1.前言
项目使用脚手架create-react-app搭建
Redux版本: "^4.0.5"
2.基本概念
(1)redux是什么,解决什么问题
redux简单来说就是状态管理容器,主要负责组件状态的存储和管理。我们都知道react本身内部有state状态,我们目前所做的单页应用state都非常多,包括一些服务器响应数据、缓存数据和组件UI状态等等,并且随着组件层级和数量的增多,组件间的状态会难以维护,所以我们使用redux来管理,它只需要管理store这个状态树。
因此,项目中常使用react + redux架构,其他的状态管理容器也有Flux等等,这里我们只说redux。
(2)react + redux
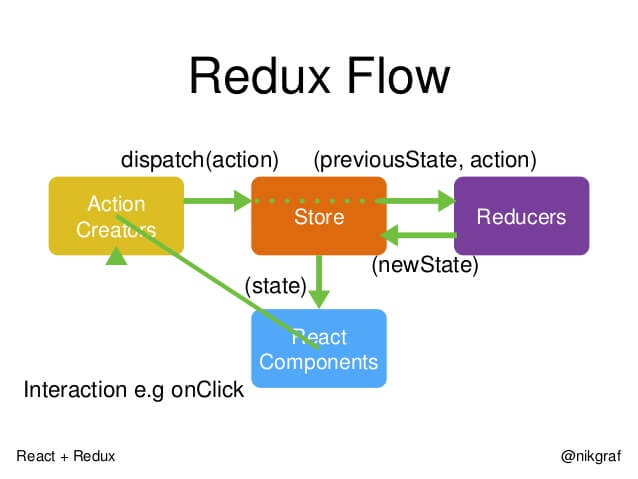
3.源码分析
首先,我们从安装的本地库文件夹node_modules里找到redux。
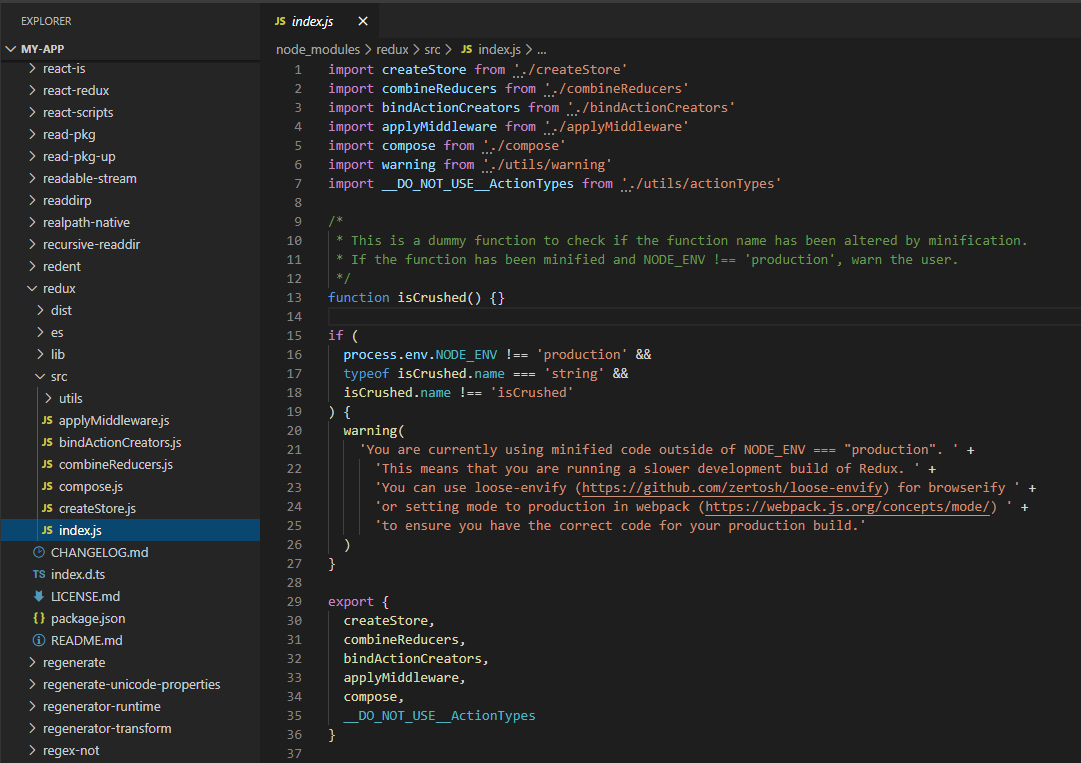
可以看到redux暴露出来主要有createStore、combineReducers、bindActionCreators、applyMiddleware和compose这5个函数,本篇先从createStore开始说起。
整体看上去,createStore主要有这几个函数组成。
export default function createStore(reducer, preloadedState, enhancer) {
if (
(typeof preloadedState === 'function' && typeof enhancer === 'function') ||
(typeof enhancer === 'function' && typeof arguments[3] === 'function')
) {
throw new Error(
'It looks like you are passing several store enhancers to ' +
'createStore(). This is not supported. Instead, compose them ' +
'together to a single function.'
