
Spring 容器之 Resource 和 ResourceLoader
这篇文章是填之前文章的坑来了,首先在 XmlBeanFactory 中,有这么一行代码 new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("spring-bean.xml"));
其中的 new ClassPathResource("spring-bean.xml")没有解释,这就是 spring 中的Resource。
其次,在 DefaultListableBeanFactory 中,new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory),中完成了对 ResourceLoader 的初始化,所谓的 ResourceLoader
就是对 Spring 资源加载的统一抽象。
在这篇文章中,对 Spring 中的资源,与资源的加载做一个统一学习。
Resource
Spring 把其资源做了一个抽象,底层使用统一的资源访问接口来访问 Spring 的所有资源。
也就是说,不管什么格式的文件,也不管文件在哪里,到 Spring 底层,都只有一个访问接口,Resource。
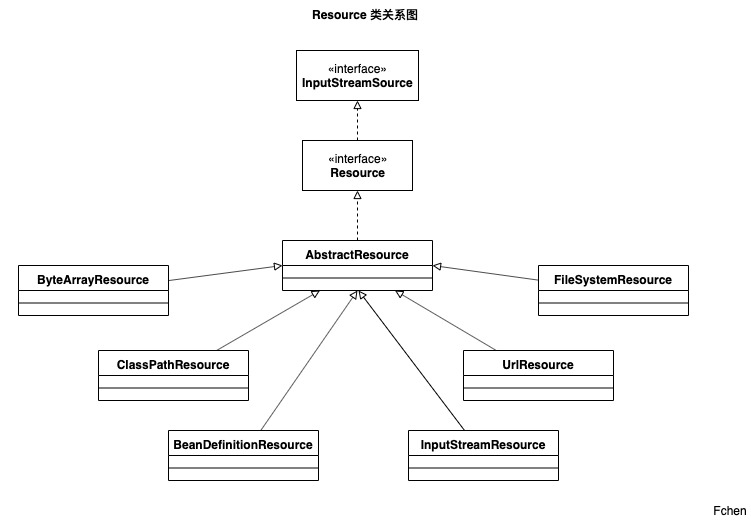 其中 AbstractResource 为 Resource 的默认实现。
其中 AbstractResource 为 Resource 的默认实现。
- InputStreamSource 封装任何返货 InputStream 的类,比如 File,Classpath 下的资源和 Byte,Array 等。
- Resource 接口抽象了所有 Spring 内部使用到的底层资源:File,URL,Classpath 等。
- ClassPathResource 用来加载 classpath 类型资源的实现。使用给定的 ClassLoader 或者给定的 Class 来加载资源。
- ByteArrayResource 对字节数组提供的数据的封装。
- FileSystemResource 文件相关。
- UrlResource url 资源的加载。
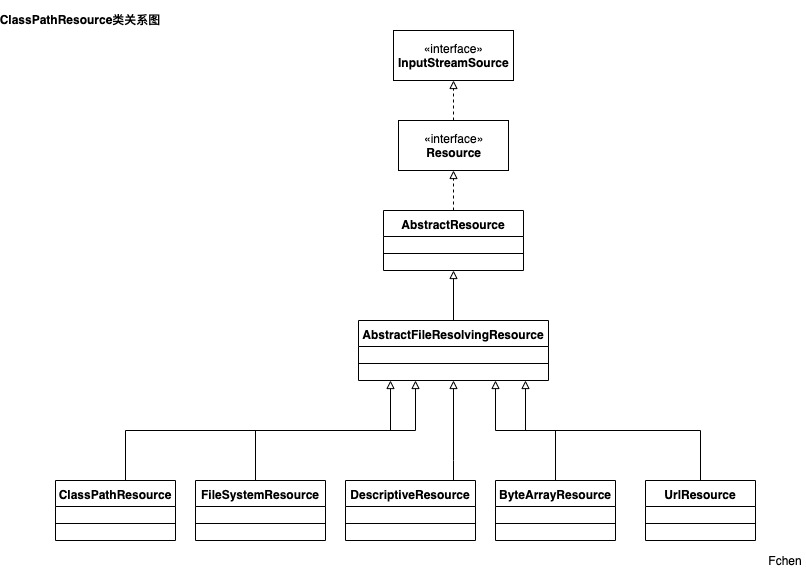
ClassPathResource 的类关系图
AbstractResource 源码实现:
public abstract class AbstractResource implements Resource {
/**
* 判断文件是否存在,若判断过程产生异常(因为会调用SecurityManager来判断),就关闭对应的流
*/
@Override
public boolean exists() {
// Try file existence: can we find the file in the file system?
