Netty服务端一般如下面代码模式,简化了 NIO编程的复杂性同时,并且借助于Pipeline模型,可以很简单的就构建出高性能、可扩展的应用程序。
public class DemoServer {
public static void main
(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { EventLoopGroup bossGroup =
new NioEventLoopGroup(); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(
new TestServerInitializer()); ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8899).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); }
finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } }}
下面我们就通过源码分析下隐藏在这些代码背后的逻辑,对Netty可以有个更加深刻的认识。
NioEventLoopGroup
Netty中每个 Channel都会通过注册方式,绑定到一个具体的NioEventLoop实例上, NioEventLoop继承抽象类SingleThreadEventLoop,内部通过单个线程模式管理所有注册到它上面的 Channel,负责这些Channel事件监听、事件处理等。 NioEventLoopGroup内部包含一组NioEventLoop,好比
NioEventLoop是用于管理Channel的其中一个线程,而 NioEventLoopGroup则对应的是管理所有Channel的线程池。
上面创建了两个NioEventLoopGroup对象,一个是用来管理 NioServerSocketChannel的,而另一个是用来管理客户端连接进来时创建的客户端对应的NioSocketChannel的。
通过跟踪NioEventLoopGroup构造过程,本身逻辑是比较简单,但是调用栈比较深,这里就不太方便代码展示,其大概完成事情可以用如下图描述:
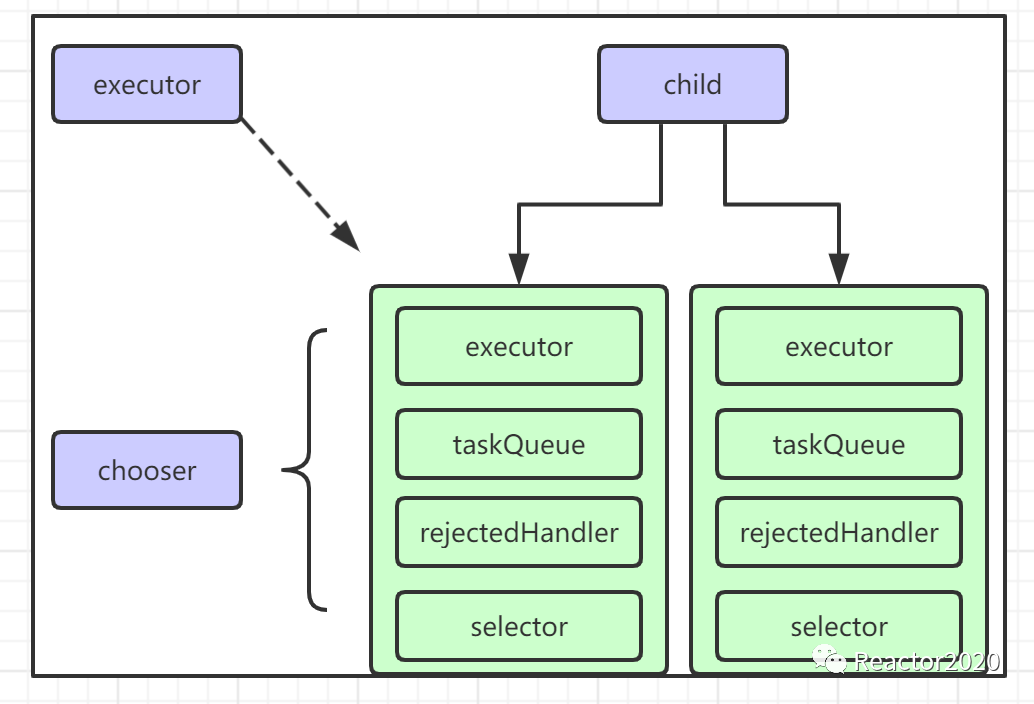
NioEventLoopGroup创建时,同时会创建三个元素: executor、chooser和 child:
-
child是一个NioEventLoop类型数组,存储Group管理的所有NioEventLoop对象,默认是CPU核数*2;NioEventLoop创建时主要包含4个元素: -
executor:每个NioEventLoop内部都会对应一个线程,executor线程池就是负责这些线程创建; -
taskQueue:NioEventLoop内部维护一个任务队列,其它线程需要NioEventLoop执行任务时,就像taskQueue提交任务即可,NioEventLoop会自动从taskQueue中获取任务执行; -
rejectedHandler:addTask()向taskQueue中提交任务失败时,所使用的拒绝策略; -
Selector:每个NioEventLoop内部维护着一个Selector,这样注册到其上面的Channel就需要向该Selector注册感兴趣的SelectionKey即可,事件轮询、事件处理都会由NioEventLoop进行处理。 -
executor:NioEventLoop通过单线程模式管理注册到其上面的所有Channel,executor线程池就是用于提供该线程的创建 -
chooser:NioEventLoopGroup管理着多个NioEventLoop,每当有一个新Channel需要注册时,就会通过chooser选取策略从中选取一个NioEventLoop用于注册。
ServerBootStrap配置
下面我们来分析下如下代码作用:
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new TestServerInitializer());ServerBootStrap是 Netty使用的一个启动引导类,上面的代码主要是为后续Netty启动提供配置数据,本身比较简单:
-
group(bossGroup, workerGroup):指定Netty使用的两大线程组,bossGroup主要供NioServerSocketChannel监听OP_ACCEPT新连接使用的线程组;workerGroup用于处理每一条客户端连接NioSocketChannel的数据读写所使用的线程组。 -
channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class):用于指定网络模型。 -
childHandler(new TestServerInitializer()):每个客户端连接进来创建NioSocketChannel,同时会给该channel创建一个pipeline用于负责处理该channel上业务逻辑,这里通过一个特殊的ChannelInitializer类型handler,借助回调实现向pipeline中添加handler。
bind
当执行到serverBootstrap.bind(8899),则表示 Netty开始进入真正的启动阶段。一路跟踪下来,会进入到doBind()方法中:
private ChannelFuture doBind
(final SocketAddress localAddress) { //创建NioServerSocketChannel -> pipeline添加ServerBootstrapAcceptor -> channel进行register,分配NioEventLoop
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister(); final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
