Paging 适用于分页加载的情况,文档简介:逐步从数据源按需加载信息。使用时需要与RecyclerView结合,让开发者无需关心数据的分页逻辑,将数据的获取逻辑完全与UI隔离,让开发者可以很简单的实现一个效果不错的分页加载。
使用需添加依赖,
implementation "androidx.paging:paging-runtime:2.1.2"
一、Paging 的组件
简单介绍Paging 的各个组件,知道各个组件是干什么的,才能好好运行。
1、PagedList
Google设计了一个新的数据结构PagedList,就是分页列表数据的容器。
PagedList 是Paging Library的关键组件,它是一个异步加载应用程序数据块或页面的集合。
在使用时可以与LiveData 配合,使用LiveData 观察者的特性,在获得数据后回调onChanged 方法,如下,
LiveData<PagedList<Title>> titlesLivePaged = mViewModel.getStudentsLivePaged();
titlesLivePaged.observe(this, new Observer<PagedList<Title>>() {
@Override
public void onChanged(PagedList<Title> titles) {
mAdapter.submitList(titles);
}
});
通过PagedListAdapter 的submitList 方法,提交PagedList 。
2、DataSource.Factory
由其名字是数据源工厂,我们可以将获取数据的逻辑写在DataSource ,让然后通过DataSource.Factory 创建DataSource。
如果是从Room 获取数据,那写法会很简单,Room 会自动帮我们完成很多事情,
@Query("SELECT * FROM title_table ORDER BY id")
DataSource.Factory<Integer, Title> getAll();
我们通过查询语句查询表里的数据,然后返回值类型写成DataSource.Factory ,DataSource.Factory 的create 方法会创建DataSource 。
如果你要自己创建一个DataSource ,例如你想直接从网络获取数据,然后展示到界面上,那就需要自定义DataSource 了,这块放在下面描述。
3、LivePagedListBuilder
由上面可知,我们有了创建数据源的工厂(DataSource.Factory),新的数据结构(PagedList),那么是如何将两者配合使用的呢?就需要用到LivePagedListBuilder 了。
LivePagedListBuilder 的构造方法,
public LivePagedListBuilder(@NonNull DataSource.Factory<Key, Value> dataSourceFactory,
@NonNull PagedList.Config config) {
...
}
public LivePagedListBuilder(@NonNull DataSource.Factory<Key, Value> dataSourceFactory,
int pageSize) {
this(dataSourceFactory, new PagedList.Config.Builder().setPageSize(pageSize).build());
}
可以传递DataSource.Factory 与int ,那么会为我们构建一个以int 值为pageSize 的默认的PagedList.Config ,
也可以传递DataSource.Factory 与PagedList.Config ,更加灵活的对分页进行配置。
看一下LivePagedListBuilder 的build 方法,
@NonNull
@SuppressLint("RestrictedApi")
public LiveData<PagedList<Value>> build() {
return create(mInitialLoadKey, mConfig, mBoundaryCallback, mDataSourceFactory,
ArchTaskExecutor.getMainThreadExecutor(), mFetchExecutor);
}
可以看到该方法,返回值类型就是LiveData<PagedList<Value>> ,所以我们可以右如下写法,
return new LivePagedListBuilder<Integer, Title>(
TitleRepository.getInstance().getAll(), // 得到DataSource.Factory<Integer, Title>
new PagedList.Config.Builder()
.setPageSize(6)
.setPrefetchDistance(1)
.setEnablePlaceholders(false)
.setInitialLoadSizeHint(6)
.build()
).build();
获得了DataSource.Factory,工厂创建数据源DataSource,通过LivePagedListBuilder 的build 方法获得LiveData<PagedList<Value>>,还对分页加载进行了相关配置,例如指定pageSize 。
4、更多可选配置 PagedList.Config
PagedList.Config config = new PagedList.Config.Builder()
.setPageSize(15) // 分页加载的数量
.setInitialLoadSizeHint(30) // 初次加载的数量
.setPrefetchDistance(10) // 预取数据的距离
.setEnablePlaceholders(false) // 是否启用占位符
.build();
分页数量 PageSize ,每页加载数据的数量,
初始加载数量,InitialLoadSizeHint ,首次加载时要加载的Item数量,
此值通常大于PageSize,因此在初始化列表时,该配置可以使得加载的数据保证屏幕可以小范围的滚动。如果未设置,则默认为PageSize的三倍。
预取距离,PrefetchDistance , 该参数配置定义了列表当距离加载边缘多远时进行分页的请求,
是否启用占位符,PlaceholderEnabled ,该配置项需要传入一个boolean值以决定列表是否开启placeholder(占位符),
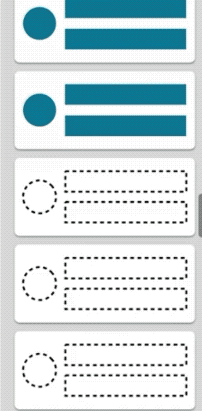
根据数据加载的情况,可能会看到还未渲染的条目,先展示占位符,随着PagedList下一页数据的异步加载完毕,伴随着RecyclerView的原生动画,新的数据会被重新覆盖渲染到placeholder对应的条目上。
5、PagedListAdapter
基于RecyclerView.Adapter 封装,PagedListAdapter 这个类还是很小的,因为相关的数据处理逻辑委托给了AsyncPagedListDiffer ,
当数据源发生改变时,实际上会通知 AsyncPagedListDiffer 的 submitList 方法,
AsyncPagedListDiffer 持有一个ListUpdateCallback ,通过其构造函数可知是AdapterListUpdateCallback,
