如果对Django基本配置还是小白的话,请移步:
第一:在setting中配置模版文件夹
My_Django/setting.py
[AppleScript]
纯文本查看
复制代码
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 | TEMPLATES = [ #模版 { 'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates', 'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')] # 模版文件夹.... ], }, ] |
第二:编写一个模版html
templates/hello/index.html
[AppleScript]
纯文本查看
复制代码
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 | <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>{{ title }}</title> </head> <body> <ul> {% for item in list%} <li>{{ item }}</li> {% endfor %} </ul> </body> </html> |
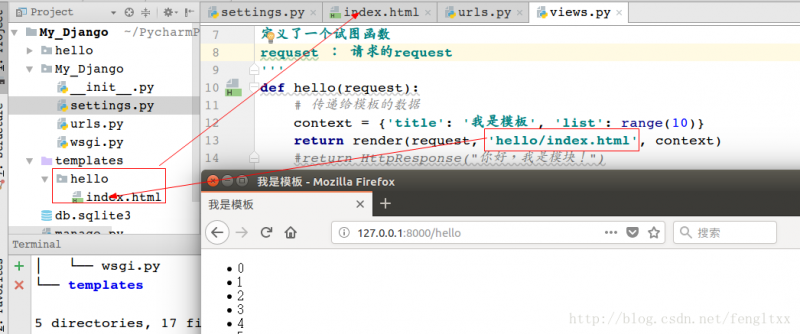
第三:使用视图函数返回模版
Django提供了一个函数render封装了以上代码 方法render包含3个参数
- 第一个参数为request对象
- 第二个参数为模板文件路径
- 第三个参数为字典,表示向模板中传递的上下文数据
hello/views.py:
[AppleScript]
纯文本查看
复制代码
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 | from django.http import HttpResponse, request from django.shortcuts import render ''' 定义了一个试图函数 requset : 请求的request ''' def hello(request): # 传递给模板的数据 context = {'title': '我是模板', 'list': range(10)} return render(request, 'hello/index.html', context) #return HttpResponse("你好,我是模块!") |
访问 效果如下: