一、数组类型length方法
第一题 ({}+{}).length
- 对象运算调用toString()方法
- 这个方法继承于Object,即{}.toString()相当于Object.prototype.toString.call({})
- 即("[object Object][object Object]").length = 30
第二题 ([]+[]).length
- 数组运算调用toString()方法
- 数组本身有toString()方法
- (""+"").length = 0
第三题 (function(){}).length
- 函数有length()方法,即形参的个数,该函数没有,所以为0
二、封装typeof
typeof({})->"object",typeof([])->"object",typeof(null)->"object",typeof(new Number())->"object",typeof(new String())->"object",typeof(new Boolean())->"object",封装装一个函数,解决这个问题
function typeOf(value) {
if(value === null){
return 'null'
}
return typeof(value) === 'object' ? {
'[object Object]':'Object',
'[object Array]':'Array',
'[object Number]':'o-Number',
'[object String]':'o-String',
'[object Boolean]':'o-Boolean',
}[({}).toString.call(value)] : typeof(value);
}
三、数组方法及特性
不改变原数组
- es3
- concat 返回 拼接后的数组
- join 返回 在数组元素中插入指定元素后的字符串
- slice 返回 截取后的数组
- toString 返回 数组的字符串
- es5
- every 返回 布尔值
- some 返回 布尔值
- filter 返回 数组元素符合过滤条件之后的数组
- reduce
- 例如
var arr = [1,2,3],res=[]; arr.reduce(function(prev,vlaue){ prev.push(value + 1); return prev; },res) - reduceRight
改变原数组
- es3
- pop 返回 删除的数组最后一个元素
- push 返回 长度
- shift 返回 删除的数组第一个元素
- unshift 返回 长度
- reverse 返回 倒序的数组
- sort 返回 正序的数组
- splice 返回 新数组
- es5
不确定改不改变
- es5
- forEach 没有返回值
- 例如
//操作带有数组下标时 var arr = [1,2,3]; arr.forEach(function(value,index){ arr[index] += 1 }) - map 返回 新数组
- 例如
//操作了引用关系,会改变原数组 var arr = [{value:1},{value:2},{value:3}],res = []; res = arr.map(function(value,index){ value.name = index; return value; } console.log(arr,res)
- forEach 没有返回值
四、从事件冒泡到事件代理的机制
事件冒泡
当一个元素接收到事件的时候,会把他接收到的事件传给父级,一直传到window
事件代理
function(e){
//事件对象
var e = e || window.event,
//事件源对象
tar = e.target || e.srcElement,
className = tar.className;
switch(className){
case 'inner1':
console.log('我是innner1');
break;
case 'inner2':
console.log('我是innner2');
break;
default:
break;
}
}
- 子元素事件触发都会冒泡到父元素上去,子元素完成各自不同到功能,可以通过给父级元素绑定事件处理函数到方式,让子元素触发事件的同时,通过冒泡,让父级绑定的处理函数执行
- 通过事件源对象取去找到当前点击的元素,去判断,再触发相应程序
例题:创建ul,里边50个li,每个li有删除功能,考虑性能优化
<script type="text/html" id="tpl">
<li>这是第{{num}}项<button>删除</button></li>
</script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var oList = document.createElement('ul'),
tpl = document.getElementById('tpl').innerHTML,
list = '';
for (var i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
list += tpl.replace(/{{(.*?)}}/, (i + 1));
}
oList.innerHTML = list;
document.body.appendChild(oList)
oList.addEventListener('click', removeItem, false);
function removeItem(e) {
var e = e || window.event,
tar = e.target || e.srcElement,
tagName = tar.tagName.toLowerCase();
if (tagName === 'button') {
tar.parentNode.remove();
}
}
</script>
五、减少http请求的方法
从输入url到页面呈现,发生了什么?
