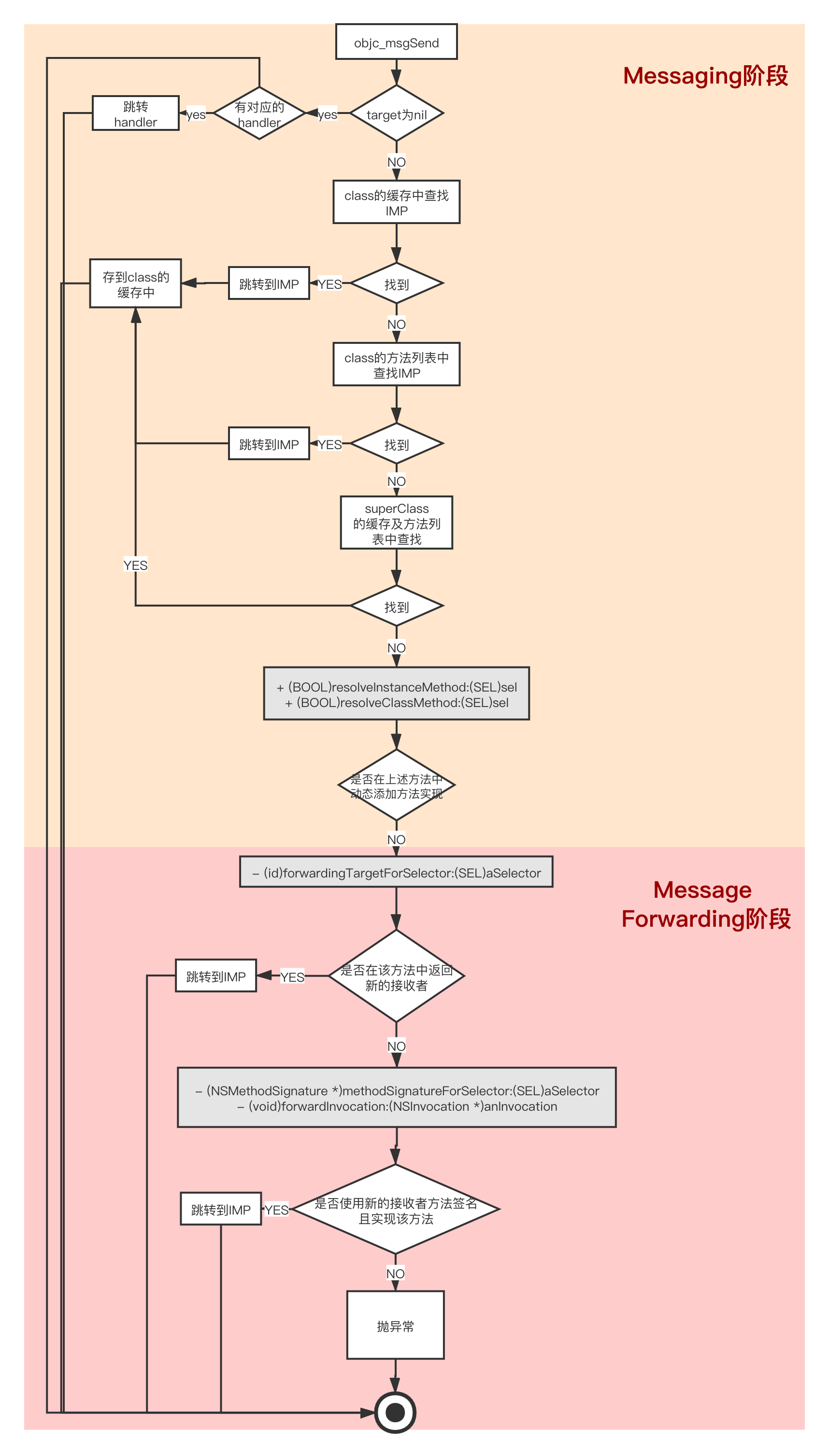
开发者在编码时,可以向任意一个对象(包括nil)发送消息,即使消息没有实现,编译也会通过。在编译阶段,只确定了要向接受者发送这条消息,至于接受者将如何响应和处理这条消息,在运行时Runtime负责对象的创建即消息的发送及转发。
- objc_msgSend介绍
- 消息发送阶段(Messaging阶段)
- 消息转发(Message Forwarding阶段)
- 消息发送及转发流程图
objc_msgSend介绍
Object-C中的【object message】在编译阶段会被转化成objc_msgSend方法:
/*
self:方法接受对象
op:方法选择器
*/
id objc_msgSend(id self, SEL op, ...)
