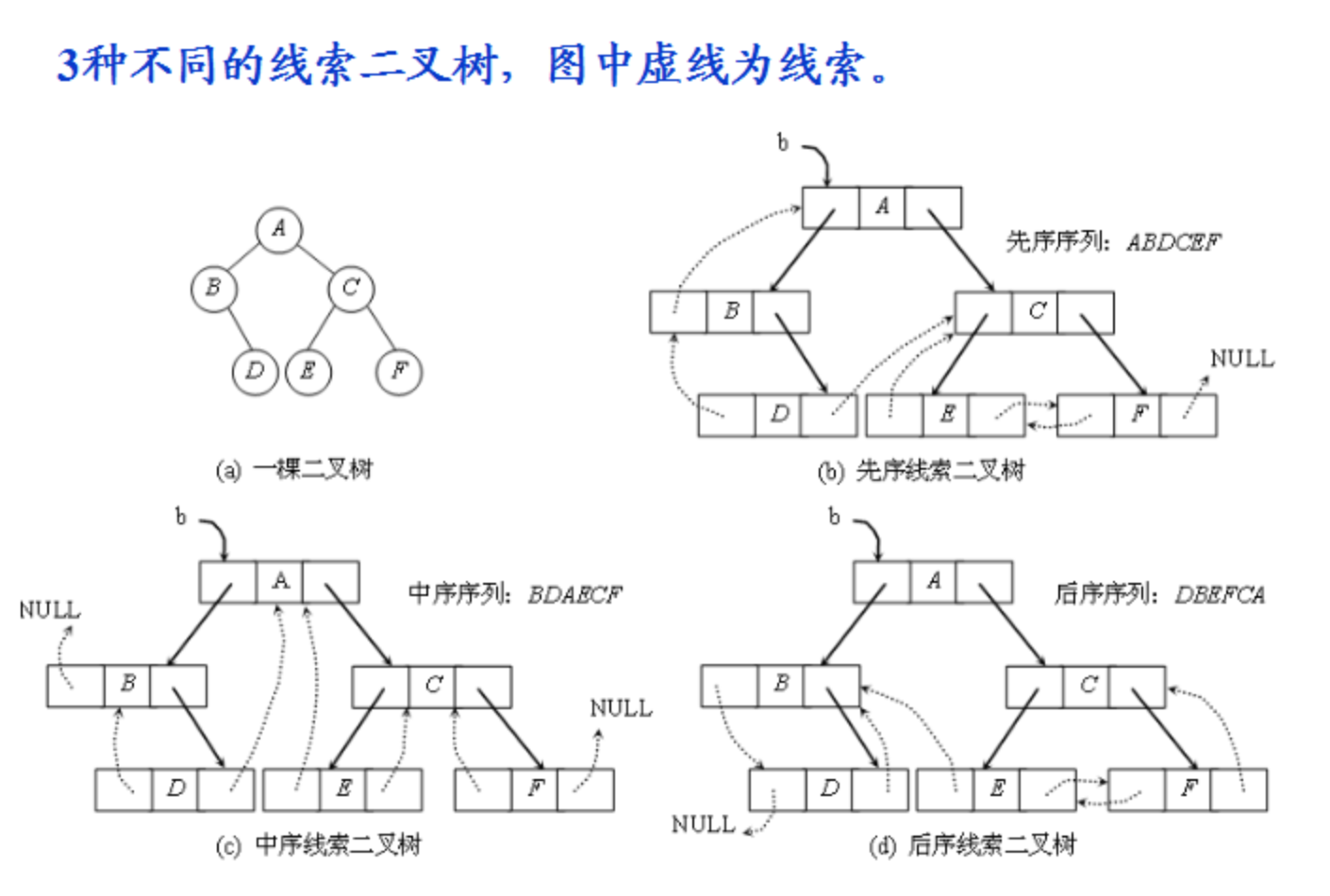
1、线索化二叉树
对于n个结点的二叉树,在二叉链存储结构中有n+1个空链域,利用这些空链域存放在某种遍历次序下该结点的前驱结点和后继结点的指针,这些指针称为线索,加上线索的二叉树称为线索二叉树。
这种加上了线索的二叉链表称为线索链表,相应的二叉树称为线索二叉树(Threaded BinaryTree)。根据线索性质的不同,线索二叉树可分为前序线索二叉树、中序线索二叉树和后序线索二叉树三种。
注意:线索链表解决了无法直接找到该结点在某种遍历序列中的前驱和后继结点的问题,解决了二叉链表找左、右孩子困难的问题。
#include "string.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "math.h"
#include "time.h"
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAXSIZE 100 /* 存储空间初始分配量 */
/* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */
typedef int Status;
typedef char CElemType;
/* 字符型以空格符为空 */
CElemType Nil='#';
#pragma mark--二叉树构造
int indexs = 1;
typedef char String[24]; /* 0号单元存放串的长度 */
String str;
Status StrAssign(String T,char *chars) {
int i;
if(strlen(chars)>MAXSIZE)
return ERROR;
else {
T[0]=strlen(chars);
for(i=1;i<=T[0];i++)
T[i]=*(chars+i-1);
return OK;
}
}
/* Link==0表示指向左右孩子指针, */
/* Thread==1表示指向前驱或后继的线索 */
typedef enum {Link,Thread} PointerTag;
/* 线索二叉树存储结点结构*/
typedef struct BiThrNode {
//数据
CElemType data;
//左右孩子指针
struct BiThrNode *lchild,*rchild;
//左右标记
PointerTag LTag;
PointerTag RTag;
}BiThrNode,*BiThrTree;
/*1 打印
*/
Status visit(CElemType e) {
printf("%c ",e);
return OK;
}
/*2 构造二叉树
按照前序输入线索二叉树结点的值,构造二叉树T
*/
Status CreateBiThrTree(BiThrTree *T) {
CElemType h;
//scanf("%c",&h);
//获取字符
h = str[indexs++];
if (h == Nil) {
*T = NULL;
} else {
*T = (BiThrTree)malloc(sizeof(BiThrNode));
if (!*T) {
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
//生成根结点(前序)
(*T)->data = h;
//递归构造左子树
CreateBiThrTree(&(*T)->lchild);
//存在左孩子->将标记LTag设置为Link