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")
public AsyncPagedListDiffer(@NonNull RecyclerView.Adapter adapter,
@NonNull DiffUtil.ItemCallback<T> diffCallback) {
mUpdateCallback = new AdapterListUpdateCallback(adapter);
mConfig = new AsyncDifferConfig.Builder<>(diffCallback).build();
}
看一下AdapterListUpdateCallback 类,
/**
* ListUpdateCallback that dispatches update events to the given adapter.
*
* @see DiffUtil.DiffResult#dispatchUpdatesTo(RecyclerView.Adapter)
*/
public final class AdapterListUpdateCallback implements ListUpdateCallback {
@NonNull
private final RecyclerView.Adapter mAdapter;
/**
* Creates an AdapterListUpdateCallback that will dispatch update events to the given adapter.
*
* @param adapter The Adapter to send updates to.
*/
public AdapterListUpdateCallback(@NonNull RecyclerView.Adapter adapter) {
mAdapter = adapter;
}
/** {@inheritDoc} */
@Override
public void onInserted(int position, int count) {
mAdapter.notifyItemRangeInserted(position, count);
}
/** {@inheritDoc} */
@Override
public void onRemoved(int position, int count) {
mAdapter.notifyItemRangeRemoved(position, count);
}
/** {@inheritDoc} */
@Override
public void onMoved(int fromPosition, int toPosition) {
mAdapter.notifyItemMoved(fromPosition, toPosition);
}
/** {@inheritDoc} */
@Override
public void onChanged(int position, int count, Object payload) {
mAdapter.notifyItemRangeChanged(position, count, payload);
}
}
可见还是调用了RecyclerView.Adapter 的相应更新方法。
二、Paging 使用案例
先从简单的入手,然后扩展。
结合Room 实现一个简单的案例
“最小应用”,一个最基本的使用Paging 分页加载,从Room 获取数据的案例。
1、设置好我们的RecyclerView ,Paging 是要结合RecyclerView 的。
recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.paging_rv);
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(this, RecyclerView.VERTICAL, false));
mAdapter = new MyPagedAdapter();
recyclerView.setAdapter(mAdapter);
2、PagedListAdapter
public class MyPagedAdapter extends PagedListAdapter<Title, MyPagedAdapter.MyViewHolder> {
protected MyPagedAdapter() {
super(new DiffUtil.ItemCallback<Title>() {
@Override
public boolean areItemsTheSame(@NonNull Title oldItem, @NonNull Title newItem) {
return oldItem.getId() == newItem.getId();
}
@Override
public boolean areContentsTheSame(@NonNull Title oldItem, @NonNull Title newItem) {
return oldItem.getNum() == newItem.getNum();
}
});
}
@NonNull
@Override
public MyViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext());
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.paged_item, parent, false);
return new MyViewHolder(view);
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull MyViewHolder holder, int position) {
Title student = getItem(position);
if (student != null) {
holder.textView.setText(String.valueOf(student.getNum()));
}
}
static class MyViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
TextView textView;
public MyViewHolder(@NonNull View itemView) {
super(itemView);
textView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.text_paged);
}
}
}
实现onCreateViewHolder 与onBindViewHolder ,写法与之前的差不多,不同的是需要在构造函数中,向父类传入,DiffUtil.ItemCallback<T> ,用来比较是否相同,这里比较的id 与num ,都相同则代表数据是没有变的,这个比较标准需要你来指定。
3、构建PagedList ,
@Dao
public interface TitleDao {
@Query("SELECT * FROM title_table ORDER BY id")
DataSource.Factory<Integer, Title> getAll();
...