return regFuture; } /** * register完成,则执行doBind0()进行server端口绑定 */
if (regFuture.isDone()) { ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise(); doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
return promise; } else {
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
//register还未完成,则添加listener,待注册完成再执行doBind0()进行server端口绑定 regFuture.addListener(
new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override
public void
operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) { promise.setFailure(cause); }
else { promise.registered(); doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise); } } });
return promise; }}
这个方法主要完成两件事:
-
initAndRegister():Channel相关的初始化和注册,这里核心逻辑:创建Channel并进行各种初始化,最后把Channel注册到NioEventLoop上,并启动NioEventLoop线程开始处理事件轮询、事件处理; -
doBind0():待initAndRegister()执行完成后执行doBind0()方法,initAndRegister()是个异步方法,所以在执行doBind0()之前使用regFuture.isDone()判断下是否Channel注册完成,如果没有完成则通过addListener()添加一个listener,等待完成后再执行doBind0()。经过上步骤,channel准备工作基本都准备差不多了,这时还差一步:将channel绑定到具体端口上。
initAndRegister
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() { Channel channel = null; try { /** * * 通过反射方式创建IO模型类型,具体类型有serverBootstrap.channel()方法指定,比如:NioServerSocketChannel * NioServerSocketChannel创建时,构造方法中会触发创建jdk channel创建 * 同时会创建对应的配置类:NioServerSocketChannelConfig(tcp参数配置) */ channel = channelFactory.newChannel(); /** * 初始化channel,由子类bootstrap或者serverBootStrap进行实现,可视为一个模板方法 * ServerBootStrap逻辑:options、attrs等初始化,同时向pipeline中添加一个InboundHandler:ServerBootstrapAcceptor * * new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(serverSocketChannel, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs) * 这样NioServerSocketChannel接收到OP_ACCEPT事件时,就可以利用这些参数给代表客户端连接的SocketChannel初始化 */ init(channel);// } catch (Throwable t) { if (channel != null) { // channel can be null if newChannel crashed (eg SocketException("too many open files")) channel.unsafe().closeForcibly(); // as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor return new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t); } // as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor //还没有注册到线程池。使用默认线程GlobalEventExecutor return new DefaultChannelPromise(new FailedChannel(), GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t); } /** * 将NioServerSocketChannel注册到Reactor主线程池上 ,即给当前创建的Channel分配一个NioEventLoop线程 */ ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel); if (regFuture.cause() != null) { if (channel.isRegistered()) { channel.close(); } else { channel.unsafe().closeForcibly(); } } return regFuture;}这个方法主要完成3件事:
-
channelFactory.newChannel():采用工厂模式创建一个Channel实例,serverBootstrap.channel()方法指定创建的实例类型,比如:.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class); -