)
}
//调用createStore传值preloadedState = enhancer, enhancer = undefined时
//preloadedState处理为undefined,enhancer重新赋值为传入的reloadedState
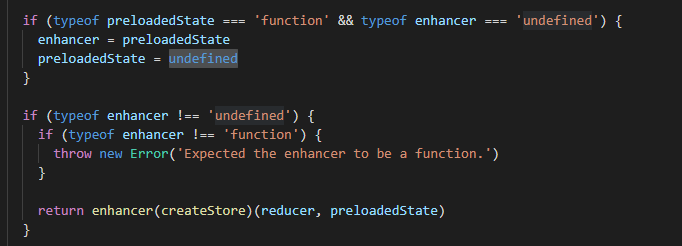
if (typeof preloadedState === 'function' && typeof enhancer === 'undefined') {
enhancer = preloadedState
preloadedState = undefined
}
if (typeof enhancer !== 'undefined') {
if (typeof enhancer !== 'function') {
throw new Error('Expected the enhancer to be a function.')
}
return enhancer(createStore)(reducer, preloadedState)
}
if (typeof reducer !== 'function') {
throw new Error('Expected the reducer to be a function.')
}
let currentReducer = reducer
let currentState = preloadedState
let currentListeners = []
let nextListeners = currentListeners
let isDispatching = false
function getState() {...}
function subscribe(listener) {...}
function dispatch(action) {...}
function replaceReducer(nextReducer) {...}
function observable() {...}
}
首先介绍下三个参数
reducer: A function that returns the next state tree, given the current state tree and the action to handle
状态计算函数,通过当前state和用户触发的action,计算nextState。
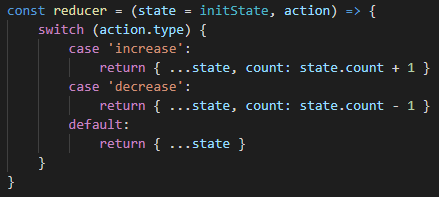
- The initial state. You may optionally specify it
- to hydrate the state from the server in universal apps, or to restore a
- previously serialized user session.
- If you use
combineReducersto produce the root reducer function, this must be - an object with the same shape as
combineReducerskeys 它是初始的state,用户可以选择第二个参数不传递iniState,而传递enhance时,代码会将preloadedState处理成undefined
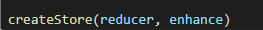
enhance
- The store enhancer. You may optionally specify it
- to enhance the store with third-party capabilities such as middleware,
- time travel, persistence, etc. The only store enhancer that ships with Redux
- is
applyMiddleware().