}
public class TitleRepository {
...
public DataSource.Factory<Integer, Title> getAll() {
return titleDao.getAll();
}
}
用上面提到的LivePagedListBuilder 把数据源的数据,构建成LiveData<PagedList<Title>> 类型。
public LiveData<PagedList<Title>> getStudentsLivePaged() {
return new LivePagedListBuilder<Integer, Title>(
TitleRepository.getInstance().getAll(), // 得到DataSource.Factory<Integer, Title>
new PagedList.Config.Builder()
.setPageSize(6)
.setPrefetchDistance(1)
.setEnablePlaceholders(false)
.setInitialLoadSizeHint(12)
.build()
).setBoundaryCallback(boundaryCallback)
.build();
}
4、通过PagedListAdapter 的submitList 方法对PagedList 进行提交。
titlesLivePaged = mViewModel.getStudentsLivePaged();
titlesLivePaged.observe(this, new Observer<PagedList<Title>>() {
@Override
public void onChanged(PagedList<Title> titles) {
mAdapter.submitList(titles);
}
});
这样就可以将数据库里的数据分页展示出来,根据我们的设置,开始先加载12 项,之后一页6 项的加载。
自定义DataSource
之前是用了Room 的便捷性自动为我们创建了相关DataSource ,但学会了自定义DataSource 才能更好的理解Paging 。
Paging库里提供了DataSource 的三个子类,根据不同场景选择使用,
PageKeyedDataSource<Key, Value> ,适用于目标数据根据页信息请求数据的场景,
即Key 字段是页相关的信息。比如请求的数据的参数包含类似next/previous页数的信息。
ItemKeyedDataSource<Key, Value> ,适用于目标数据的加载依赖特定item 的信息,
即Key字段包含的是Item 里的信息,比如需要根据第N项的信息加载第N+1项的数据,
传参需要传入第N项的ID 。
PositionalDataSource<T> ,适用于目标数据总数固定,通过特定的位置加载数据,
这里Key是Integer类型的位置信息,T即Value。比如从数据库中的1200条开始加在20条数据。
理论上,任选其一大多数情况下都能实现出来的,只是在某些情况更适合哪个的问题了。
这里选用了PositionalDataSource ,
public class CustomDataSource extends PositionalDataSource<Blog> {
@Override
public void loadInitial(@NonNull LoadInitialParams params, @NonNull LoadInitialCallback<Blog> callback) {
int pageSize = params.requestedLoadSize; //首次加载的数据条数
int offset = 0; // 请求的数据的偏移位置
int position = computeInitialLoadPosition(params, pageSize);
callback.onResult(DataUtil.httpRequest(pageSize, offset), position);
}
@Override
public void loadRange(@NonNull LoadRangeParams params, @NonNull LoadRangeCallback<Blog> callback) {
int pageSize = params.loadSize;
int offset = params.startPosition;
callback.onResult(DataUtil.httpRequest(pageSize, offset));
}
}
这里继承PositionalDataSource ,需要实现两个方法loadInitial 与loadRange ,由名字可知,一个是首次加载,一个是滑动加载下一页,根据具体情况,自行计算,每一页的大小pageSize 与初始偏移位置offset ,当然这些需要视接口情况而定啦。
