内容来自OpenCV-Python Tutorials 自己翻译整理
目标
轮廓的面积、周长、重心、边界
相关函数
矩
图像矩可以计算图像的质心,面积等等。
图像的矩
函数 cv2.moments()会计算图像的矩,并返回一个字典
(findContours应该返回三个参数,样例里的代码只返回两个,报错了)
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('3.jpg',0)
ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,0)
img,contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, 1, 2)
cnt = contours[0]
M = cv2.moments(cnt)
print(M)
结果
{'m00': 0.0, 'm10': 0.0, 'm01': 0.0, 'm20': 0.0, 'm11': 0.0, 'm02': 0.0, 'm30': 0.0, 'm21': 0.0, 'm12': 0.0, 'm03': 0.0, 'mu20': 0.0, 'mu11': 0.0, 'mu02': 0.0, 'mu30': 0.0, 'mu21': 0.0, 'mu12': 0.0, 'mu03': 0.0, 'nu20': 0.0, 'nu11': 0.0, 'nu02': 0.0, 'nu30': 0.0, 'nu21': 0.0, 'nu12': 0.0, 'nu03': 0.0}
1
(结果居然全是0,轮廓找的不好)
根据这些矩的值可以得到重心
<span class="MathJax" id="MathJax-Element-1-Frame" tabindex="0" data-mathml="Cx=M10M00" role="presentation" style="box-sizing: border-box; outline: 0px; display: inline; line-height: normal; text-align: left; word-spacing: normal; word-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; word-break: break-all; position: relative;">Cx=M10M00Cx=M10M00
<span class="MathJax" id="MathJax-Element-2-Frame" tabindex="0" data-mathml="Cy=M01M00" role="presentation" style="box-sizing: border-box; outline: 0px; display: inline; line-height: normal; text-align: left; word-spacing: normal; word-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; word-break: break-all; position: relative;">Cy=M01M00Cy=M01M00 cx = int(M['m10']/M['m00']) cy = int(M['m01']/M['m00']) cv2.contourArea()函数可以计算面积,也可以使用矩 M[‘m00’] img = cv2.imread('3.jpg',0) ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,0) img,contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, 1, 2) area = cv2.contourArea(cnt)#计算面积 <span class="MathJax" tabindex="0" data-mathml="Cy=M01M00" role="presentation" style="box-sizing: border-box; outline: 0px; display: inline; line-height: normal; text-align: left; word-wrap: normal; float: none; direction: ltr; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-width: 0px; min-height: 0px; border: 0px; word-break: break-all; position: relative;"> 使用 cv2.arcLength()计算,第二个参数表示轮廓是闭合(True)还是打开的 img = cv2.imread('3.jpg',0) ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,0) img,contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, 1, 2) perimeter = cv2.arcLength(cnt,True)
将得到的轮廓近似为更少点组成的形状,使用 Douglas-Peucker algorithm 例如要在图像中寻找一个矩形,由于种种原因,不能得到一个完整矩形,现在可以使用此函数,函数的第二个参数epsilon是从原始轮廓到近似轮廓的最大距离,epsilon对结果影响很大。 epsilon = 0.1*cv2.arcLength(cnt,True) approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(cnt,epsilon,True)
使用cv2.convexHull()来计算凸包,所谓凸包,打个比方,给你一个木板,在木板上面钉一大堆钉子,然后找一根皮筋在上面一围,形成的图形就是凸包。 hull = cv2.convexHull(points[, hull[, clockwise[, returnPoints]]
img = cv2.imread('3.jpg',0) ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,0) img,contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, 1, 2) hull = cv2.convexHull(cnt)
将returnPoints设置为False则会输出点的索引 img = cv2.imread('3.jpg',0) ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,0) img,contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, 1, 2) hull = cv2.convexHull(cnt,returnPoints=False)
k = cv2.isContourConvex(cnt) 就是找到图形对象最高点、最低点、最左点、最右点,画出一个矩形边界 使用函数 cv2.boundingRect()计算 (x,y)为矩形左上角的坐标,(w,h)是矩形的宽和高 x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt) img = cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,255,0),2 矩形包围盒的面积最小,考虑到了对象的旋转(原理使用到到了PCA方法,可以去搜) 返回Box2D结构,包含左上角坐标(x,y)矩形宽,高(w,h),以及旋转角度 rect = cv2.minAreaRect(cnt) box = cv2.boxPoints(rect) cv2.drawContours(img,[box],0,(0,0,255),2)  绿色的就是直边界包围盒,红色的是最小矩形包围盒 最小外接圆
使用函数 cv2.minEnclosingCircle()得到
返回圆心和半径 (x,y),radius = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(cnt) img = cv2.circle(img,center,radius,(0,255,0),2) ellipse = cv2.fitEllipse(cnt) cv2.ellipse(img,ellipse,(0,255,0),2) 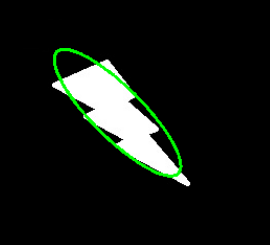 直线拟合 根据图像中的点拟合出一条直线
rows,cols = img.shape[:2] [vx,vy,x,y] = cv2.fitLine(cnt, cv2.DIST_L2,0,0.01,0.01) lefty = int((-x*vy/vx) + y) righty = int(((cols-x)*vy/vx)+y) cv2.line(img,(cols-1,righty),(0,lefty),(0,255,0),2) 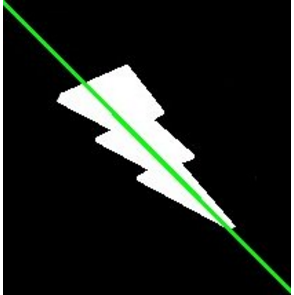
|