if ((*T)->lchild) (*T)->LTag = Link;
//递归构造右子树
CreateBiThrTree(&(*T)->rchild);
//存在右孩子->将标记RTag设置为Link
if ((*T)->rchild) (*T)->RTag = Link;
}
return OK;
}
/*
3 中序遍历二叉树T, 将其中序线索化,Thrt指向头结点
*/
BiThrTree pre; /* 全局变量,始终指向刚刚访问过的结点 */
/* 中序遍历进行中序线索化*/
void InThreading(BiThrTree p) {
if (p) {
//递归左子树线索化
InThreading(p->lchild);
//无左孩子
if (!p->lchild) {
//前驱线索
p->LTag = Thread;
//左孩子指针指向前驱
p->lchild = pre;
} else {
p->LTag = Link;
}
//前驱没有右孩子
if (!pre->rchild) {
//后继线索
pre->RTag = Thread;
//前驱右孩子指针指向后继(当前结点p)
pre->rchild = p;
} else {
pre->RTag = Link;
}
//保持pre指向p的前驱
pre = p;
//递归右子树线索化
InThreading(p->rchild);
}
}
/* 中序遍历二叉树T,并将其中序线索化,Thrt指向头结点 */
Status InOrderThreading(BiThrTree *Thrt , BiThrTree T) {
*Thrt=(BiThrTree)malloc(sizeof(BiThrNode));
if (! *Thrt) {
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
//建立头结点;
(*Thrt)->LTag = Link;
(*Thrt)->RTag = Thread;
//右指针回指向
(*Thrt)->rchild = (*Thrt);
/* 若二叉树空,则左指针回指 */
if (!T) {
(*Thrt)->lchild=*Thrt;
} else {
(*Thrt)->lchild=T;
pre=(*Thrt);
//中序遍历进行中序线索化
InThreading(T);
//最后一个结点rchil 孩子
pre->rchild = *Thrt;
//最后一个结点线索化
pre->RTag = Thread;
(*Thrt)->rchild = pre;
}
return OK;
}
/*中序遍历二叉线索树T*/
Status InOrderTraverse_Thr(BiThrTree T) {
BiThrTree p;
p=T->lchild; /* p指向根结点 */
while(p!=T) { /* 空树或遍历结束时,p==T */
while(p->LTag==Link)
p=p->lchild;
if(!visit(p->data)) /* 访问其左子树为空的结点 */
return ERROR;
while(p->RTag==Thread&&p->rchild!=T) {
p=p->rchild;
visit(p->data); /* 访问后继结点 */
}
p=p->rchild;
}
return OK;
}
swift实现
enum PointerTag {
case Link
case Thread
}
class BiThrTree<T> {
var data:T
var lchild:BiThrTree? ,rchild:BiThrTree?