loadInitial 方法里的position 是将获得的数据插入到列表的什么位置。
前面我们知道DataSource.Factory 创建DataSource ,那么来实现一下,这个还是相当简单的,
public class CustomDataSourceFactory extends DataSource.Factory<Integer, Blog> {
@NonNull
@Override
public DataSource<Integer, Blog> create() {
return new CustomDataSource();
}
}
继承DataSource.Factory 实现create 方法,返回自定义的DataSource 实例即可。
return new LivePagedListBuilder<Integer, Blog>(
new CustomDataSourceFactory(),
new PagedList.Config.Builder()
.setPageSize(6)
.setPrefetchDistance(1)
.setEnablePlaceholders(false)
.setInitialLoadSizeHint(6)
.build()
).build();
这样使用就可以啦。
Paging 数据加载与展示
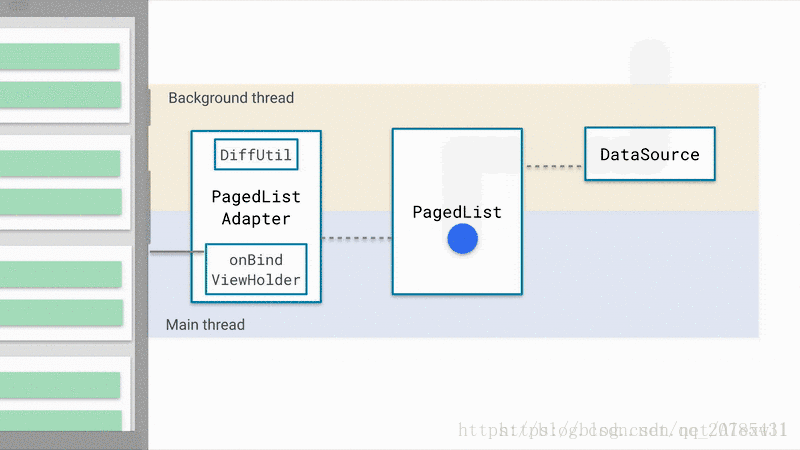
跟进Paging 源码,走了一下流程,感受一下Paging 的工作流程,这样还是有助于理解Paging 的,这里做一下笔记。
LiveData 的observe 方法
titlesLivePaged.observe(this, new Observer<PagedList<Title>>() {
@Override
public void onChanged(PagedList<Title> titles) {
mAdapter.submitList(titles);
}
});
我们这样设置观察者,来看看做了哪些事情吧,
@MainThread
public void observe(@NonNull LifecycleOwner owner, @NonNull Observer<? super T> observer) {
...
LifecycleBoundObserver wrapper = new LifecycleBoundObserver(owner, observer);
...
owner.getLifecycle().addObserver(wrapper);
}
getLifecycle得到的是什么呢?不妨看一下LifecycleOwner 的一个实现类ComponentActivity ,看看它的getLifecycle 方法,发现是LifecycleRegistry类,跟进它的addObserver 方法,
@Override
public void addObserver(@NonNull LifecycleObserver observer) {
...
ObserverWithState statefulObserver = new ObserverWithState(observer, initialState);
...
statefulObserver.dispatchEvent(lifecycleOwner, upEvent(statefulObserver.mState));
...
}
添加观察者的时候,这个dispatchEvent 方法会调用一次,
void dispatchEvent(LifecycleOwner owner, Event event) {
State newState = getStateAfter(event);
mState = min(mState, newState);
mLifecycleObserver.onStateChanged(owner, event);
mState = newState;
}
最终会调用LifecycleBoundObserver的的onStateChanged方法,
@Override
public void onStateChanged(@NonNull LifecycleOwner source,
@NonNull Lifecycle.Event event) {
if (mOwner.getLifecycle().getCurrentState() == DESTROYED) {
removeObserver(mObserver);
return;
}
activeStateChanged(shouldBeActive());
}
跟进activeStateChanged 方法,
void activeStateChanged(boolean newActive) {
...