// SEL类型定义
typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;
objc_selector是一个映射到方法的C字符串,Objc中不同类的同一个方法名的方法所对应的方法选择器是一样的,方法名字相同,参数类型不同,方法选择其也是一样的。
objc_msgSend方法做了如下几件事情:
-
检查selectors是否是需要忽略的;
-
检查target是否是nil
- 如果是nil,并且有相应的处理nil的函数,则跳转到该函数;
- 如果是nil,没有对应的处理函数,则清理现场并返回;这也是nil对象调用方法不会崩溃的原因。
-
如果target不为nil,则通过对象的isa指针找到对应的类,在类对象中的缓存中查找方法对应的IMP实现。
如果找到,就跳转进去,如果找不到就在类的方法列表中查找,如果没有,在父类的缓存及方法列表中查找,直到根类NSObject。如果没有就进入消息转发阶段了。
消息发送阶段(Messaging阶段)
源码之下无秘密,下面就从runtime的源码中,来看下方法查找与转发的具体实现,关键入口方法:
// objc-runtime-new.mm
/*
cls:类名
sel:方法选择器
inst:cls或者subclass的实例对象
initialize = NO,尝试避免调用 +initialize(可能会失败)
cache = YES,在加锁的缓存查找之前,会进行不加锁的缓存查找,如果找到则直接返回IMP,提高查找效率;cache = NO,则跳过不加锁查找这一步,直接进行加锁查找,加锁是为了防止在缓存读取时动态添加方法,保证线程安全。
resolver:在继承类中找不到IMP时,是否进行消息解析。
*/
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver)
-
在本类的缓存中查找
// Try this class's cache. imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel); if (imp) goto done; -
在该类的方法列表中查找
// Try this class's method lists. meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(cls, sel); if (meth) { log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, cls); imp = meth->imp; goto done; } -
在父类中(缓存&方法列表)查找
// Try superclass caches and method lists. curClass = cls; // 向上遍历继承关系 直到NSObject.superclass = nil while ((curClass = curClass->superclass)) { // Superclass cache. // 在父类的缓存中查找 imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel); if (imp) { //在继承体系及resolve之后都没有找到IMP,会将sel的IMP设置为_objc_msgForward_impcache放入缓存中(步骤5),imp == (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache 标志着没有找到IMP,需要消息转发,所以调用break;终止在父类中的循环查找。 if (imp != (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) { // Found the method in a superclass. Cache it in this class. // 在父类的缓存中找到IMP后,存到本类的缓存中。问什么存在本类的缓存中呢?因为第一步的查找是本类的缓存开始的,提高查找效率。 log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass); goto done; } else { // Found a forward:: entry in a superclass. // Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method // resolver for this class first. break; } } // Superclass method list. // 缓存中没有 到父类方法列表中查找 meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel); if (meth) { // 找到后放入本类的缓存中 log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, curClass); imp = meth->imp; goto done; } } -
都没有找到,尝试方法解析一次。
// No implementation found. Try method resolver once. // 4 都没有找到 尝试方法解析一次 if (resolver && !triedResolver) { runtimeLock.unlockRead(); /* 方法解析 */ _class_resolveMethod(cls, sel, inst); // Don't cache the result; we don't hold the lock so it may have // changed already. Re-do the search from scratch instead. triedResolver = YES; goto retry; }其中_class_resolveMethod方法的具体实现如下:
void _class_resolveMethod(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst) { /* 如果是实例方法会调用 + (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel 如果是类方法会调用 + (BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel 如果开发者在resolve方法中动态添加了IMP 在下面的retry即重新走一遍的方法查找流程中 会找到并存入缓存中 */ if (! cls->isMetaClass()) { // try [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel] _class_resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst); } else { // try [nonMetaClass resolveClassMethod:sel] // and [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel] _class_resolveClassMethod(cls, sel, inst); if (!lookUpImpOrNil(cls, sel, inst, NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/)) { _class_resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst); } } }_class_resolveInstanceMethod方法的具体实现:
static void _class_resolveInstanceMethod(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst) { if (! lookUpImpOrNil(cls->ISA(), SEL_resolveInstanceMethod, cls, NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/)) { // Resolver not implemented. return; } BOOL (*msg)(Class, SEL, SEL) = (typeof(msg))objc_msgSend; bool resolved = msg(cls, SEL_resolveInstanceMethod, sel); // Cache the result (good or bad) so the resolver doesn't fire next time. // +resolveInstanceMethod adds to self a.k.a. cls IMP imp = lookUpImpOrNil(cls, sel, inst, NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/); if (resolved && PrintResolving) { if (imp) { _objc_inform("RESOLVE: method %c[%s %s] " "dynamically resolved to %p", cls->isMetaClass() ? '+' : '-', cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel), imp); } else { // Method resolver didn't add anything? _objc_inform("RESOLVE: +[%s resolveInstanceMethod:%s] returned YES" ", but no new implementation of %c[%s %s] was found", cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel), cls->isMetaClass() ? '+' : '-', cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel)); } } }注意:
- lookUpImpOrNil与lookUpImpOrForward的实现很像,区别在于当找不到IMP时,lookUpImpOrForward中会将IMP赋值为**_objc_msgForward_impcache**,存入缓存并返回,用于后面的消息转发,体现在步骤5;而lookUpImpOrNil会返回nil,不进行消息转发。
- _objc_msgForward_impcache,是放在IMP缓存中的一个标记,标记在继承系统以及方法resolve时都没有找到IMP,用于后面的消息转发,在步骤3遍历父类缓存列表时,如果发现sel对应的IMP是_objc_msgForward_impcache,就停止向上父类的查找。
开发者通过重写resolveInstanceMethod实现方法解析:
#import "Person.h" /* Person类声明了- (void)sweepFloor方法,但未实现。 */ //自定义方法实现 void sweepImp (id self,SEL _cmd){ NSLog(@"sweepImp"); } + (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel { if ([NSStringFromSelector(sel) isEqualToString:@"sweepFloor"]) { //添加方法- (void)sweepFloor的实现为sweepImp class_addMethod(self, sel, (IMP)sweepImp, "v@:"); } return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel]; } /* 补充介绍:方法参数编码类型 为了帮助运行时系统,编译器将每个方法的返回参数和传入参数的类型编码为字符串,并将该字符串与方法选择器关联。 class_addMethod(Class _Nullable cls, SEL _Nonnull name, IMP _Nonnull imp, const char * _Nullable types) class_addMethod的最后一个参数types为方法的返回参数&传入参数类型编码后字符,这里需要开发者手动传入,可以通过@encode(type)获取对应编码字符。 - (void)getTypes { char *voidChar = @encode(void); char *seletorChar = @encode(SEL); char *idChar = @encode(id); NSLog(@"参数编码:%s %s %s",voidChar,seletorChar,idChar);//参数编码:v @ : } */ -
如果在resolve方法中没有IMP 进行消息转发(Message Forwarding)
// No implementation found, and method resolver didn't help. // Use forwarding. // 5 如果在resolve方法中没有IMP,将imp赋值为_objc_msgForward_impcache,存入缓存中,然后进行消息转发(Message Forwarding),用于外部使用的IMP必须转换为_objc_msgForward或者_objc_msgForward_stret //_objc_msgForward_impcache为函数指针,存储在方法缓存中。 imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache; cache_fill(cls, sel, imp, inst);至此,消息发送阶段已完成,进入消息转发阶段。
消息转发(Message Forwarding阶段)
在执行_objc_msgForward之后会调用objc_forward_handler函数,objc_forward_handler的值为objc_defaultForwardHandler:
objc_defaultForwardHandler(id self, SEL sel)
{
_objc_fatal("%c[%s %s]: unrecognized selector sent to instance %p "
"(no message forward handler is installed)",
class_isMetaClass(object_getClass(self)) ? '+' : '-',
object_getClassName(self), sel_getName(sel), self);
}
void *_objc_forward_handler = (void*)objc_defaultForwardHandler;
上面这句打印就是我们经常在xcode崩溃中见到的方法为实现的崩溃日志。
在执行objc_forward_handler之前,开发者可以通过重写类的一下方法,实现消息转发。
-
为方法指定新的接受者
#import "Person.h" #import "SweepRobot.h" //类为Person,声明了sweepFloor(扫地)方法却未实现,转发给扫地机器人(SweepRobot对象)实现 - (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector { NSLog(@"%s_%@",__FUNCTION__,NSStringFromSelector(aSelector)); if ([NSStringFromSelector(aSelector) isEqualToString:@"sweepFloor"]) { return [SweepRobot new]; } return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector]; }#import "SweepRobot.h" @implementation SweepRobot - (void)sweepFloor { NSLog(@"%@ %s实现",[self class],__func__); } @end -
获取方法签名,创建NSInvocation
@interface Person () @property (nonatomic,strong)SweepRobot *robot; @end - (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector { NSLog(@"%s",__FUNCTION__); return [self.robot methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector]; } - (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation { NSLog(@"%s anInvocation:%@",__FUNCTION__,anInvocation); [anInvocation invokeWithTarget:self.robot]; } - (SweepRobot *)robot { if (!_robot) { _robot = [SweepRobot new]; } return _robot; }
消息发送及转发流程图