概述
通常来说,操作系统对于单个进程中能打开的文件数是有限制的,而数据库需要频繁的操作文件。为了方便使用,pg实现了VFD(Virtual File Description,虚拟文件描述符)机制,本质是对与底层文件操作的一层封装,这样所有需要直接操作文件的地方可以调用VFD,避免上层还需要管理文件操作符。
这层封装主要是采用了一个LRU(Leaset Recently Used)缓存池来管理本进程中打开的所有VFD。当LRU池未满时,进程可以直接申请一个VFD用来打开一个物理文件;而当LRU池已满后,进程需要先从池中删除一个VFD并关闭其物理文件,这样打开新的文件时就不会因为超出操作系统的限制而打开文件失败。
以下代码分析基于pg12.1版本,不过从代码来看,VFD的机制从9.2到现在基本没什么变动
VFD机制详述
VFD链表元素
pg使用Vfd结构体来构造链表元素,进而实现LRU缓存池(本质即循环链表)。
typedef struct vfd
{
int fd; /* current FD, or VFD_CLOSED if none */
unsigned short fdstate; /* bitflags for VFD's state */
ResourceOwner resowner; /* owner, for automatic cleanup */
File nextFree; /* link to next free VFD, if in freelist */
File lruMoreRecently; /* doubly linked recency-of-use list */
File lruLessRecently;
off_t fileSize; /* current size of file (0 if not temporary) */
char *fileName; /* name of file, or NULL for unused VFD */
/* NB: fileName is malloc'd, and must be free'd when closing the VFD */
int fileFlags; /* open(2) flags for (re)opening the file */
mode_t fileMode; /* mode to pass to open(2) */
} Vfd;
- fd记录该VFD所对应的物理文件描述符。如果当前VFD没有打开文件描述符(即没有对应的物理文件描述符),则其值为VFD_CLOSED(VFD_CLOSED=-1)
- fdstate是VFD的标志位:①如果它的第0位置1,即为FD_DIRTY,表明该文件的内容已被修改过,但还没有写回磁盘,在关闭此文件是要将该文件同步到磁盘里。②如果它的第1位置1,即为FD_TEMPORARY,表明该文件是临时文件,需要在关闭时删除
- nextfree指向下一个空闲的VFD,其数据类型File其实是一个整数(不是<stdio.h>里面的FILE),用来表示VFD在VFD数组中的下标
- lruMoreRecently指向比该VFD最近更不常用的VFD,这里的More做打开时长更长(即更旧)来理解
- lruLessRecently指向比该VFD最近更常用的VFD,这里的Less做打开时长更短(即更新)来理解
- fileSize表示文件大小
- fileName表示该VFD对应文件的文件名,如果是空闲的VFD,则fileName位空值
- fileFlags表示该文件打开时的标志,包括只读、只写、读写等
- fileMode表示文件创建时所指定的模式
VfdCache数组
通过VFD链表元素组成一个链表,可以用于表示和管理一个pg后台近程所打开的文件
由于每个节点(Vfd结构体)保存有nextFree字段和LRU相关字段,所以VfdCache数组实际上包含了两个链表数据结构:一是nextFree指针所形成的单链表,另一个是由lruMoreRecently和lruLessRecently两个指针所形成的LRU双向循环链表。这两个链表是交杂在一起的,整体是一个VfdCache连续数组
VfdCache数组的建立分为多步:
- 当后台进程启动时(一个客户端对应一起后台进程),会调用InitFileAccess函数创建VfdCache头,即VfdCache[0].
void
InitFileAccess(void)
{
Assert(SizeVfdCache == 0); /* call me only once */
/* initialize cache header entry */
VfdCache = (Vfd *) malloc(sizeof(Vfd));
if (VfdCache == NULL)
ereport(FATAL,
(errcode(ERRCODE_OUT_OF_MEMORY),
errmsg("out of memory")));
MemSet((char *) &(VfdCache[0]), 0, sizeof(Vfd));
VfdCache->fd = VFD_CLOSED;
SizeVfdCache = 1;
/* register proc-exit hook to ensure temp files are dropped at exit */
on_proc_exit(AtProcExit_Files, 0);
}
- 进程打开第一个文件时(调用AllocateVfd函数),将调用AllocateVfd来初始化VfdCache数组。此时,所有的数组元素中fd字段还都是VFD_CLOSED,通过nextFree来一一串联,即下面将会说到的Freelist链表。
- 当Freelist链表上没有空闲节点时,就会新申请一块更大的内存(在原数组的基础上扩大一倍),并把原有的VfdCache数组搬迁过来。这也是通过AllocateVfd的逻辑来实现
static File
AllocateVfd(void)
{
Index i;
File file;
DO_DB(elog(LOG, "AllocateVfd. Size %zu", SizeVfdCache));
Assert(SizeVfdCache > 0); /* InitFileAccess not called? */
if (VfdCache[0].nextFree == 0)
{
/*
* The free list is empty so it is time to increase the size of the
* array. We choose to double it each time this happens. However,
* there's not much point in starting *real* small.