if (wasInactive && mActive) {
onActive();
}
if (LiveData.this.mActiveCount == 0 && !mActive) {
onInactive();
}
if (mActive) {
dispatchingValue(this);
}
}
第一次调用的时候会满足条件,然后就调用到LiveData 的onActive 方法,
所以,在调用observe 为LiveData 设置观察者,会调用到LiveData 的onActive 方法。
创建LiveData<PagedList<Value>>
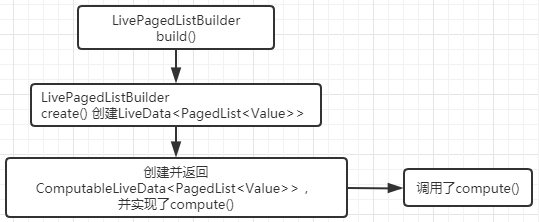
public LiveData<PagedList<Value>> build() {
return create(mInitialLoadKey, mConfig, mBoundaryCallback, mDataSourceFactory,
ArchTaskExecutor.getMainThreadExecutor(), mFetchExecutor);
}
LivePagedListBuilder 的create() ,
@AnyThread
@NonNull
@SuppressLint("RestrictedApi")
private static <Key, Value> LiveData<PagedList<Value>> create(
@Nullable final Key initialLoadKey,
@NonNull final PagedList.Config config,
@Nullable final PagedList.BoundaryCallback boundaryCallback,
@NonNull final DataSource.Factory<Key, Value> dataSourceFactory,
@NonNull final Executor notifyExecutor,
@NonNull final Executor fetchExecutor) {
return new ComputableLiveData<PagedList<Value>>(fetchExecutor) {
@Nullable
private PagedList<Value> mList;
@Nullable
private DataSource<Key, Value> mDataSource;
private final DataSource.InvalidatedCallback mCallback =
new DataSource.InvalidatedCallback() {
@Override
public void onInvalidated() {
invalidate();
}
};
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") // for casting getLastKey to Key
@Override
protected PagedList<Value> compute() {
@Nullable Key initializeKey = initialLoadKey;
if (mList != null) {
initializeKey = (Key) mList.getLastKey();
}
do {
if (mDataSource != null) {
mDataSource.removeInvalidatedCallback(mCallback);
}
mDataSource = dataSourceFactory.create();
mDataSource.addInvalidatedCallback(mCallback);
mList = new PagedList.Builder<>(mDataSource, config)
.setNotifyExecutor(notifyExecutor)
.setFetchExecutor(fetchExecutor)
.setBoundaryCallback(boundaryCallback)
.setInitialKey(initializeKey)
.build();
} while (mList.isDetached());
return mList;
}
}.getLiveData();
}
从这个create 方法可见,该方法是先创建了一个ComputableLiveData 对象,实现了其compute 方法,在compute 方法创建了PagedList<Value> ,最后调用其getLiveData() 返回LiveData 对象。
ComputableLiveData 的compute 方法创建了PagedList ,那么这个compute 方法什么时候调用的呢?
ComputableLiveData 构造函数,
public ComputableLiveData(@NonNull Executor executor) {
mExecutor = executor;
mLiveData = new LiveData<T>() {
@Override
protected void onActive() {
mExecutor.execute(mRefreshRunnable);
}
};
}
创建了LiveData ,在我们调用observe 方法,会执行onActive 方法,那么便会执行这个mRefreshRunnable ,而且还是在子线程(executor 是fetchExecutor),看一下mRefreshRunnable ,
@VisibleForTesting
final Runnable mRefreshRunnable = new Runnable() {
@WorkerThread
@Override
public void run() {
...
T value = null;
while (mInvalid.compareAndSet(true, false)) {
computed = true;
value = compute();
}
if (computed) {
mLiveData.postValue(value);
}
...