init(channel):对创建的Channel进行各种初始化,比如:options、attrs等设置,同时向pipeline中添加一个非常重要的handler:ServerBootstrapAcceptor;
new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(serverSocketChannel, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs)ServerBootstrapAcceptor连接处理器是 Server端非常重要的一个InBound类型的 handler,当NioServerSocketChannel轮询 OP_ACCEPT事件接收到客户端连接进来时,客户端连接各种设置等工作就是由这个Acceptor连接器完成。
-
config().group().register(channel):将Channel注册到NioEventLoop上,由NioEventLoop负责channel的各种管理,NioEventLoop会通过单个线程轮询其内部持有的Selector上事件,并进行处理;
newChannel()比较简单,这里就不展开了,核心点主要在于 init(channel)和register(channel)这两个方法。
init
void init(Channel channel) throws Exception { final Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> options = options0(); synchronized (options) { setChannelOptions(channel, options, logger); } final Map<AttributeKey<?>, Object> attrs = attrs0(); synchronized (attrs) { for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: attrs.entrySet()) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") AttributeKey<Object> key = (AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey(); channel.attr(key).set(e.getValue()); } } ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline(); final EventLoopGroup currentChildGroup = childGroup; final ChannelHandler currentChildHandler = childHandler; final Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] currentChildOptions; final Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object>[] currentChildAttrs; synchronized (childOptions) { currentChildOptions = childOptions.entrySet().toArray(newOptionArray(0)); } synchronized (childAttrs) { currentChildAttrs = childAttrs.entrySet().toArray(newAttrArray(0)); } /** * 给NIOServerChannel绑定的pipeline添加一个ChannelInitializer */ p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() { @Override public void initChannel(final Channel ch) throws Exception { final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); ChannelHandler handler = config.handler(); if (handler != null) { pipeline.addLast(handler); } ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor( ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs)); } }); } });}这个方法主要完成2件事:
-
给
NioServerSocketChannel设置option、attr等; -
给
NioServerSocketChannel绑定的Pipeline添加一个ChannelInitializer,通过ChannelInitializer间接的向pipeline中添加一个用户指handler,还会添加一个对NioServerSocketChannel非常重要的handler:ServerBootstrapAcceptor连接器,客户端连接进来处理入口就是这个连接器。
顺便我们来看下通过pipeline.addLast()方式向 pipeline添加handler逻辑:
public
final ChannelPipeline addLast
(EventExecutorGroup group, String name, ChannelHandler handler) {
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx;
