本周工作概述
target\riscv\cpu.ctarget\riscv\csr.c
target\riscv\cpu.c
扩展ISA及寄存器定义
static const char riscv_exts[26] = "IEMAFDQCLBJTPVNSUHKORWXYZG";
定义了riscv目前所有扩展
const char * const riscv_int_regnames[] = {
"x0/zero", "x1/ra", "x2/sp", "x3/gp", "x4/tp", "x5/t0", "x6/t1",
"x7/t2", "x8/s0", "x9/s1", "x10/a0", "x11/a1", "x12/a2", "x13/a3",
"x14/a4", "x15/a5", "x16/a6", "x17/a7", "x18/s2", "x19/s3", "x20/s4",
"x21/s5", "x22/s6", "x23/s7", "x24/s8", "x25/s9", "x26/s10", "x27/s11",
"x28/t3", "x29/t4", "x30/t5", "x31/t6"
};
定义riscv整数寄存器
const char * const riscv_fpr_regnames[] = {
"f0/ft0", "f1/ft1", "f2/ft2", "f3/ft3", "f4/ft4", "f5/ft5",
"f6/ft6", "f7/ft7", "f8/fs0", "f9/fs1", "f10/fa0", "f11/fa1",
"f12/fa2", "f13/fa3", "f14/fa4", "f15/fa5", "f16/fa6", "f17/fa7",
"f18/fs2", "f19/fs3", "f20/fs4", "f21/fs5", "f22/fs6", "f23/fs7",
"f24/fs8", "f25/fs9", "f26/fs10", "f27/fs11", "f28/ft8", "f29/ft9",
"f30/ft10", "f31/ft11"
};
定义了浮点数寄存器
之后定义了中断和异常名
初始化
之后是一些设置函数,如下:
static void set_misa(CPURISCVState *env, target_ulong misa)
{
env->misa_mask = env->misa = misa;
}
看一下CPURISCVState这个结构体的内容:
struct CPURISCVState {
target_ulong gpr[32];
uint64_t fpr[32]; /* assume both F and D extensions */
target_ulong pc;
target_ulong load_res;
target_ulong load_val;
target_ulong frm;
target_ulong badaddr;
target_ulong guest_phys_fault_addr;
target_ulong priv_ver;
target_ulong misa;
target_ulong misa_mask;
uint32_t features;
...
后面内容还有很多,这里不都列出来了。
这个结构体中记录了riscv CPU当前的状态信息,其中的变量含义如下:
- misa:machine-level isa,记录使用的ISA都有哪些,即扩展ISA
- priv_ver:privileged architecture proposal 文档有多个版本,需要指定是哪个版本的规范,目前最新版本是1.11
- resetvec:Reset Vector adress. 当reset时,pc值得重置地址
The RISC-V Instruction Set Manual, Volume II: Privileged Architecture, Version 1.10 states:
Upon reset, a hart’s privilege mode is set to M. The pc is set to an implementation-defined reset vector.