store的增强器,用来增强store的功能,这里概念上就不多介绍,主要使用的中间件有redux-thunk,redux-saga,redux-promise,redux-logger等。
(1)初始化
let currentReducer = reducer
let currentState = preloadedState
let currentListeners = [] //初始化监听函数数组
let nextListeners = currentListeners
let isDispatching = false //reducer进行标志位,reducer在进行计算nextState时,isDispatching为true,不可打断。
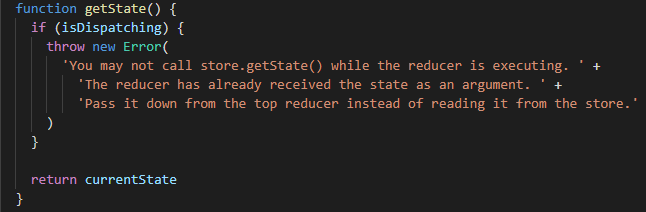
(2)getState:顾名思义,就是返回当前的state。
function dispatch(action) {
//前一部分忽略不看
if (!isPlainObject(action)) {
throw new Error(
'Actions must be plain objects. ' +
'Use custom middleware for async actions.'
)
}
if (typeof action.type === 'undefined') {
throw new Error(
'Actions may not have an undefined "type" property. ' +
'Have you misspelled a constant?'
)
}
if (isDispatching) {
throw new Error('Reducers may not dispatch actions.')
}
//currentReducer在初始化时就赋值为我们传入的reduce,根据当前state和action,计算出nextState。