*/
Size newCacheSize = SizeVfdCache * 2;
Vfd *newVfdCache;
if (newCacheSize < 32)
newCacheSize = 32;
/*
* Be careful not to clobber VfdCache ptr if realloc fails.
*/
newVfdCache = (Vfd *) realloc(VfdCache, sizeof(Vfd) * newCacheSize);
if (newVfdCache == NULL)
ereport(ERROR,
(errcode(ERRCODE_OUT_OF_MEMORY),
errmsg("out of memory")));
VfdCache = newVfdCache;
/*
* Initialize the new entries and link them into the free list.
*/
for (i = SizeVfdCache; i < newCacheSize; i++)
{
MemSet((char *) &(VfdCache[i]), 0, sizeof(Vfd));
VfdCache[i].nextFree = i + 1;
VfdCache[i].fd = VFD_CLOSED;
}
VfdCache[newCacheSize - 1].nextFree = 0;
VfdCache[0].nextFree = SizeVfdCache;
/*
* Record the new size
*/
SizeVfdCache = newCacheSize;
}
file = VfdCache[0].nextFree;
VfdCache[0].nextFree = VfdCache[file].nextFree;
return file;
}
Freelist链表
在VfdCache数组中,由头结点VfdCache[0]开始,通过访问nextFree指针,可以遍历目前所有空闲节点。链表结构概览如下:
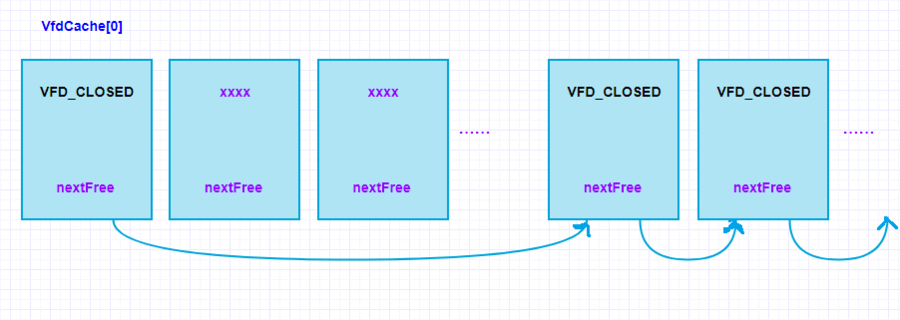
从图可以看到,随着文件的不断打开关闭,Freelist链表内的指针会逐渐失去原有的顺序,变得杂乱无章(两个Freelist链表元素之间可能还隔了若干个LRU链表元素)。但是,无论我们总是能够通过头结点,通过nextFree字段来访问获取空闲VFD节点信息。
LRU双向循环链表
在VFD节点中,lruMoreRecently和lruLessRecently两个字段,作为双链表的指针,将所有打开的文件链接两个闭合的环,形成一个LRU池。如图所示:
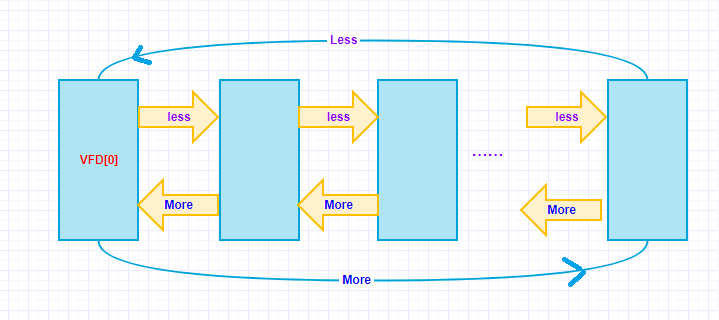
注意:此图为逻辑视图,实际在VFD数组中,LRU链的顺序是无序的。与Freelist类似,两个LRU链表元素之间可能还隔了若干个Freelist链表元素
数组元素的变化
所有节点都是属于VfdCache数组的,但是会在Freelist链表和LRU双向循环链表间变动。
- 当打开一个文件时,会申请Vfd,这时将从Freelist链表中删除一个元素,将其加入到LRU链表中
- 当LRU池满之后,如果仍然需要打开一个新文件,首先需要先从LRU链表中删除一个元素,将其加入到Freelist链表,然后再执行上一步操作
通过上述方式实现VFD进制,使得一个进程可以操作无限个文件。
范例
以下为一个示例,仅仅保留了Vfd中用于链表的部分和fd操作符,同时去除大量优化性功能,实现了一个简单的vfd管理功能。
- vfd.h文件
#ifndef VFD_H
#define VFD_H
typedef int File;
extern void InitFileAccess();
extern File PathNameOpenFile(const char *fileName);
#endif // VFD_H
- vfd.cpp文件
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory.h>
#include <io.h>
#include "vfd.h"
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
typedef struct vfd {
FILE *fd;
File nextFree; /* link to next free VFD, if in freelist */
File lruMoreRecently; /* doubly linked recency-of-use list */
File lruLessRecently;
char *fileName; /* name of file, or NULL for unused VFD */
/* NB: fileName is malloc'd, and must be free'd when closing the VFD */
} Vfd;
// use LRU cache as a fixed size
#define LRU_SIZE 2
// must bigger than LRU_SIZE to avoid vfd running out
#define VFD_CACHE_SIZE 6
static vfd *VfdCache;
static File openFiles;