- features:记录MMU、PMP特性支持情况
回到设置函数的位置:
static void set_misa(CPURISCVState *env, target_ulong misa)
{
env->misa_mask = env->misa = misa;
}
设置了misa包括哪些,即使用哪些扩展
static void set_priv_version(CPURISCVState *env, int priv_ver)
{
env->priv_ver = priv_ver;
}
设置当前的privileged version,即Supervisor Mode和Machine Mode遵循那种规范
static void set_feature(CPURISCVState *env, int feature)
{
env->features |= (1ULL << feature);
}
关于ULL:参考链接
由于下面的原因:
S extension denotes that Supervisor mode exists, however it is possible to have a core that support S mode but does not have an MMU and there is currently no bit in misa to indicate whether an MMU exists or not so a cpu features bitfield is required, likewise for optional PMP support
故设置了feature位,用于设置如下特性:
enum {
RISCV_FEATURE_MMU,
RISCV_FEATURE_PMP,
RISCV_FEATURE_MISA
};
static void set_resetvec(CPURISCVState *env, int resetvec)
{
#ifndef CONFIG_USER_ONLY
env->resetvec = resetvec;
#endif
}
当没有指定用户自定义的情况下,设置reset vector内容
一个典型的RISC-V CPU初始化例子
在设置了macu扩展,且无MMU的情况下,CPU核心初始化函数如下:
static void rv32imacu_nommu_cpu_init(Object *obj)
{
CPURISCVState *env = &RISCV_CPU(obj)->env;
set_misa(env, RV32 | RVI | RVM | RVA | RVC | RVU);
set_priv_version(env, PRIV_VERSION_1_10_0);
set_resetvec(env, DEFAULT_RSTVEC);
set_feature(env, RISCV_FEATURE_PMP);
}
RISC-V CPU类
实际上target\riscv\cpu.c定义了一个类,并完成了其实现方法。通过对这个文件的总览,我们得以了解C实现面向对象编程的方法。
代码的最后一行是cpu.c最终要完成的工作,即声明一个TYPE:
DEFINE_TYPES(riscv_cpu_type_infos)
其定义如下:
static const TypeInfo riscv_cpu_type_infos[]
先看一下TypeInfo是什么:
// include\qom\object.h
struct TypeInfo
{
const char *name;
const char *parent;
size_t instance_size;
void (*instance_init)(Object *obj);
void (*instance_post_init)(Object *obj);
void (*instance_finalize)(Object *obj);
bool abstract;
size_t class_size;
void (*class_init)(ObjectClass *klass, void *data);
void (*class_base_init)(ObjectClass *klass, void *data);
void *class_data;
InterfaceInfo *interfaces;
};
从而对应riscv_cpu_type_infos定义:
static const TypeInfo riscv_cpu_type_infos[] = {
{
.name = TYPE_RISCV_CPU,
.parent = TYPE_CPU,
.instance_size = sizeof(RISCVCPU),
.instance_init = riscv_cpu_init,
.abstract = true,
.class_size = sizeof(RISCVCPUClass),
.class_init = riscv_cpu_class_init,
},
DEFINE_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_ANY, riscv_any_cpu_init),
...
}
- name: The name of the type
- parent: The name of the parent type
- instance_size: The size of the object (derivative of #Object). If @instance_size is 0, then the size of the object will be the size of the parent object.