var lTag:PointerTag, rTag:PointerTag
init(data:T, lchild:BiThrTree? = nil, rchild:BiThrTree? = nil, lTag:PointerTag = .Link, rTag:PointerTag = .Link) {
self.data = data
self.lchild = lchild
self.rchild = rchild
self.lTag = lTag
self.rTag = rTag
}
func visit() -> Void {
print(String(describing: data))
}
}
let str = "ABDH##I##EJ###CF##G##"
var index = 0
/*
构造二叉树
按照前序输入线索二叉树结点的值,构造二叉树T
*/
func create() -> BiThrTree<Character>? {
let hc = str[str.index(str.startIndex, offsetBy: index)]
index += 1
if hc == "#" {
return nil
} else {
let tree = BiThrTree(data: hc)
tree.lchild = create()
if tree.lchild != nil {
tree.lTag = .Link
}
tree.rchild = create()
if tree.rchild != nil {
tree.rTag = .Link
}
return tree
}
}
/*
中序遍历二叉树T, 将其中序线索化,Thrt指向头结点
*/
var pre:BiThrTree<Character>? = nil
func inThreading(tree:BiThrTree<Character>?) -> Void {
if let p = tree {
inThreading(tree: p.lchild)
if p.lchild == nil {
p.lTag = .Thread
p.lchild = pre
} else {
p.lTag = .Link
}
if pre?.rchild == nil {
pre?.rTag = .Thread
pre?.rchild = p
} else {
pre?.rTag = .Link
}
pre = p
inThreading(tree: p.rchild)
}
}
/* 中序遍历二叉树T,并将其中序线索化,Thrt指向头结点 */
func inOrderThreading(_ tree:BiThrTree<Character>?) -> BiThrTree<Character> {
let thrt = BiThrTree<Character>(data: "#")
thrt.lTag = .Link
thrt.rTag = .Thread
thrt.rchild = thrt
if tree == nil {
thrt.lchild = thrt
} else {
thrt.lchild = tree
pre = thrt
inThreading(tree: tree)
pre?.rchild = thrt
pre?.rTag = .Thread
thrt.rchild = pre
}
return thrt
}
/*中序遍历二叉线索树T*/
func inOrderTraverse_Thr(_ tree:BiThrTree<Character>) -> Void {
var p:BiThrTree<Character>? = tree.lchild
while p !== tree {
while p!.lTag == .Link {
p = p?.lchild
}
p?.visit()
while p!.rTag == .Thread && p?.rchild !== tree {
p = p?.rchild
p?.visit()
}
p = p?.rchild
}
}
var tree = create()
tree = inOrderThreading(tree)
inOrderTraverse_Thr(tree!)
2、哈夫曼编码
#include "string.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
const int MaxValue = 10000;//初始设定的权值最大值
const int MaxBit = 4;//初始设定的最大编码位数
const int MaxN = 10;//初始设定的最大结点个数
typedef struct HaffNode {
int weight;
int flag;
int parent;
int leftChild;
int rightChild;
}HaffNode;
typedef struct Code {//存放哈夫曼编码的数据元素结构
int bit[MaxBit];//数组
int start; //编码的起始下标
int weight;//字符的权值
}Code;
//1.
//根据权重值,构建哈夫曼树;
//{2,4,5,7}
//n = 4;
void Haffman(int weight[],int n,HaffNode *haffTree) {
int j,m1,m2,x1,x2;
//1.哈夫曼树初始化
//n个叶子结点. 2n-1
for(int i = 0; i < 2*n-1;i++){
if(i<n)
haffTree[i].weight = weight[i];
else
haffTree[i].weight = 0;
haffTree[i].parent = 0;
haffTree[i].flag = 0;
haffTree[i].leftChild = -1;
haffTree[i].rightChild = -1;
}
//2.构造哈夫曼树haffTree的n-1个非叶结点
for (int i = 0; i< n - 1; i++) {
m1 = m2 = MaxValue;
x1 = x2 = 0;
//2,4,5,7
for (j = 0; j< n + i; j++) {//循环找出所有权重中,最小的二个值--morgan
if (haffTree[j].weight < m1 && haffTree[j].flag == 0) {
m2 = m1;
x2 = x1;
m1 = haffTree[j].weight;
x1 = j;
} else if(haffTree[j].weight<m2 && haffTree[j].flag == 0) {
m2 = haffTree[j].weight;
x2 = j;
}
}
//3.将找出的两棵权值最小的子树合并为一棵子树
haffTree[x1].parent = n + i;
haffTree[x2].parent = n + i;
//将2个结点的flag 标记为1,表示已经加入到哈夫曼树中
haffTree[x1].flag = 1;
haffTree[x2].flag = 1;
//修改n+i结点的权值
haffTree[n + i].weight = haffTree[x1].weight + haffTree[x2].weight;
//修改n+i的左右孩子的值
haffTree[n + i].leftChild = x1;
haffTree[n + i].rightChild = x2;
}
}
/*
2 哈夫曼编码
由n个结点的哈夫曼树haffTree构造哈夫曼编码haffCode
//{2,4,5,7}
*/
void HaffmanCode(HaffNode haffTree[], int n, Code haffCode[]) {
//1.创建一个结点cd
Code *cd = (Code * )malloc(sizeof(Code));
int child, parent;
//2.求n个叶结点的哈夫曼编码
for (int i = 0; i<n; i++) {
//从0开始计数
cd->start = 0;
//取得编码对应权值的字符
cd->weight = haffTree[i].weight;
//当叶子结点i 为孩子结点.
