超出的字引号省略
overflow:hidden;//隐藏多出的字
text-overfolw:ellipsis; // 多出的字用 省略号代替
white-spacs:nowrap;// 文本不会换行,连续的空白符被合并
DIV水平垂直居中方法汇总
方法一:不确定当前div的宽度和高度,采用transform:translate(-50%,-50%);当前div的父级添加相对定位(position:relative)
div{
background:red;
position:absolute;
left:50%;
top:50%;
//transform 属性向元素应用 2D 或 3D 转换。该属性允许我们对元素进行旋转、缩放、移动或倾斜。
transform:translate(-50%,-50%)
}
方法二:绝对定位方法:确定了当前div的宽度,margin值为当前div宽度一半的负值
div{
width:600px;
height:600px;
background:red;
position:absolute;
left:50%;
top:50%;
margin-left:-300px;
margin-top:-300px;
}
方法三:绝对定位方法:绝对定位下top left right bottom都设置0
div.child{
width:600px;
height:600px;
background:red;
position:absolute;
left:0;
top:0;
bottom:0;
right:0;
margin:auto;
}
方法四: 弹性布局:当前div的父级添加flex css样式
.box{
height:800px;
-webkit-display:flex;
display:flex;
//侧轴对齐
-webkit-align-items:center;
align-item:center;
-webkit-justify-content:center;
//主轴 横轴
justify-content:center;
border:1px solid #ccc
}
div.child{
width:600px;
height:600px;
background-color:red;
}
方法五: table-cell实现水平垂直居中:table-cell middle center组合使用
.table-cell {
display:table-cell;
vertical-align:middle;
text-align:center;
width:240px;
height:180px;
border:1px solid #666
}
方法六:绝对定位 calc()函数动态计算实现水平垂直居中
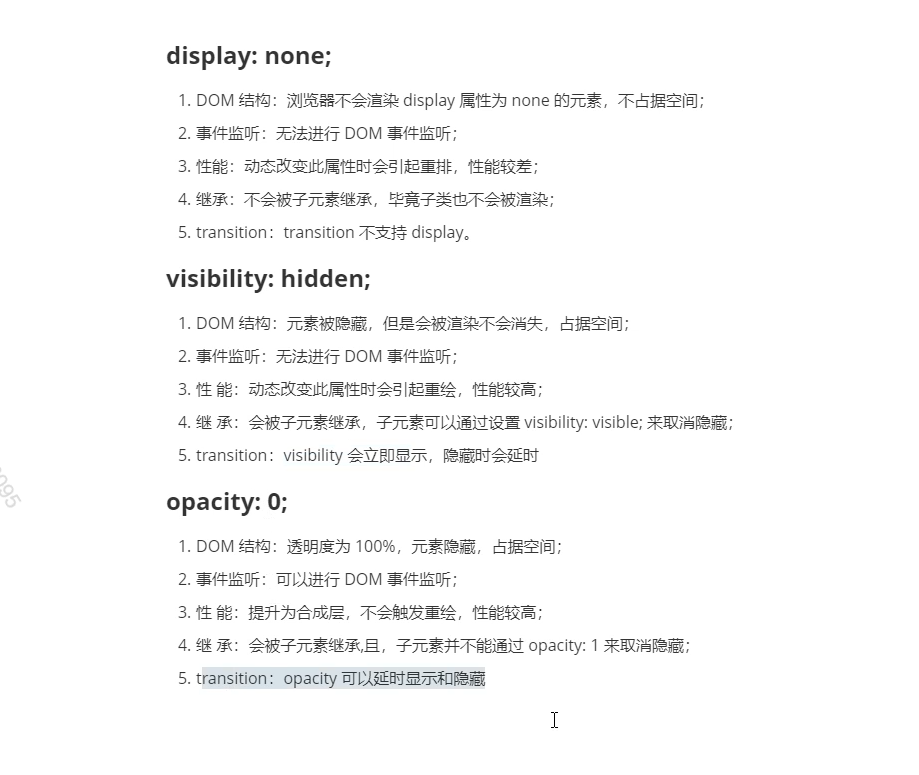
display visibility opacity 区别
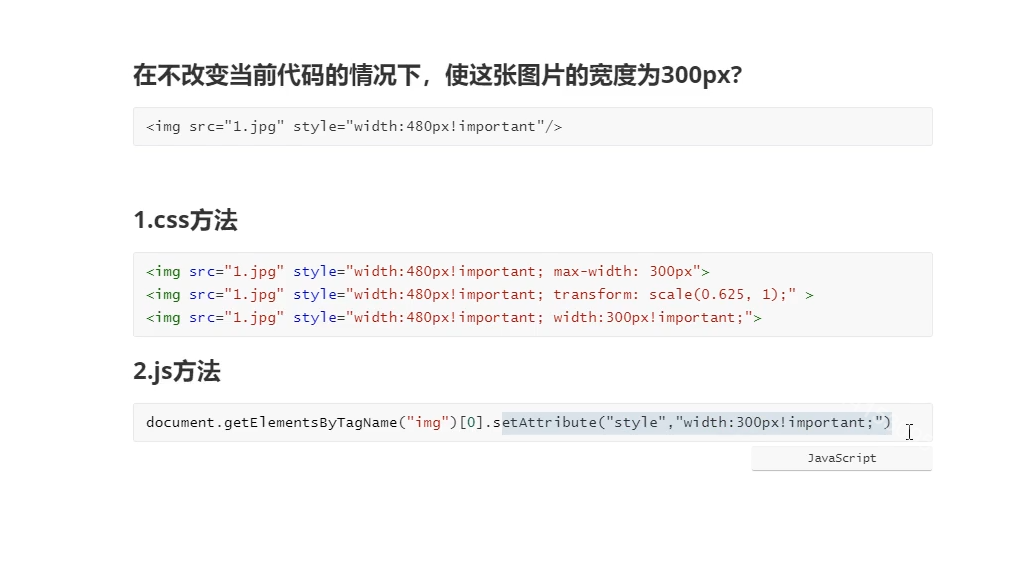
cs优先级之内联宽度覆盖
Flex 用语
align-items: center; 垂直居中
justify-content: center; 水平居中
parselnt与map遍历组合题
parselnt()函数解析一个字符串参数,并返回一个指定基数的整数(数学系统的基础)
const intvalue = parseInt(string[,radix]);
string 要被解析的值.如果参数不是一个字符串,则将其转换为字符串(使用ToString抽象操作)。字符串开头的空白符会被忽略。
radix 一个介于2和36之间的整数(数学系统的基础),表示上诉字符串的基数。默认为10,返回值 返回一个整数或NaN
parseInt(100);//100
parseInt(100,10);//100
parseInt(100,2);//4
['1','2','3'].map((item,index)=>{
return parseInt(item,index)
})
即返回的值分别为:
parseInt('1',0) //1
parseInt('2',1) //NaN 没有一进制
parseInt('3',2) //, 3不是二进制