-
1.url输入,回车
-
2.DNS解析:解析URL变成相应服务器的IP地址或者代理服务器的IP地址
-
3.浏览器网络向相应发起TCP/IP请求
三次握手: - 客户端向服务端发送连接请求,并进入等待服务器确认状态 - 服务器收到请求并确认,发给客户端,进入等待客户端确认状态 - 客户端进入连接建立状态后,向服务端发送消息已收到建立连接的请求,服务端收到消息进入连接建立状态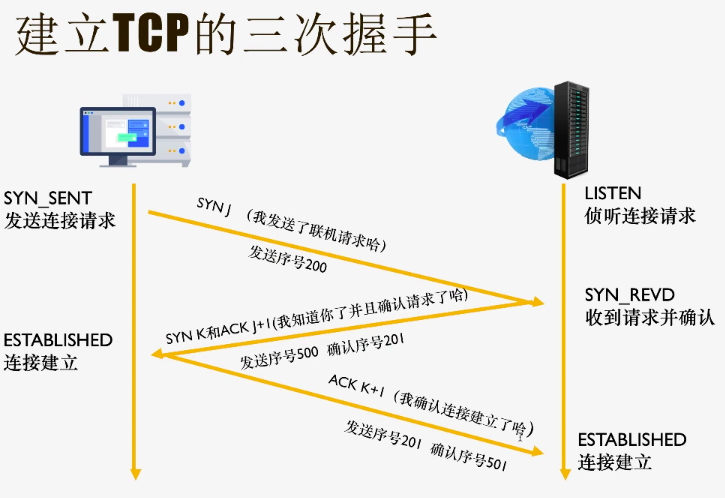
-
4.建立TCP/IP连接
-
5.浏览器网络发起HTTP请求
-
6.等待 响应过程
-
7.下载HTML资源
-
8.解析HTML
-
9.遇到html里的资源,再次发起HTTP请求,下载资源
四次挥手 -
10.时间线
-
11.呈现页面
5~9HTTP请求耗费时间最多,占整个80%,所以要减少http请求,怎么减少?
-
雪碧图
-
base64编码图片,但是增加了代码量
-
合并脚本和样式表代码
-
配置多个域名和CDN加速
用域名在第三方服务器进行解析,从而生成CDN加速域名 -
尽量使用浏览器的缓存机制
-
image maps图片地图
六、两栏布局和三栏布局
两栏布局
<div class="item">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</div>
- 法一、left绝对定位:
- 父元素相对定位
- left定宽,绝对定位,left:0,top:0
- righ宽100%,pading-left:left的宽,box-sizing:border-box
- 法二、right绝对定位:
- 父元素相对定位、overflow:hidden
- left定宽
- right绝对定位,left:0,top:0,margin-left:left宽, padding-right:left宽,box-sizing:border-box
三栏布局
圣杯布局
<div class="container">
//先加载middle
<div class="middel"></div>
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</div>
.container{
height: 500px;
//圣杯空出来位置:margin:0 right宽 0 left宽;
margin: 0 200px 0 150px;
}
.middle,.left,.right{
//左浮、相对定位
float: left;
position: relative;
height: 100%;
}
.middle{
//宽100%
width: 100%;
background-color: green;
}
.left{
//移到本行最左边
left:-150px;
width: 150px;
//移到上一行最左边
margin-left: -100%;
background-color: orange;
}
.right{
//移到最右边
right: -200px;
width: 200px;
//移到上一行
margin-left: -200px;
background-color: red;
}
双飞翼布局
<div class="container">
<div class="middle">
//在main中写内容
<div class="main">aaa</div>
</div>
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</div>
.container{
height: 500px;
}
.middle,.left,.right{
float: left;
height: 100%;
}
.middle{
width: 100%;
background-color: green;
}
.main{
//控制显示区域
margin: 0 200px 0 150px;
}
.left{
width: 150px;
//到上一行最左边
margin-left: -100%;
background-color: orange;
}
.right{
width: 200px;
//到上一行最右边
margin-left: -200px;
background-color: red;
}
七、用正则进行模版替换的方法
{{title}} 替换为 我是一个测试标题
<div class="box"></div>
<script type="text/html" id="tpl">
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<p>{{content}}</p>
</script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var oBox = document.getElementsByClassName('box')[0]
var tpl = document.getElementById('tpl').innerHTML;
var res = tpl.replace(/{{(.*?)}}/g, function (node, key) {
//node:{{title}},key:title
return {
title: '我是一个测试标题',
content: '我是一个测试内容'
}[key];
})
oBox.innerHTML = res
</script>
/{{(.*?)}}/g
// 匹配
g 全局
{{}} 匹配{{}}
. 任意字符
* 出现0次~多次
? 非贪婪匹配(正则匹配默认是贪婪模式:例如{{title}}{{}}会匹配最左边的{{,到最右边的}})
() 匹配到内容
八、选项卡的实现
<style>
.wrap {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
margin: 50px auto;
}
.tab {
height: 50px;
}
.tab .item {
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 100%;
text-align: center;
line-height: 50px;
}
.tab .item.current {
background-color: #000;
color: #fff;
}
.page {
position: relative;
height: 450px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.page .item {
display: none;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
font-size: 100px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 450px;
}
.page .item.active {
display: block;
}
</style>
<div class="wrap">
<div class="tab J_tab">