child = i;
//找到child 的双亲结点;
parent = haffTree[child].parent;
//由叶结点向上直到根结点
while (parent != 0) {
if (haffTree[parent].leftChild == child)
cd->bit[cd->start] = 0;//左孩子结点编码0
else
cd->bit[cd->start] = 1;//右孩子结点编码1
//编码自增
cd->start++;
//当前双亲结点成为孩子结点
child = parent;
//找到双亲结点
parent = haffTree[child].parent;
}
int temp = 0;
for (int j = cd->start - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
temp = cd->start-j-1;
haffCode[i].bit[temp] = cd->bit[j];
}
//把cd中的数据赋值到haffCode[i]中.
//保存好haffCode 的起始位以及权值;
haffCode[i].start = cd->start;
//保存编码对应的权值
haffCode[i].weight = cd->weight;
}
}
let MAXVALUE = 10000
struct HaffNode {
var weight:Int;
var flag:Int;
var parent:Int;
var leftChild:Int;
var rightChild:Int;
}
struct Code {
var bit = Array<Int>()
var start:Int
var weight:Int
}
//
//根据权重值,构建哈夫曼树;
//{2,4,5,7}
//n = 4;
func Haffman(_ weight:Array<Int>) -> Array<HaffNode> {
var i = 0, j = 0, m1 = MAXVALUE, m2 = MAXVALUE, x1 = 0, x2 = 0
//1.哈夫曼树初始化
//n个叶子结点. 2n-1
let n = weight.count
var haffTree = Array<HaffNode>();
while i < 2*n-1 {
var haff = HaffNode.init(weight: 0, flag: 0, parent: 0, leftChild: -1, rightChild: -1)
if i < n {
haff.weight = weight[i]
}
haffTree.append(haff)
i += 1
}
i = 0
while i < n-1 {
m1 = MAXVALUE; m2 = MAXVALUE; x1 = 0; x2 = 0; j = 0
while j < n + i {
if haffTree[j].weight < m1 && haffTree[j].flag == 0 {
m2 = m1
x2 = x1
m1 = haffTree[j].weight
x1 = j
} else if haffTree[j].weight < m2 && haffTree[j].flag == 0 {
m2 = haffTree[j].weight;
x2 = j;
}
j += 1
}
haffTree[x1].parent = n + i
haffTree[x2].parent = n + i
haffTree[x1].flag = 1
haffTree[x2].flag = 1
haffTree[n + i].weight = haffTree[x1].weight + haffTree[x2].weight
haffTree[n + i].leftChild = x1
haffTree[n + i].rightChild = x2
i += 1
}
return haffTree
}
/*
哈夫曼编码
由n个结点的哈夫曼树haffTree构造哈夫曼编码haffCode
//{2,4,5,7}
*/
func HaffmanCode(haffTree:Array<HaffNode>) -> Array<Code> {
var codeArray = Array<Code>()
//1.创建一个结点cd
var child = 0, parent = 0, i = 0
//2.求n个叶结点的哈夫曼编码
while i < haffTree.count {
var cd = Code.init(start: 0, weight: 0)
var code = Code(start: 0, weight: 0);
//从0开始计数
cd.start = 0
//取得编码对应权值的字符
cd.weight = haffTree[i].weight
//当叶子结点i 为孩子结点.
child = i
//找到child 的双亲结点;
parent = haffTree[child].parent
//由叶结点向上直到根结点
while parent != 0 {
if haffTree[parent].leftChild == child {
cd.bit.append(0)//左孩子结点编码0
} else {
cd.bit.append(1)//右孩子结点编码1
}
cd.start += 1
//当前双亲结点成为孩子结点
child = parent
//找到双亲结点
parent = haffTree[child].parent
}
var j = cd.start - 1 //temp = 0,
while j >= 0 {
// temp = cd.start - j - 1
code.bit.append(cd.bit[j])
j -= 1
}
//把cd中的数据赋值到haffCode[i]中.
//保存好haffCode 的起始位以及权值;
code.start = cd.start;
//保存编码对应的权值
code.weight = cd.weight;
codeArray.append(code)
i += 1
}
return codeArray
}
let haffmantree = Haffman([2,4,5,7])
print(haffmantree)
let haffcode = HaffmanCode(haffTree: haffmantree)
print(haffcode)