try {
return getFile().exists();
}
catch (IOException ex) {
// Fall back to stream existence: can we open the stream?
try {
getInputStream().close();
return true;
}
catch (Throwable isEx) {
return false;
}
}
}
/**
* 这个重写的方法始终返回true,表示可读
*/
@Override
public boolean isReadable() {
return exists();
}
/**
* 这个重写方法始终返回false,表示没有打开
*/
@Override
public boolean isOpen() {
return false;
}
/**
* 这个从写的方法始终返回false,表示不是一个文件
*/
@Override
public boolean isFile() {
return false;
}
/**
* 抛出 FileNotFoundException 异常
*/
@Override
public URL getURL() throws IOException {
throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() + " cannot be resolved to URL");
}
/**
* 基于 getURL() 返回的 URL 构建 URI
*/
@Override
public URI getURI() throws IOException {
URL url = getURL();
try {
return ResourceUtils.toURI(url);
}
catch (URISyntaxException ex) {
throw new NestedIOException("Invalid URI [" + url + "]", ex);
}
}
/**
* 抛出 FileNotFoundException 异常,交给子类实现
*/
@Override
public File getFile() throws IOException {
throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() + " cannot be resolved to absolute file path");
}
/**
* 根据 getInputStream() 的返回结果构建 ReadableByteChannel
*/
@Override
public ReadableByteChannel readableChannel() throws IOException {
return Channels.newChannel(getInputStream());
}
/**
* 获取资源的长度
* 这个资源内容长度实际就是资源的字节长度,通过全部读取一遍来判断
*/
@Override
public long contentLength() throws IOException {
InputStream is = getInputStream();
try {
long size = 0;
byte[] buf = new byte[256];
int read;
while ((read = is.read(buf)) != -1) {
size += read;
}
return size;
}
finally {
try {
is.close();
}
catch (IOException ex) {
}
}
}
/**
* 返回资源最后的修改时间
*/
@Override
public long lastModified() throws IOException {
File fileToCheck = getFileForLastModifiedCheck();
long lastModified = fileToCheck.lastModified();
if (lastModified == 0L && !fileToCheck.exists()) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() +
" cannot be resolved in the file system for checking its last-modified timestamp");
}
return lastModified;
}
protected File getFileForLastModifiedCheck() throws IOException {
return getFile();
}
@Override
public Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException {
throw new FileNotFoundException("Cannot create a relative resource for " + getDescription());
}
/**
* 获取资源名称,默认返回 null
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public String getFilename() {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) {
return (this == other || (other instanceof Resource &&
((Resource) other).getDescription().equals(getDescription())));
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return getDescription().hashCode();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return getDescription();
}
}
