
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
1.应用
1.1 使用方式
使用方式一:这种方式也是现在项目中经常用到的方式,从这篇文章开始,就正式进入到 Spring IOC 源码解析。。。
public class MyTestStart {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ann = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfig.class);
MyService myService = ann.getBean(MyService.class);
myService.test();
}
}
使用方式二:以编程的方式构建 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,通过无参构造器初始化,然后通过 Register 方法
注册。
public class MyTestStart {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
ctx.register(MyConfig.classs);
ctx.refresh();
MyService myService = ctx.getBean(MyService.class);
myService.test();
}
}
当然也可以通过使用包扫描的方式,来使用 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。
public class MyTestStart {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
ctx.scan("com.fchen");
ctx.refresh();
MyService myService = ctx.getBean(MyService.class);
myService.test();
}
}
1.2 配置类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.fchen")
public class MyConfig {
}
1.3 Service类
@Service
public class MyService {
private Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyService.class);
public void test(){
System.out.println("Hello,MyService");
}
}
2.源码解析
2.1 类关系图
还是熟悉的套路,在看源码之前,先看类关系图,先整体后细节。类关系图如下:
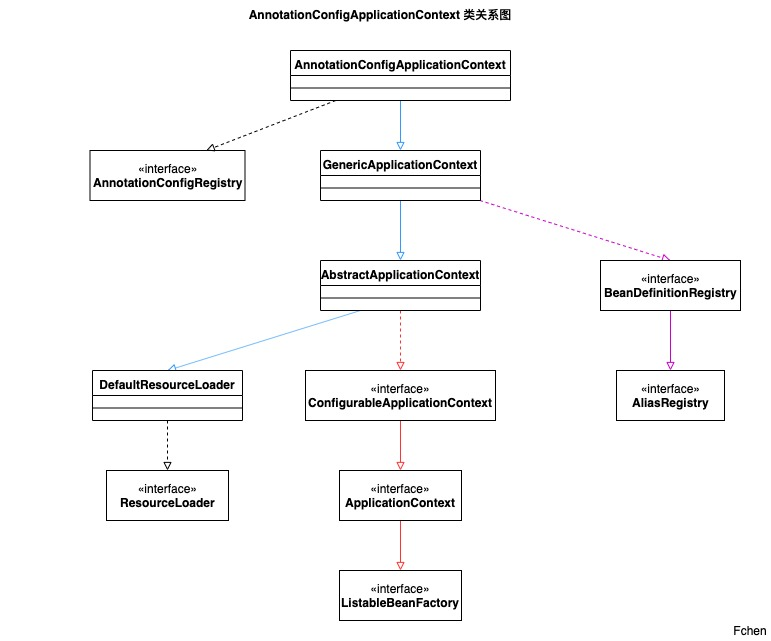
- 1.从红色的线可以看出,这个 IOC 容器是属于
ApplicationContext这一条设计路线,这就意味着他的功能更加的丰富。 - 2.从蓝色的这条线可以看出,该类同样是
Resource的子类实现。关于Spring 中资源与资源加载的文章,上一篇文章中有详细介绍。 - 3.紫色这条线,还没有学习到,但是这一路劲也是极为重要,实现完成BeanDefinition向容器中注册。
- 4.最后上述的 使用方式二 之所以可以这样使用是应为 实现了
AnnotationConfigRegistry这个接口。通过register ()完成编程式使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。
2.2 源码实现
从容器的使用来看,都是通过 ApplicationContext ann = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("XXX"); 来完成容器的初始化。
就从这里入手,来一点点揭开 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 的神秘面纱...
有参构造方法
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
/**
* 调用默认的构造方法,由于该类有父类,
* 故而先调用父类的构造方法,在调用自己的构造方法
* 在自己的构造方法中初始一个读取器和一个扫描器,
* 第①部分!!!
*/
this();
/**
* 向spring 的容器中注册bean
* 第②部分!!!
*/
register(componentClasses);
/**
* 初始化spring的环境
* 第③部分!!!
*/
refresh();
}
有参构造方法
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
/**
* 实例化 读取器
* 将spring中加了注解的类转化为 一个 spring当中bean的描述文件
*/
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
/**
* 实例化 扫描器
* 能够扫描一个类,并转换为 spring当中bean的描述文件
* 不通过显示的调用scanner的方法的情况下,spring中的包不是由该scanner扫描
* 而是由Spring 在实例化 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader时
* 自己new的一个 ClasspathBeanDefinitionScanner 对象扫描完成的
* 即:这里初始化的扫描器通过程序员显示的调用才会生效。
*/
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
在有惨的构造方法中,方法的调用逻辑分为三个部分,在后面的文章中都会有详细的介绍。在无参数的构造方法中主要是完成了
读取器 与 扫描器 的初始化。他们在类中的定义如下:
/**
* 定义一个读取被加了注解的 bean的读取器
*/
private final AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader;
/**
* 定义一个包的扫描器
*/
private final ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner;
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 为通过编程的方式注册 Bean 提供适配,将spring中加了注解的类转化为一个 spring 当中 Bean
的描述文件。当然最终的注册都是通过 BeanDefinitionRegistry 来完成的。
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 将定义在类路径上的 Bean 转化为一个spring 当中 Bean 的描述文件,同样最终的注册都是
通过BeanDefinitionRegistry 来完成的。
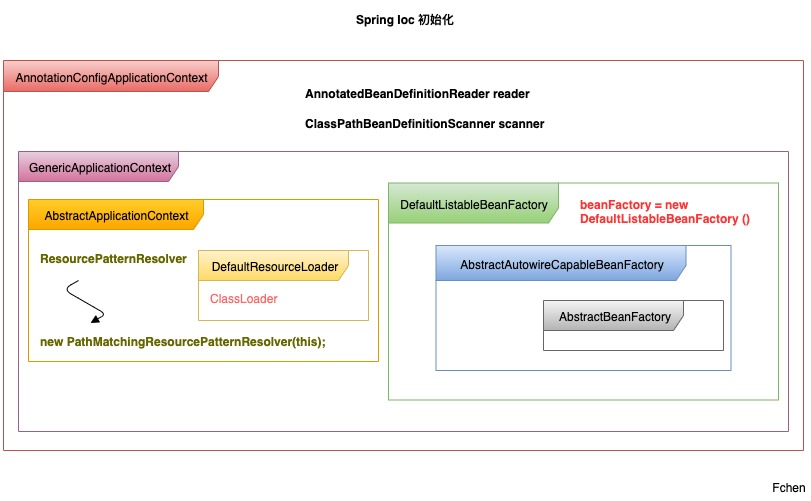
以AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 为IoC容器的实现,容器初始化图:
本文使用 mdnice 排版