synchronized (this) { checkMultiplicity(handler); newCtx = newContext(group, filterName(name, handler), handler); addLast0(newCtx);
//当前Channel还未注册,需要先封装成PendingHandlerAddedTask,并链表方式挂载到Pipeline的pendingHandlerCallbackHead变量下,待后续注册完成后再回调
if (!registered) { newCtx.setAddPending(); callHandlerCallbackLater(newCtx,
true);
return this; }
//注册完成,且当前线程和Channel绑定线程不是同一个,则用Channel的绑定线程执行 EventExecutor executor = newCtx.executor();
if (!executor.inEventLoop()) { callHandlerAddedInEventLoop(newCtx, executor);
return this; } } callHandlerAdded0(newCtx);
return this;}
pipeline是一个双向链表,刚创建完成时默认有两个节点: head和tail,如下图:
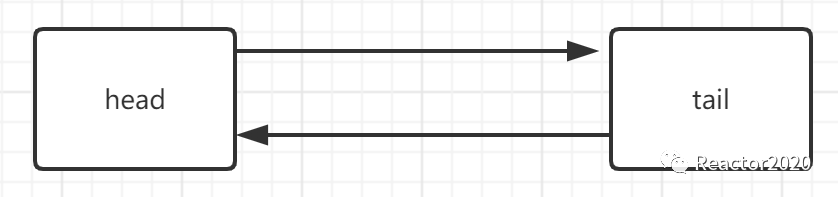
执行p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer())后是如下图:

如上面代码,pipeline不是直接将 handler添加进来,而是封装成 handlerContext。执行 addLast0(newCtx)将 handler对应的 HandlerContext添加进来后,正常情况下这时需要回调 handler#handlerAdded()方法。 handler#handlerAdded()执行是需要在
channel注册的 NioEventLoop线程中执行才行,所以有 if
(!executor.inEventLoop())这个判断。但是,当前是在主线程
main中,且 channel因为还没有注册完成,所以当前 channel和 NioEventLoop根本就还没有绑定到一起,所以是没法执行的,这里会进入 if
(!registered)流程:将
handlerContext封装成一个 PendingHandlerAddedTask实例,先挂载到 pipeline的 pendingHandlerCallbackHead全局变量下,待后续 channel注册完成后再来处理 handler#handlerAdded()。还有个问题,如果添加多个 handler,
PendingHandlerAddedTask有个 next,可以把它们串成一个链表即可。
register
这样,我们把 init()方法的主要逻辑基本都分析完成了,现在我们再回过头看下 initAndRegister方法中另外一个重要逻辑: config().group().register(channel)。这里的 config().group()就是获取的是之前传入的用于处理 server端线程组: EventLoopGroup
bossGroup
=
new
NioEventLoopGroup()。
NioEventLoopGroup#register()第一步就是使用 chooser选取一个其管理的 NioEventLoop,默认选取策略很简单,就是使用一个递增序列 idx,然后和数组长度取模即可:
executors[idx.getAndIncrement() & executors.length -
1]
选取好 NioEventLoop后,调用 NioEventLoop#register(channel)方法, NioEventLoop#register(channel)方法又会调用 channle的 Unsafe对象的 register进行处理,并把自己即 NioEventLoop作为参数传入:
promise.channel().unsafe().register(
this, promise);
Channel创建时同时创建一个UnSafe对象,主要用于处理与java底层socket相关操作。
所以, register()方法跑了一圈最后还是在 channel中的 Unsafe#register()方法中进行处理, NioEventLoopGroup只是利用 chooser选取一个 NioEventLoop作为参数传入到 register()方法中。
我们来看下 Unsafe#register()方法做了哪些事情。
1、后面这个 eventLoop就是将刚才利用 chooser选取的 NioEventLoop,通过赋值给 channel的 eventLoop字段上,即完成了 channel和 NioEventLoop的关联;
AbstractChannel.
this.eventLoop = eventLoop;
2、调用 register0()方法, register0()方法需要在 NioEventLoop线程中执行才行,所以这里也使用 if
(eventLoop.inEventLoop())判断下,当前是主线程
main,所以会进入到 else逻辑处理中,把执行逻辑封装成任务提交到 NioEventLoop的任务队列 taskQueue中:
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) { register0(promise);}
else {
try { eventLoop.execute(
new Runnable() {
@Override
public
void
run
() { register0(promise); } }); }
catch (Throwable t) { logger.warn(
"Force-closing a channel whose registration task was not accepted by an event loop: {}", AbstractChannel.