}
};
这里主要看一下,在mRefreshRunnable 的run 方法,调用了compute() ,而这个value 自然就是生成的PagedList<Value> ,执行mLiveData.postValue(value); 这样会在主线程回调LiveData 的onChanged 方法,我们也就可以获得PagedList ,提交给PagedListAdapter 了。
DataSource 的数据填充到PagedList
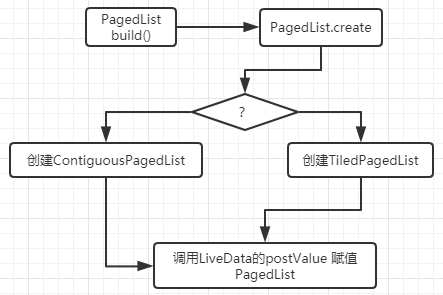
@NonNull
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess") /* synthetic access */
static <K, T> PagedList<T> create(@NonNull DataSource<K, T> dataSource,
@NonNull Executor notifyExecutor,
@NonNull Executor fetchExecutor,
@Nullable BoundaryCallback<T> boundaryCallback,
@NonNull Config config,
@Nullable K key) {
if (dataSource.isContiguous() || !config.enablePlaceholders) {
int lastLoad = ContiguousPagedList.LAST_LOAD_UNSPECIFIED;
if (!dataSource.isContiguous()) {
//noinspection unchecked
dataSource = (DataSource<K, T>) ((PositionalDataSource<T>) dataSource)
.wrapAsContiguousWithoutPlaceholders();
if (key != null) {
lastLoad = (Integer) key;
}
}
ContiguousDataSource<K, T> contigDataSource = (ContiguousDataSource<K, T>) dataSource;
return new ContiguousPagedList<>(contigDataSource,
notifyExecutor,
fetchExecutor,
boundaryCallback,
config,
key,
lastLoad);
} else {
return new TiledPagedList<>((PositionalDataSource<T>) dataSource,
notifyExecutor,
fetchExecutor,
boundaryCallback,
config,
(key != null) ? (Integer) key : 0);
}
}
根据DataSource 的连续性与config.enablePlaceholders ,决定去创建ContiguousPagedList ,还是 TiledPagedList ,这里如果是使用的PageKeyedDataSource 的话,那么将会创建的是ContiguousPagedList ,看一下使用PageKeyedDataSource 的情况,
ContiguousPagedList(
@NonNull ContiguousDataSource<K, V> dataSource,
@NonNull Executor mainThreadExecutor,
@NonNull Executor backgroundThreadExecutor,
@Nullable BoundaryCallback<V> boundaryCallback,
@NonNull Config config,
final @Nullable K key,
int lastLoad) {
super(new PagedStorage<V>(), mainThreadExecutor, backgroundThreadExecutor,
boundaryCallback, config);
mDataSource = dataSource;
mLastLoad = lastLoad;
...
mDataSource.dispatchLoadInitial(key,
mConfig.initialLoadSizeHint,
mConfig.pageSize,
mConfig.enablePlaceholders,
mMainThreadExecutor,
mReceiver);
}
跟进一下dispatchLoadInitial 方法,我们看的是使用的PageKeyedDataSource 的情况,
@Override
final void dispatchLoadInitial(@Nullable Key key, int initialLoadSize, int pageSize,
boolean enablePlaceholders, @NonNull Executor mainThreadExecutor,
@NonNull PageResult.Receiver<Value> receiver) {
LoadInitialCallbackImpl<Key, Value> callback =
new LoadInitialCallbackImpl<>(this, enablePlaceholders, receiver);
loadInitial(new LoadInitialParams<Key>(initialLoadSize, enablePlaceholders), callback);
// If initialLoad's callback is not called within the body, we force any following calls
// to post to the UI thread. This constructor may be run on a background thread, but
// after constructor, mutation must happen on UI thread.
callback.mCallbackHelper.setPostExecutor(mainThreadExecutor);
}
这里的loadInitial 方法,就是我们在自定义PageKeyedDataSource 的时候,实现的初次加载的方法,将首次加载数据的逻辑写在了该方法,
@Override
public void loadInitial(@NonNull LoadInitialParams<Integer> params, @NonNull LoadInitialCallback<Integer, Shoe> callback) {
...
List<Shoe> shoes = mShoeRepository.getPageShoes(startIndex, endIndex);
callback.onResult(shoes, null, nextKey);
}
而且还会调用到callback 的 onResult 方法,这个callback 就是LoadInitialCallbackImpl ,
@Override
public void onResult(@NonNull List<Value> data, @Nullable Key previousPageKey,
@Nullable Key nextPageKey) {
...
mCallbackHelper.dispatchResultToReceiver(new PageResult<>(data, 0, 0, 0));
}
跟进,
void dispatchResultToReceiver(final @NonNull PageResult<T> result) {
...
mReceiver.onPageResult(mResultType, result);
}
这个mReceiver 是ContiguousPagedList 的 mReceiver (我们看的是PageKeyedDataSource 这种情况)
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess") /* synthetic access */
PageResult.Receiver<V> mReceiver = new PageResult.Receiver<V>() {
// Creation thread for initial synchronous load, otherwise main thread
// Safe to access main thread only state - no other thread has reference during construction
@AnyThread
@Override
public void onPageResult(@PageResult.ResultType int resultType,
@NonNull PageResult<V> pageResult) {
...