<div class="item current">选项1</div>
<div class="item">选项2</div>
<div class="item">选项3</div>
</div>
<div class="page J_page">
<div class="item active">页面1</div>
<div class="item">页面2</div>
<div class="item">页面3</div>
</div>
</div>
第一种
; (function (doc) {
var oTab = doc.getElementsByClassName('J_tab')[0],
oPage = doc.getElementsByClassName('J_page')[0],
tabItems = oTab.getElementsByClassName('item'),
pageItems = oPage.getElementsByClassName('item');
var init = function () {
bindEvent();
}
function bindEvent() {
oTab.addEventListener('click', tabClick, false)
}
function tabClick(e) {
var e = e || window.event,
tar = e.target || e.srcElement,
className = tar.className;
if (className === 'item') {
//伪数组调用数组方法
var curIdx = Array.prototype.indexOf.call(tabItems,tar);
for (var i = 0; i < tabItems.length; i++) {
tabItems[i].className = 'item';
pageItems[i].className = 'item';
}
tar.className += ' current';
pageItems[curIdx].className += ' active';
}
}
init();
})(document)
第二种
不用循环:
; (function (doc) {
var oTab = doc.getElementsByClassName('J_tab')[0],
oPage = doc.getElementsByClassName('J_page')[0],
tabItems = oTab.getElementsByClassName('item'),
pageItems = oPage.getElementsByClassName('item'),
curIdx = 0;
var init = function () {
bindEvent();
}
function bindEvent() {
oTab.addEventListener('click', tabClick, false)
}
function tabClick(e) {
var e = e || window.event,
tar = e.target || e.srcElement,
className = tar.className;
if (className === 'item') {
tabItems[curIdx].className = 'item';
pageItems[curIdx].className = 'item';
curIdx = Array.prototype.indexOf.call(tabItems,tar);
tabItems[curIdx].className += ' current';
pageItems[curIdx].className += ' active';
}
}
init();
})(document)
九、媒体查询进行屏幕适配
@media screen and (min-width: 480px) and (max-width: 767px){
html{
background-color: red;
}
}
十、px、em、rem
-
px
相对于屏幕像素 -
em
父级元素设置的font-size = 1em -
rem
根元素HTML设置到font-size = 1rem
<script>
document.documentElement.style.fontSize = document.documentElement.clientWidth / 37.5 +'px';
</script>
十一、['1','2','3'].map(parseInt)
- parseInt(string, radix)
- string 要解析的字符串
- radix 要解析的数字的基数(进制)
- 返回解析后的数字。
- 先转整数,把它看成对应进制,再转成十进制,return出来
- map(function(item,index,array){})
- return 一个数组
- parseInt接受了item,index两个参数
- parseInt('1',0)->1
- parseInt('2',1)->NaN
- parseInt('3',2)->NaN
- 答案是[1,NaN,NaN]
十二、this
例一、
function test(){
this.a = 1;
console.log(this);//window
console.log(this.a);//1
}
test();
console.log(a);//1
例二、
var a = 1;
function test(){
console.log(this);//window
console.log(this.a);//1
}
test();
例三、
var a = 1;
function test(){
'use strict';
console.log(this);//undefined
console.log(this.a);//报错
}
test();
例四、
var obj = {
a:1,
test:function(){
console.log(this);//obj
console.log(this.a);//1
}
}
obj.test();
例五、
function test(a){
this.a = a
console.log(this.a);//1
console.log(window.a);//1
}
test(1);
例六、
function test(a){
this.a = a
console.log(this.a);//1
console.log(window.a);//undefined
}
new test(1);
例七、
var a = 1;
function test(a) {
this.a = a
}
test.prototype.say = function () {
console.log(this);//test函数
console.log(this.a);//undefined,因为test函数的上没有定义a
console.log(a);//1
}
test.prototype.say();
例八、
function test(a) {
