typedef int EdgeType; /* 边上的权值类型应由用户定义 */ /* 邻接矩阵结构 */ typedef struct { VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; /* 顶点表 */ EdgeType arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];/* 邻接矩阵,可看作边表 */ int numVertexes, numEdges; /* 图中当前的顶点数和边数 */ }MGraph; /* 邻接表结构****************** */ typedef struct EdgeNode {/* 边表结点 */ int adjvex; /* 邻接点域,存储该顶点对应的下标 */ int weight; /* 用于存储权值,对于非网图可以不需要 */ struct EdgeNode *next; /* 链域,指向下一个邻接点 */ }EdgeNode; typedef struct VertexNode {/* 顶点表结点 */ int in; /* 顶点入度 */ char data; /* 顶点域,存储顶点信息 */ EdgeNode *firstedge;/* 边表头指针 */ }VertexNode, AdjList[MAXVEX]; typedef struct { AdjList adjList; int numVertexes,numEdges; /* 图中当前顶点数和边数 */ }graphAdjList,*GraphAdjList; /*构建一个邻接矩阵*/ void CreateMGraph(MGraph *G) { int i, j; //1. 确定图的顶点数以及边数 G->numEdges=15; G->numVertexes=9; /*2.读入顶点信息,建立顶点表 */ G->vexs[0]='A'; G->vexs[1]='B'; G->vexs[2]='C'; G->vexs[3]='D'; G->vexs[4]='E'; G->vexs[5]='F'; G->vexs[6]='G'; G->vexs[7]='H'; G->vexs[8]='I'; /*3. 初始化图中的边表*/ for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++) { for ( j = 0; j < G->numVertexes; j++) { G->arc[i][j]=0; } } /*4.将图中的连接信息输入到边表中*/ G->arc[0][1]=1; G->arc[0][5]=1; G->arc[1][2]=1; G->arc[1][8]=1; G->arc[1][6]=1; G->arc[2][3]=1; G->arc[2][8]=1; G->arc[3][4]=1; G->arc[3][7]=1; G->arc[3][6]=1; G->arc[3][8]=1; G->arc[4][5]=1; G->arc[4][7]=1; G->arc[5][6]=1; G->arc[6][7]=1; /*5.无向图是对称矩阵.构成对称*/ for(i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++) { for(j = i; j < G->numVertexes; j++) { G->arc[j][i] =G->arc[i][j]; } } } /* 利用邻接矩阵构建邻接表*/ void CreateALGraph(MGraph G,GraphAdjList *GL){ //1.创建邻接表,并且设计邻接表的顶点数以及弧数 *GL = (GraphAdjList)malloc(sizeof(graphAdjList)); (*GL)->numVertexes = G.numVertexes; (*GL)->numEdges = G.numEdges; //2. 从邻接矩阵中将顶点信息输入 for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++) { //顶点入度为0 (*GL)->adjList[i].in = 0; //顶点信息 (*GL)->adjList[i].data = G.vexs[i]; //顶点边表置空 (*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge = NULL; } //3. 建立边表 EdgeNode *e; for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < G.numVertexes; j++) { if (G.arc[i][j] == 1) { //创建边表中的邻近结点 i->j e = (EdgeNode *)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode)); //邻接序号为j e->adjvex = j; //将当前结点的指向adjList[i]的顶点边表上 e->next = (*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge; (*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge = e; //顶点j 上的入度++; (*GL)->adjList[j].in++; // //创建边表中的邻近结点 j->i // e = (EdgeNode *)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode)); // //邻接序号为j // e->adjvex = i; // //将当前结点的指向adjList[i]的顶点边表上 // e->next = (*GL)->adjList[j].firstedge; // (*GL)->adjList[j].firstedge = e; // //顶点j 上的入度++; // (*GL)->adjList[i].in++; } } } } /* 循环队列的顺序存储结构 */ typedef struct { int data[MAXSIZE]; int front; /* 头指针 */ int rear; /* 尾指针,若队列不空,指向队列尾元素的下一个位置 */ }Queue; /* 初始化一个空队列Q */ Status InitQueue(Queue *Q) { Q->front=0; Q->rear=0; return OK; } /* 若队列Q为空队列,则返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE */ Status QueueEmpty(Queue Q) { if(Q.front==Q.rear) /* 队列空的标志 */ return TRUE; else return FALSE; } /* 若队列未满,则插入元素e为Q新的队尾元素 */ Status EnQueue(Queue *Q,int e) { if ((Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE == Q->front) /* 队列满的判断 */ return ERROR; Q->data[Q->rear]=e; /* 将元素e赋值给队尾 */ Q->rear=(Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE;/* rear指针向后移一位置, */ /* 若到最后则转到数组头部 */ return OK; } /* 若队列不空,则删除Q中队头元素,用e返回其值 */ Status DeQueue(Queue *Q,int *e) { if (Q->front == Q->rear) /* 队列空的判断 */ return ERROR; *e=Q->data[Q->front]; /* 将队头元素赋值给e */ Q->front=(Q->front+1)%MAXSIZE; /* front指针向后移一位置, */ /* 若到最后则转到数组头部 */ return OK; } /* 邻接表广度优先遍历*/ Boolean visited[MAXSIZE]; /* 访问标志的数组 */ void BFSTraverse(GraphAdjList GL) { //1.创建结点 EdgeNode *p; Queue Q; InitQueue(&Q); //2.将访问标志数组全部置为"未访问状态FALSE" for(int i = 0; i < GL->numVertexes; i++) visited[i] = FALSE; //3.对遍历邻接表中的每一个顶点(对于连通图只会执行1次,这个循环是针对非连通图) for (int i = 0 ;i < GL->numVertexes;i++) { //4.判断当前结点是否被访问过. if(!visited[i]){ visited[i] = TRUE; //打印顶点 printf("%c ",GL->adjList[i].data); EnQueue(&Q, i); while (!QueueEmpty(Q)) { DeQueue(&Q, &i); p = GL->adjList[i].firstedge; while (p) { //判断 if (!visited[p->adjvex]) { visited[p->adjvex] = TRUE; printf("%c ",GL->adjList[p->adjvex].data); EnQueue(&Q, p->adjvex); } p = p->next; } } } } }