static File AllocateVfd();
static void FreeVfd(File file);
static void LruDelete(File file);
static void ReleaseLruFiles();
void InitFileAccess()
{
VfdCache = (Vfd *)malloc(VFD_CACHE_SIZE * sizeof(Vfd));
if (VfdCache == nullptr) {
cout << "ERROR: out of memory" << endl;
exit(1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < VFD_CACHE_SIZE; i++) {
memset((char *)&(VfdCache[i]), 0, sizeof(Vfd));
VfdCache[i].fd = nullptr;
VfdCache[i].nextFree = i + 1;
}
VfdCache[VFD_CACHE_SIZE - 1].nextFree = 0;
VfdCache[0].nextFree = 1;
openFiles = 0;
}
static File AllocateVfd()
{
File file = VfdCache[0].nextFree;
VfdCache[0].nextFree = VfdCache[file].nextFree;
return file;
}
static void FreeVfd(File file)
{
Vfd *vfdP = &VfdCache[file];
cout << "INFO: " << vfdP->fileName << " is going to release" << endl;
if (vfdP->fileName != nullptr) {
free(vfdP->fileName);
vfdP->fileName = nullptr;
}
vfdP->nextFree = VfdCache[0].nextFree;
VfdCache[0].nextFree = file;
}
static void LruDelete(File file)
{
Vfd *vfdP = &VfdCache[file];
if (fclose(vfdP->fd)) {
cout << "ERROR: can not close file: " << vfdP->fileName << endl;
exit(1);
}
vfdP->fd = nullptr;
VfdCache[vfdP->lruLessRecently].lruMoreRecently = vfdP->lruMoreRecently;
VfdCache[vfdP->lruMoreRecently].lruLessRecently = vfdP->lruLessRecently;
FreeVfd(file);
openFiles--;
}
File PathNameOpenFile(const char *fileName)
{
Vfd *vfdP;
File file;
char *fnamecopy = strdup(fileName);
if (fnamecopy == nullptr) {
cout << "ERROR: out of memory" << endl;
exit(1);
}
ReleaseLruFiles();
file = AllocateVfd();
vfdP = &VfdCache[file];
FILE *fd = fopen(fnamecopy, "r");
if (fd == nullptr) {
cout << "ERROR: can not open file: " << fnamecopy << endl;
exit(1);
}
vfdP->fd = fd;
vfdP->fileName = fnamecopy;
vfdP->lruMoreRecently = 0;
vfdP->lruLessRecently = VfdCache[0].lruLessRecently;
VfdCache[0].lruLessRecently = file;
VfdCache[vfdP->lruLessRecently].lruMoreRecently = file;
openFiles++;
return file;
}
static void ReleaseLruFiles()
{
while(openFiles >= LRU_SIZE) {
cout << "INFO: LRU pool is full, need to clear file: " << VfdCache[VfdCache[0].lruMoreRecently].fileName << endl;
LruDelete(VfdCache[0].lruMoreRecently);
}
}
- main.cpp文件
#include "vfd.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
InitFileAccess();
PathNameOpenFile("../1.cnf");
PathNameOpenFile("../2.cnf");
PathNameOpenFile("../3.cnf");
PathNameOpenFile("../4.cnf");
}