- instance_init: This function is called to initialize an object. The parent class will have already been initialized so the type is only responsible for initializing its own members.
- abstract: If this field is true, then the class is considered abstract and cannot be directly instantiated. 即,抽象类,无法被直接实例化。
- class_size: The size of the class object (derivative of #ObjectClass) for this object. If @class_size is 0, then the size of the class will be assumed to be the size of the parent class. This allows a type to avoid implementing an explicit class type if they are not adding additional virtual functions.
- class_init: This function is called after all parent class initialization has occurred to allow a class to set its default virtual method pointers. This is also the function to use to override virtual methods from a parent class.
总体来看,这部分相当于C++的底层C实现
现在我们回到riscv的cpu中来看,重点看类的构造函数riscv_cpu_class_init。函数中完成了risc-v CPU类的初始化,并注册了CPUClass。对于CPUClass的注册如下:
cc->class_by_name = riscv_cpu_class_by_name;
cc->has_work = riscv_cpu_has_work;
cc->do_interrupt = riscv_cpu_do_interrupt;
cc->cpu_exec_interrupt = riscv_cpu_exec_interrupt;
cc->dump_state = riscv_cpu_dump_state;
cc->set_pc = riscv_cpu_set_pc;
cc->synchronize_from_tb = riscv_cpu_synchronize_from_tb;
cc->gdb_read_register = riscv_cpu_gdb_read_register;
cc->gdb_write_register = riscv_cpu_gdb_write_register;
cc->gdb_num_core_regs = 33;
#if defined(TARGET_RISCV32)
cc->gdb_core_xml_file = "riscv-32bit-cpu.xml";
#elif defined(TARGET_RISCV64)
cc->gdb_core_xml_file = "riscv-64bit-cpu.xml";
#endif
cc->gdb_stop_before_watchpoint = true;
cc->disas_set_info = riscv_cpu_disas_set_info;
#ifndef CONFIG_USER_ONLY
cc->do_transaction_failed = riscv_cpu_do_transaction_failed;
cc->do_unaligned_access = riscv_cpu_do_unaligned_access;
cc->get_phys_page_debug = riscv_cpu_get_phys_page_debug;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TCG
cc->tcg_initialize = riscv_translate_init;
cc->tlb_fill = riscv_cpu_tlb_fill;
#endif
/* For now, mark unmigratable: */
cc->vmsd = &vmstate_riscv_cpu;
除此之外,需要设置DeviceClass,包括当前device的realize和parent device的realize,同时,还有前面提到的reset相关动作:
device_class_set_parent_realize(dc, riscv_cpu_realize, &mcc->parent_realize);
device_class_set_parent_reset(dc, riscv_cpu_reset, &mcc->parent_reset);
看一下riscv_cpu_realize函数。首先声明必要变量:
CPUState *cs = CPU(dev);
RISCVCPU *cpu = RISCV_CPU(dev);
CPURISCVState *env = &cpu->env;
RISCVCPUClass *mcc = RISCV_CPU_GET_CLASS(dev);
int priv_version = PRIV_VERSION_1_11_0;
target_ulong target_misa = 0;
Error *local_err = NULL;