ResourceLoader
。我们还是从ResourceLoader的类图入手,
可以看到 DefaultResourceLoader 为 ResourceLoader 默认实现。然后 ResourceLoader 为所有 Spring IoC 容器的父接口。这也就说明
所有的 IOC 容器都是具有加载资源的能力。
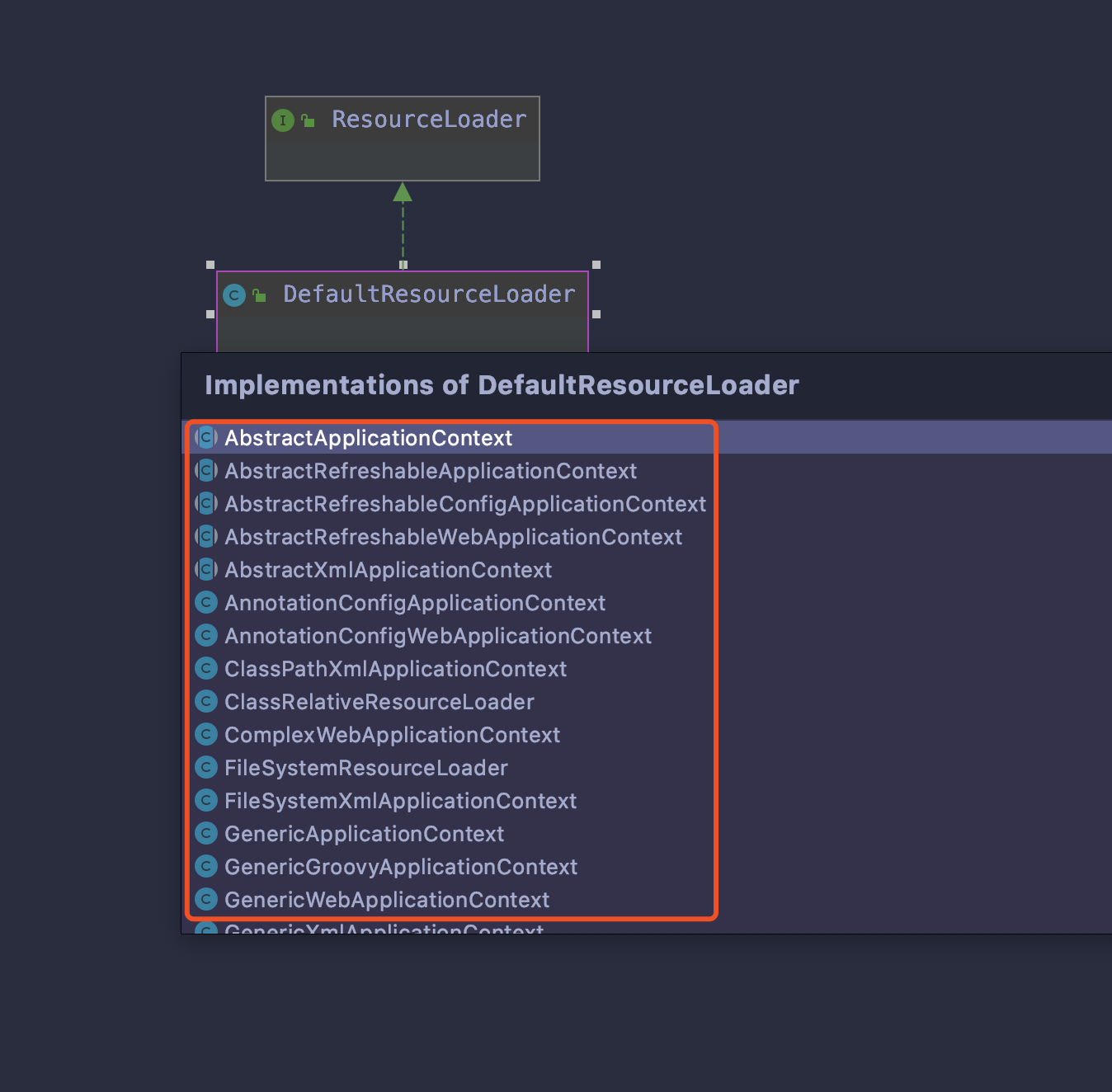
下面再来看看 ResourceLoader 与 DefaultResourceLoader 中的代码:
ResourceLoader 源码方法
public interface ResourceLoader {
/** 用于从类路径加载的伪URL前缀: "classpath:" */
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX;
/**
* 根据所提供资源的路径 location 返回 Resource 实例
*/
Resource getResource(String location);
/**
* 返回 ClassLoader 实例,对于想要获取 ResourceLoader
* 使用的 ClassLoader 用户来说,可以直接调用该方法来获取
*/
@Nullable
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
ResourceLoader 默认实现
public class DefaultResourceLoader implements ResourceLoader {
@Nullable
private ClassLoader classLoader;
private final Set<ProtocolResolver> protocolResolvers = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
private final Map<Class<?>, Map<Resource, ?>> resourceCaches = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(4);
/**
* 创建默认的 ClassLoader
*/
public DefaultResourceLoader() {
this.classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
/**
* 创建默认的 ClassLoader,将传入的 ClassLoader 赋值给变量
*/
public DefaultResourceLoader(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.classLoader = classLoader;
}
public void setClassLoader(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.classLoader = classLoader;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return (this.classLoader != null ? this.classLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
/**
* 添加protocolResolvers
*/
public void addProtocolResolver(ProtocolResolver resolver) {
Assert.notNull(resolver, "ProtocolResolver must not be null");
this.protocolResolvers.add(resolver);
}
public Collection<ProtocolResolver> getProtocolResolvers() {
return this.protocolResolvers;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> Map<Resource, T> getResourceCache(Class<T> valueType) {
return (Map<Resource, T>) this.resourceCaches.computeIfAbsent(valueType, key -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
}
public void clearResourceCaches() {
this.resourceCaches.clear();
}
/**
* 取得Resource 的具体过程
* @param location the resource location
* @return
*/
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
for (ProtocolResolver protocolResolver : getProtocolResolvers()) {
// 看有没有自定义的ProtocolResolver,
// 如果有则先根据自定义的ProtocolResolver解析location得到Resource
Resource resource = protocolResolver.resolve(location, this);
if (resource != null) {
return resource;
}
}
if (location.startsWith("/")) {
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
/* 处理带有classpath 表示的Resource*/
else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// Try to parse the location as a URL...
/* 处理URL 标识的Resource 定位*/
URL url = new URL(location);
return (ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url) ? new FileUrlResource(url) : new UrlResource(url));
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// No URL -> resolve as resource path.
/*
* 如果既不是classpath,也不是URL标识的Resource定位,则把getResource的
* 重任交给getResourcePath(),这个是一个 protected 的方法,默认的实现是
* 得到一个 ClassPathContextResource,这个方法常常会用子类来实现
* 例如: FileSystemXmlApplicationContext#getResourceByPath()
*/
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
return new ClassPathContextResource(path, getClassLoader());
}
/**
* 通过实现ContextResource接口 明确表示下文相关路径的ClassPathResource,此方法重点在于实现ContextResource
*/
protected static class ClassPathContextResource extends ClassPathResource implements ContextResource {
// 通过调用父类的构造方法创建
public ClassPathContextResource(String path, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
super(path, classLoader);
}
@Override
public String getPathWithinContext() {
return getPath();
}
@Override
public Resource createRelative(String relativePath) {
String pathToUse = StringUtils.applyRelativePath(getPath(), relativePath);
return new ClassPathContextResource(pathToUse, getClassLoader());
}
}
}
ResourceLoader 的扩展
ResourceLoader 用来加载 Spring 定义的资源,DefaultResourceLoader 是ResourceLoader默认的实现 ResourcePatternResolver
是 ResourceLoader 的扩展,它支持根据指定的资源路径匹配模式每次返回多个 Resource 实例。PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 为
ResourcePatternResolver 最常用的子类,它除了支持 ResourceLoader 和 ResourcePatternResolver 新增的 classpath*: 前缀外,
还支持 Ant 风格的路径匹配模式(类似于 **/*.xml)。
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 是ResourceLoader 的子类实现,同样他的作用是用来加载资源Resource。通过 PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver
的构造方法可以看出,ResourceLoader的初始化,如果与传入则用传入对象完成初始化。没有传入则采用默认的子类实现。代码如下:
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver() {
// 使用无参 构造器 指定使用DefaultResourceLoader
this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
}
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(resourceLoader, "ResourceLoader must not be null");
// 若指定了 ResourceLoader 则使用指定的
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 指定类加载器的 通过给定的类加载器完成 ResourceLoader 的实例化
this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader(classLoader);
}
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 是用来加载资源的,通过下面的代码来看看,它是如何得到 Resource的:
通过初始化话的 ResourceLoader 获取单个 Resource。
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) {
// 委托给初始化的ResourceLoader 获取资源
return getResourceLoader().getResource(location);
}
下面这个方法获取到的是 Resource[]:
@Override
public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location pattern must not be null");
// 以 classpath*: 开头
if (locationPattern.startsWith(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX)) {
// 路径包含通配符
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()))) {
// a class path resource pattern
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// 路径不包含通配符
return findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()));
}
}
else {
int prefixEnd = (locationPattern.startsWith("war:") ? locationPattern.indexOf("*/") + 1 :
locationPattern.indexOf(':') + 1);
// 路径包含通配符
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd))) {
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// a single resource with the given name
return new Resource[] {getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
}
}
}
找到 classes 路径下和所有 jar 包中的所有相匹配的资源
protected Resource[] findAllClassPathResources(String location) throws IOException {
String path = location;
// 路径中以 "/" 开头 将 "/" 去掉
if (path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
// 这里是真正的方法
Set<Resource> result = doFindAllClassPathResources(path);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Resolved classpath location [" + location + "] to resources " + result);
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[0]);
}
真正加载 Resource的地方,这也符合 Spring 一以贯之的风格,真正做事的方法都是 doXXX来完成的。
protected Set<Resource> doFindAllClassPathResources(String path) throws IOException {
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(16);
// 获取 classLoader
ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader();
// //通过classloader来加载资源目录,这里也会去找寻classpath路径下的jar包或者zip包
Enumeration<URL> resourceUrls = (cl != null ? cl.getResources(path) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(path));
while (resourceUrls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = resourceUrls.nextElement();
// 将找到的路径转化为 Resource 对象并添加到 Set 集合中
result.add(convertClassLoaderURL(url));
}
if ("".equals(path)) {
// The above result is likely to be incomplete, i.e. only containing file system references.
// We need to have pointers to each of the jar files on the classpath as well...
// 加载jar协议的资源
addAllClassLoaderJarRoots(cl, result);
}
return result;
}
本文使用 mdnice 排版