this, t); closeForcibly(); closeFuture.setClosed(); safeSetFailure(promise, t); }}
eventLoop.execute()方法中处理不只是简单将 task放入到 taskQueue中,我们来看下其还做了哪些事:
public
void
execute
(Runnable task) {
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop(); addTask(task);
if (!inEventLoop) { startThread();
if (isShutdown()) {
boolean reject =
false;
try {
if (removeTask(task)) { reject =
true; } }
catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) { }
if (reject) { reject(); } } }
if (!addTaskWakesUp && wakesUpForTask(task)) { wakeup(inEventLoop); }}
这个方法主要完成3件事:
-
addTask(task):将刚才对register0()调用封装的任务提交到taskQueue中,后续线程就从taskQueue提取任务进行执行; -
startThread():NioEventLoop是采用单线程模式管理注册上来的channel,startThread()方法就是启动这个线程,要开始干活了。在调用前有个判断if (!inEventLoop)判断是否当前线程就是NioEventLoop线程,如果都是当前线程了,肯定也就不需要启动了,这里inEventLoop是false执行启动。NioEventLoop线程启动后,核心逻辑就是在循环中不断重复三件事:事件轮询selector.select()、事件处理processSelectedKeys()和任务队列处理runAllTasks(),这里面涉及的逻辑也比较多,这节先暂时不展开,后续单独分析。 -
wakeup():唤醒NioEventLoop线程,NioEventLoop在启动后,重复执行三件事,其中selector.select(timeout)会有阻塞,这里执行wakeup()就是把NioEventLoop从select()阻塞中唤醒,这样才能及时处理提交到任务队列中的任务。
eventLoop.execute()分析完成后, register0()方法任务已被添加到taskQueue中,然后启动 NioEventLoop线程开始干活,最后通过wakeup()唤醒 NioEventLoop让其去处理taskQueue中的任务,所以,这时我们需要再回头看下 register0()方法。
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) { try { if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) { return; } boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered; doRegister(); neverRegistered = false; registered = true; pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded(); safeSetSuccess(promise); pipeline.fireChannelRegistered(); if (isActive()) {//这里实际返回false,channelActive()不会在这里触发 if (firstRegistration) { pipeline.fireChannelActive(); } else if (config().isAutoRead()) { beginRead(); } } } catch (Throwable t) { closeForcibly(); closeFuture.setClosed(); safeSetFailure(promise, t); }}这个方法主要完成3件事:
-
doRegister():这里会真正调用java api完成channel注册到selector上:javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this)。这里注意点如下: -
注册到的是
channel绑定的NioEventLoop里面的这个Selector上; -
千万注意:这里注册的
SelectionKey=0,表示当前只是channel注册到selector,但是还不会有任何事件被监听到,真正绑定OP_ACCEPT是在后续绑定端口时; -
最后一个参数把
this当成attachment添加进去,this就是server端NioServerSocketChannel这个实例,后续selector轮询到OP_ACCEPT事件后,可以直接将NioServerSocketChannel提取出来,然后执行accept()方法获取到客户端连接; -
pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded():之前分析过向pipeline添加handler时,由于channel还没有注册完成,所以现将handler封装成PendingHandlerAddedTask挂载到pipeline.pendingHandlerCallbackHead字段下,如果有多个即串成链表。因为这里channel已经注册完成,这里就是处理pendingHandlerCallbackHead,完成handler#handlerAdded()方法回调。注意:ChannelInitializer#handlerAdded()方法中会触发initChannel()方法调用,所以,这时用户handler和ServerBootstrapAcceptor才会被加入到pipeline中,添加完成后ChannelInitializer即完成了它的使用,会从pipeline中移除:
p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() { @Override public void initChannel(final Channel ch) throws Exception { final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); ChannelHandler handler = config.handler(); if (handler != null) { pipeline.addLast(handler); } ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor( ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs)); } }); }});-
pipeline.fireChannelRegistered():回调handler#channelRegistered()方法; -
最后尝试执行
pipeline.fireChannelActive()去激活channel,执行前有个判断:if (isActive()),只有当channel绑定到具体端口isActive()才会返回true,所以这里执行不到。
总结
分析到这里,doBind()方法中两个重要方法: initAndRegister()和doBind0()的第一个方法已全部分析完成, initAndRegister()还是完成了相当多的任务,其核心逻辑总结下:创建NioServerSocketChannel,然后进行各种配置初始化,最重要的一步是把 channel注册到NioEventLoop上,
NioEventLoop采用单线程模式轮询事件、处理事件。handler回调方法: handlerAdded()和channelRegistered()也会在上面执行过程中被触发调用。
长按识别关注, 持续输出原创