之后执行了:
cpu_exec_realizefn(cs, &local_err);
这一函数定义在exec.c中,推测是在虚拟机层面上注册CPU
之后又是对几个参数的配置,对pri_version设置:
if (cpu->cfg.priv_spec) {
if (!g_strcmp0(cpu->cfg.priv_spec, "v1.11.0")) {
priv_version = PRIV_VERSION_1_11_0;
} else if (!g_strcmp0(cpu->cfg.priv_spec, "v1.10.0")) {
priv_version = PRIV_VERSION_1_10_0;
} else if (!g_strcmp0(cpu->cfg.priv_spec, "v1.9.1")) {
priv_version = PRIV_VERSION_1_09_1;
} else {
error_setg(errp,
"Unsupported privilege spec version '%s'",
cpu->cfg.priv_spec);
return;
}
}
set_priv_version(env, priv_version);
set_resetvec(env, DEFAULT_RSTVEC);
之后是对misa的设置。注意,i和e基本指令集不兼容,若用户同时设置了i和e,需要进行错误处理。
Somewhere we can deliver a patch
In cpu.c, we found there are several cpu entities with corresponding propertities. For example, for SIFIVE there are:
DEFINE_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_E31, rv32imacu_nommu_cpu_init),
DEFINE_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_E34, rv32imafcu_nommu_cpu_init),
DEFINE_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_U34, rv32gcsu_priv1_10_0_cpu_init),
for RISCV32, and
DEFINE_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_E51, rv64imacu_nommu_cpu_init),
DEFINE_CPU(TYPE_RISCV_CPU_SIFIVE_U54, rv64gcsu_priv1_10_0_cpu_init),
for RISCV64. However, we can find more entities from the website of SIFIVE:
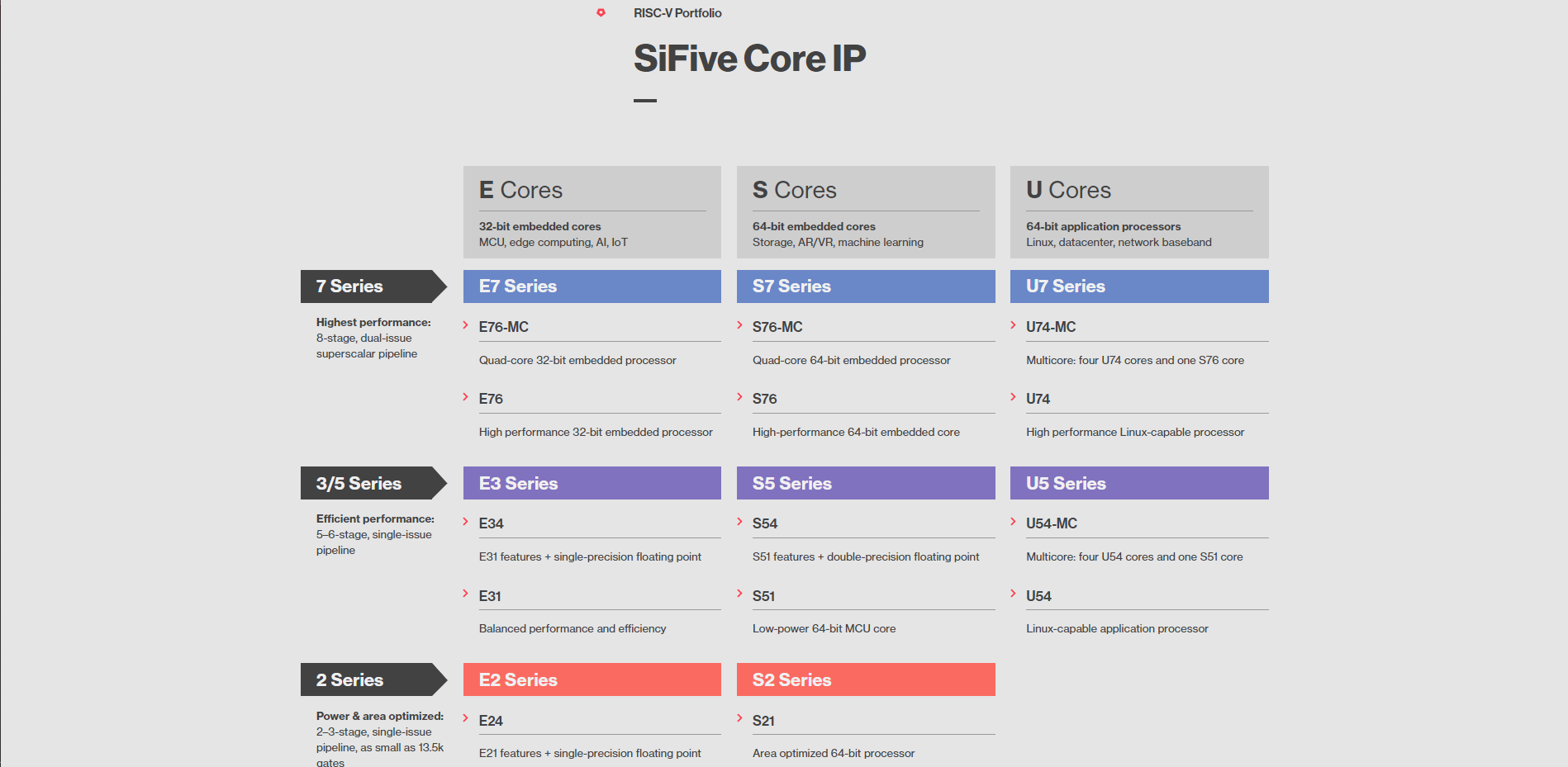
Coincidently, I have found a patch doing exactly the same thing: github.com/qemu/qemu/c…
And we may add the following cores: www.sifive.com/cores/s54 www.sifive.com/cores/e76
Perhaps I will try doing this in the next week.
target\riscv\csr.c
Several public APIs to modify CSR function table is defined first in this file. And then follows those APIs used to change various CSRs.
Check the manual for details about CSR(Control and Status Registers):
- The RISC-V Instruction Set Manual, Volume I: User-Level ISADocument Version 2.2, Session 2.8
- The RISC-V Instruction Set Manual, Volume II: Privileged Architecture Version 1.10, Chapter 2
Q: Why using '&' option?
void riscv_get_csr_ops(int csrno, riscv_csr_operations *ops)
{
*ops = csr_ops[csrno & (CSR_TABLE_SIZE - 1)];
}
The APIs in csr.c are plain and easy to understand, so we're not going to explain them here, for we can guess the usage from the name of the functions and the implementations are just the same. However, it is much more important to understand CSR itself and relevant parts through the manual, yet there is still a lot of reading work for me to do in the coming weeks.
一些词汇
- hart: hardware thread