this.a = a
}
test.prototype.say = function () {
console.log(this.a);//333
}
var t = new test(333);
t.say();
例九、this绑定问题
- 法一、保存this
<button id="btn">点击</button>
<script>
oBtn = document.getElementById('btn');
oBtn.onclick = function () {
this.innerHTML = '加载中';
this.disabled = true;
//保存this
that = this
setTimeout(function () {
//this->window
that.innerHTML = '点击';
that.disabled = false;
},2000)
}
</script>
- 法二、绑定this
<button id="btn">点击</button>
<script>
oBtn = document.getElementById('btn');
oBtn.onclick = function () {
this.innerHTML = '加载中';
this.disabled = true;
setTimeout(function () {
//this->window
that.innerHTML = '点击';
that.disabled = false;
}.bind(this),2000)
}
</script>
- 法三、箭头函数
<button id="btn">点击</button>
<script>
oBtn = document.getElementById('btn');
oBtn.onclick = function () {
this.innerHTML = '加载中';
this.disabled = true;
setTimeout(()=> {
this.innerHTML = '点击';
this.disabled = false;
},2000)
}
</script>
call、apply、bind区别
- call/apply 改变this指向 并且立即执行
- call(context,原函数的参数们依次排列)
- apply(context,原函数的参数集合 用数组装载)
- bind 改变this指向 并返回一个新函数 写法同call
十三、IE6BUG
1.盒子浮动,他的margin变成二倍
解决:display:inline或者display:block
2.非浮动元素和浮动元素相邻,在设置高的的盒子内部出现有3个像素间隙
解决:都浮动
3.外部盒子相对定位,内部盒子绝对定位,内部盒子的left、right、top、bottom有一个为0,且宽高是奇数,会出现1px间隙
解决:设置偶数宽高
4.img下方有白色间隙
解决:法一:block,法二:vertical-align,法三:font-size:0(不推荐)
5.空元素,给他设置0~19px高度时,高度始终是19px
解决:法一:over-flow:hidden;法二:元素内部写个注释<!---->;
法三:内部写 ;法四:font-size:0
6.3245434512344,外层元素设置了,clear:both,span里的一些内容会跑到下边去
解决:法一:所有元素加上inline,法二:margin-right:负值
7.z-index失效
解决:在外层元素设置:position:relative;z-index=1
十四、数组去重
var arr = [ 5, 4, 3, 2,1,1,2,3,4,5];
for循环
- 循环两个数组,两个数组相比较,不重复就push
function uniqueArr(array) { var _arr = [], isRepeat; for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { isRepeat = false; for (let j = 0; j < _arr.length; j++) { if(_arr[j] == arr[i]){ isRepeat = true; break; } } if(!isRepeat){ _arr.push(arr[i]) } } return _arr } - 循环两次数组,项和后边的项相比较,存在重复的的break,不存在重复的push
function uniqueArr(array) { var _arr = [], isRepeat; for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { isRepeat = false; for (let j = i+1; j < array.length; j++) { if(array[i] == arr[j]){ isRepeat = true; break; } } if(!isRepeat){ _arr.push(arr[i]) } } return _arr }
filter
function uniqueArr(array) {
return array.filter(function (item,index) {
//这个元素的第一次出现的下标==当前filter循环到的下标,则返回,说明是不重复的;如果不相等,说明已经出现过,是重复的
return array.indexOf(item) === index;
})
}
forEach
function uniqueArr(array) {
var _arr = [];
array.forEach(function (item) {
if(_arr.indexOf(item) === -1){
_arr.push(item)
}
})
return _arr
}
sort
function uniqueArr(array) {
var _arr = [];
//先简单排序
arr.sort();
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
//arr当前元素和后一个元素不同,push
//if(array[i] !== arr[i+1]){
//或,arr当前元素和新数组_arr不同,push
if(array[i] !== _arr[_arr.length-1])
_arr.push(array[i])
}
}
return _arr
}
ES6 includes
function uniqueArr(array) {
var _arr = [];
array.forEach(function (item) {
if (!_arr.includes(item)) {
_arr.push(item)
}
})
return _arr
}
indexOf和includes区别
indexOf: -1 index 具体位置,对NaN无效
includes: true false,对NaN有效
reduce
function uniqueArr(array) {
return array.sort().reduce(function (prev, item) {