//这里isDispatching在reduce执行完毕后才会置为false。它为true时,其他操作不能打断reduce的计算。
try {
isDispatching = true
currentState = currentReducer(currentState, action)
} finally {
isDispatching = false
}
//这里主要是依次执行订阅函数
const listeners = (currentListeners = nextListeners) //注意这里每次使用的都是nextListeners
for (let i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {
const listener = listeners[i]
listener()
}
return action
}
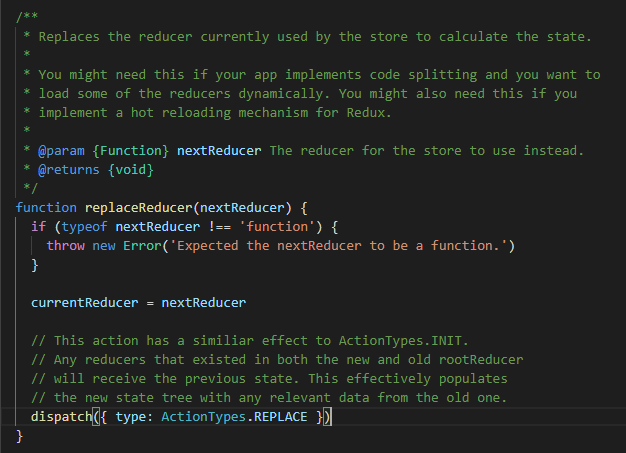
(4)replaceReducer 看原文注释就很好理解,替换当前reduce。适用的情况:动态加载reduce、hot reloading(实现redux热加载)
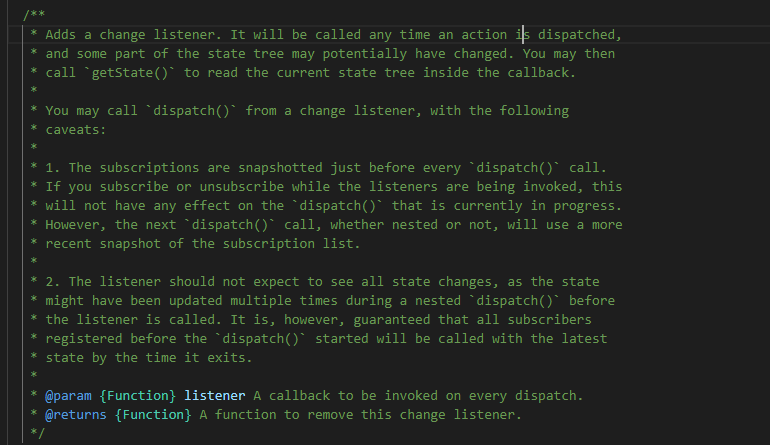
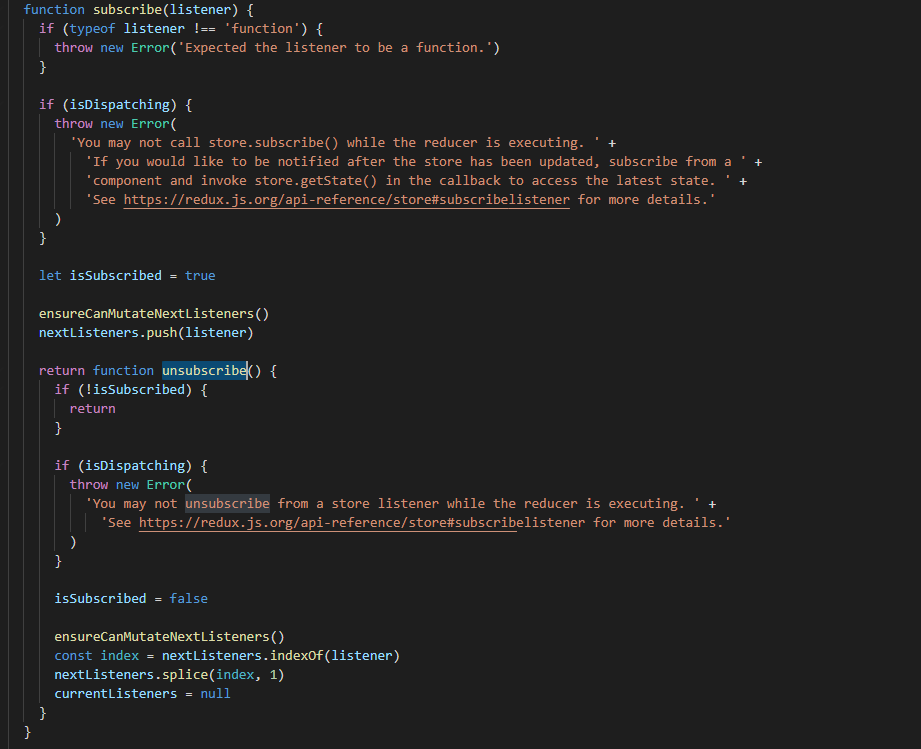
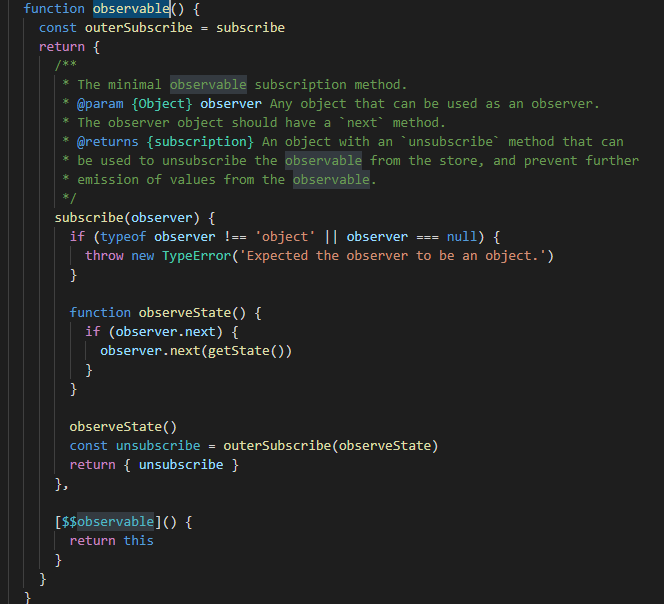
怎么说呢,以前我挺抗拒看源码,但源码看多了还是蛮有意思的,看源码并不是要求你一定要能够写出来,我觉得更多的是从中学习别人编程的思路、方法,比如人家数组方法、箭头函数、高阶函数等的使用,最近我在看compose函数的时候就更加深对数组reduce方法的理解。另外理解源码后,你也能明白项目里为什么这里这么写就能实现功能,这对于理解整个项目架构,对你在开发过程中都能带来提升。
我是一个比较懒的人,现在想了想还是多多利用业余时间学习,坚持写文章来充实和提升自己。^_^