List<V> page = pageResult.page;
if (resultType == PageResult.INIT) {
mStorage.init(pageResult.leadingNulls, page, pageResult.trailingNulls,
pageResult.positionOffset, ContiguousPagedList.this);
if (mLastLoad == LAST_LOAD_UNSPECIFIED) {
// Because the ContiguousPagedList wasn't initialized with a last load position,
// initialize it to the middle of the initial load
mLastLoad =
pageResult.leadingNulls + pageResult.positionOffset + page.size() / 2;
}
} else {
...
}
...
}
};
显然第一次是PageResult.INIT ,将数据保存到PagedList 的一个PagedStorage 类型的的成员变量mStorage 里,这样DataSource 得到的数据就填充到了PagedList ,
PagedList 创建完在ComputableLiveData 的compute 方法返回,有调用了mLiveData.postValue(value); ,所以会回调到Observer 的onChanged 方法。
加载更多
PagedListAdapter 的getItem 方法,
@Nullable
protected T getItem(int position) {
return mDiffer.getItem(position);
}
跟进,
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")
@Nullable
public T getItem(int index) {
if (mPagedList == null) {
if (mSnapshot == null) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
"Item count is zero, getItem() call is invalid");
} else {
return mSnapshot.get(index);
}
}
mPagedList.loadAround(index);
return mPagedList.get(index);
}
在返回数据之前调用了PagedList 的 loadAround 方法,
public void loadAround(int index) {
...
mLastLoad = index + getPositionOffset();
loadAroundInternal(index);
...
}
考虑使用PageKeyedDataSource 的话,最终会调用到,
@MainThread
@Override
protected void loadAroundInternal(int index) {
int prependItems = getPrependItemsRequested(mConfig.prefetchDistance, index,
mStorage.getLeadingNullCount());
int appendItems = getAppendItemsRequested(mConfig.prefetchDistance, index,
mStorage.getLeadingNullCount() + mStorage.getStorageCount());
mPrependItemsRequested = Math.max(prependItems, mPrependItemsRequested);
if (mPrependItemsRequested > 0 && mLoadStateManager.getStart() == LoadState.IDLE) {
schedulePrepend();
}
mAppendItemsRequested = Math.max(appendItems, mAppendItemsRequested);
if (mAppendItemsRequested > 0 && mLoadStateManager.getEnd() == LoadState.IDLE) {
scheduleAppend();
}
}
根据prefetchDistance 与 index 来调用schedulePrepend() 或 scheduleAppend() 哦,上拉加载更多调用的是scheduleAppend() ,
@MainThread
private void scheduleAppend() {
...
mBackgroundThreadExecutor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
...
if (mDataSource.isInvalid()) {
detach();
} else {
mDataSource.dispatchLoadAfter(position, item, mConfig.pageSize,
mMainThreadExecutor, mReceiver);
}
}
});
}
在子线程调用了dispatchLoadAfter 方法,对应就是,PageKeyedDataSource 的dispatchLoadAfter 方法,
@Override
final void dispatchLoadAfter(int currentEndIndex, @NonNull Value currentEndItem,
int pageSize, @NonNull Executor mainThreadExecutor,
@NonNull PageResult.Receiver<Value> receiver) {
@Nullable Key key = getNextKey();
if (key != null) {
loadAfter(new LoadParams<>(key, pageSize),
new LoadCallbackImpl<>(this, PageResult.APPEND, mainThreadExecutor, receiver));
} else {
receiver.onPageResult(PageResult.APPEND, PageResult.<Value>getEmptyResult());
}
}
loadAfter 方法,就是自定义PageKeyedDataSource 时,实现的方法,实现了加载更多数据的逻辑。