//先把arr简单排序,如果prev指向的数组为空,或者,prev指向的数组的最后一项和当前的item不想等,push
if (prev.length === 0 || prev[prev.length - 1] !== item) {
prev.push(item)
}
return prev
}, []);
}
Map
//Map的键名可以是一个对象
function uniqueArr(array) {
var _arr = [],
_temp = new Map();
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if(!_temp.get(array[i])){
_temp.set(array[i],1);
_arr.push(array[i])
}
}
return _arr
}
//相似地,
function uniqueArr(array) {
var _arr = [],
_temp = new Object();
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if(!_temp[array[i]]){
_temp[array[i]] = 1;
_arr.push(array[i])
}
}
return _arr
}
Set
//new Set(),不是一个数组,而是一个对象,用Array.from转换
function uniqueArr(array) {
return Array.from(new Set(array))
}
十五、移动端meta标签
renderer
<meta name="renderer" content="webkit">
<!-- 默认IE兼容模式 -->
<meta name="renderer" content="ie-comp">
<!-- 默认IE标准模式 -->
<meta name="renderer" content="ie-stand">
http-equiv
<!--IE以最高模式渲染-->
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE-edge">
viewport
<meta name="viewport" content="maximum-scale=1.0,minimum-scale=1.0,user-scalable=0,width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
十六、@import和link区别
- 从属关系不同
- link属于html标签,定义RSS,rel关联属性设置
- @import属于CSS关键字,只能引入css文件
- 加载顺序不同
- link引入的css,是同时加载的
- @import引入的css,是在页面加载完毕后被加载
- 兼容性
- link 不存在兼容性问题
- @import css2.1出现的,IE5以上才兼容
- DOM操作
- link可被DOM操作
- @import不可以 -link引入的样式权重大于@import引入的样式?
- 因为@import引入的样式在css最上边,被忽略了
十七、三角形画法
<div class="triangle"></div>
<style>
.triangle{
width: 0;
height: 0;
/* border-top: 50px solid transparent; */
border-bottom: 50px solid green;
border-left: 50px solid transparent;
border-right: 50px solid transparent;
}
</style>
十八、六边形画法
- 法一:
//两边三角形,中间长方形
<div class="hexagon"></div>
<style>
.hexagon{
position: relative;
width: 100px;
height: 173.2px;
background-color: red;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.hexagon::before,
.hexagon::after{
content: "";
display: block;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
width: 0;
height: 0;
border-top: 86.6px solid transparent;
border-bottom: 86.6px solid transparent;
}
.hexagon::before{
left: -50px;
border-right: 50px solid green;
}
.hexagon::after{
right: -50px;
border-left: 50px solid green;
}
</style>
- 法二:
//三个长方形旋转
<div class="hexagon"></div>
<style>
.hexagon {
position: relative;
width: 100px;
height: 173.2px;
border-top: 1px solid #000;
border-bottom: 1px solid #000;
margin: 0 auto;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.hexagon::before,
.hexagon::after {
content: "";
display: block;
position: absolute;
top: -1px;
left: 0;
width: 100px;
height: 173.2px;
border-top: 1px solid #000;
border-bottom: 1px solid #000;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.hexagon::before {
transform: rotate(60deg);
}
.hexagon::after {
transform: rotate(-60deg);
}
</style>
十九、数组扁平化、去重、排序
var arr = [[[1, 2, 3], [3, 4, 5, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, [11, 12, [12, 13, [14]]]]], 10];
//编写一个程序,将数组扁平化并将扁平化数组去重,最终得到一个升序且不重复的一维数组
- 1.扁平化
- 法一:
function flatten(arr) { var _arr = arr || [], fArr = [], len = _arr.length, item; for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) { item = arr[i]; _isArr(item)?fArr = fArr.concat(flatten(item)):fArr.push(item); } return fArr; function _isArr(item) { return {}.toString.call(item) === '[object Array]'; } }- 法二:
Array.prototype.flatten = function () { var _arr = this, toStr = {}.toString; if(toStr.call(_arr)!=='[object Array]'){ throw new Error('只有数组才能调用flatten方法') } //用forEach //var fArr = []; //_arr.forEach(function (item) { // toStr.call(item) === '[object Array]'? fArr = //fArr.concat(item.flatten()): fArr.push(item); //}) //用reduce return _arr.reduce(function (prev,item){ return prev.concat( toStr.call(item) === '[object Array]'?item.flatten():item ); },[]); }- 法三:
const flatten = arr => arr.reduce((prev, item) => prev.concat( {}.toString.call(item) === '[object Array]' ? flatten(item) : item),[])- 法四:
arr.flat(Infinity) - 2.去重
Array.from(new Set(arr.flat(Infinity)))
- 3.排序
Array.from(new Set(arr.flat(Infinity))).sort((a,b)=>a-b)
二十、JS模块化
解决的问题
commonjs
require
module.exports
AMD异步模块定义
define(moduleName,[module],function(){
------代码------
return {
key:value
}
})
define(给模块定义名字,需要的模块,执行的函数)
require.config({
path:{
moduleA:'js/moduleA',
moduleB:'js/moduleB'
moduleC:'js/moduleC'
}
})
require([module], callback);
require(引入的模块,回调函数)
二十一、面向对象
<div class="J_calculator">
<p>
<input type="text" placeholder="第一个数字">
<input type="text" placeholder="第二个数字">
</p>
<p>计算结果:<span class="result">0</span></p>
<p>
<button data-field="plus">+</button>
<button data-field="minus">-</button>
<button data-field="mul">*</button>
<button data-field="div">/</button>
</p>
</div>
<div class="J_calculator">
<p>
<input type="text" placeholder="第一个数字">
<input type="text" placeholder="第二个数字">
</p>
<p>计算结果:<span class="result">0</span></p>
<p>
<button data-field="plus">+</button>
<button data-field="minus">-</button>
<button data-field="mul">*</button>
<button data-field="div">/</button>
</p>
</div>
<script src="index.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Calculator(document.getElementsByClassName('J_calculator')[0]);
new Calculator(document.getElementsByClassName('J_calculator')[1]);
</script>
; (function (doc) {
var Calculator = function (dom) {
this.oCalculator = dom;
this.oFirstInput = this.oCalculator.getElementsByTagName('input')[0];
this.oSecondInput = this.oCalculator.getElementsByTagName('input')[1];
this.oResult = this.oCalculator.getElementsByClassName('result')[0];
this.init();
}
Calculator.prototype.init = function () {
this.bindEvent();
}
Calculator.prototype.bindEvent = function () {
this.oCalculator.addEventListener('click', this.onBtnClick.bind(this), false)
}
Calculator.prototype.onBtnClick = function (ev) {
var e = ev || window.event,
tar = e.target || e.srcElement,
tagName = tar.tagName.toLowerCase();
if (tagName === 'button') {
var field = tar.getAttribute('data-field'),
val1 = Number(this.oFirstInput.value) || 0,
val2 = Number(this.oSecondInput.value) || 0;
this.oResult.innerHTML = this.calculate(field,val1,val2);
}
}
Calculator.prototype.calculate = function (field,val1,val2) {
switch(field){
case 'plus':
return val1 + val2;
case 'minus':
return val1 - val2;
case 'mul':
return val1 * val2;
case 'div':
return val1 / val2;
}
}
window.Calculator = Calculator;
})(document);