Watcher
Watcher类的实现比较复杂,因为他的实例分为渲染 watcher(render-watcher)、计算属性 watcher(computed-watcher)、侦听器 watcher(normal-watcher)三种,这三个实例分别是在三个函数中构建的:mountComponent 、initComputed 和 Vue.prototype.$watch。
-
normal-watcher:我们在组件钩子函数watch 中定义的,都属于这种类型,即只要监听的属性改变了,都会触发定义好的回调函数,这类watch的expression是我们写的回调函数的字符串形式。
-
computed-watcher:我们在组件钩子函数computed中定义的,都属于这种类型,每一个 computed 属性,最后都会生成一个对应的 watcher 对象,但是这类 watcher 有个特点:当计算属性依赖于其他数据时,属性并不会立即重新计算,只有之后其他地方需要读取属性的时候,它才会真正计算,即具备 lazy(懒计算)特性。这类watch的expression是计算属性中的属性名。
-
render-watcher:每一个组件都会有一个 render-watcher, 当 data/computed 中的属性改变的时候,会调用该 render-watcher 来更新组件的视图。这类watch的expression是 function () {vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating);}。
除了功能上的区别,这三种 watcher 也有固定的执行顺序
computed-render -> normal-watcher -> render-watcher。
这样安排是有原因的,这样就能尽可能的保证,在更新组件视图的时候,computed 属性已经是最新值了,如果 render-watcher 排在 computed-render 前面,就会导致页面更新的时候 computed 值为旧数据。
render-watcher
render-watcher 在构造新的Watcher对象传了当前vue实例、updateComponent函数、空函数这三个参数。
src/core/instance/lifecycle.js
export function mountComponent (
vm: Component, // 组件实例vm
el: ?Element, // 挂载点
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
...
updateComponent = () => {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
}
...
// 会在new Watcher的时候通过get方法执行一次
// 也就是会触发第一次Dom的更新
vm._watcher = new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop)
...
return vm
}
computed-watcher
computed-watcher在构造新的Watcher对象传了当前vue实例、computed.getter || 空函数、空函数、{ lazy: true } 四个参数。
src/core/instance/state.js
const computedWatcherOptions = { lazy: true }
function initComputed (vm: Component, computed: Object) {
const watchers = vm._computedWatchers = Object.create(null)
...
for (const key in computed) {
const userDef = computed[key]
const getter = typeof userDef === 'function' ? userDef : userDef.get
...
// 为computed创建watcher
watchers[key] = new Watcher(
vm,
getter || noop,
noop,
computedWatcherOptions
)
...
}
...
}
normal-watcher
src/core/instance/state.js
Vue.prototype.$watch = function (
expOrFn: string | Function,
cb: any,
options?: Object
): Function {
const vm: Component = this
...
// options的设置见:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/#watch
options = options || {}
options.user = true
// expOrFn是监听的key,cb是监听的回调,options是监听的所有选项
const watcher = new Watcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options)
// 如果设置immediate: true 将立即以表达式的当前值触发回调
// https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/#vm-watch
if (options.immediate) {
cb.call(vm, watcher.value)
}
// 返回unWatch的方法
return function unwatchFn () {
watcher.teardown()
}
}
Watcher
src/core/observer/watcher.js
export default class Watcher {
constructor(vm: Component, expOrFn: string | Function, cb: Function, options?: Object) {
this.vm = vm
vm._watchers.push(this)
// options
if (options) {
this.deep = !!options.deep // 是否启用深度监听
this.user = !!options.user // 主要用于错误处理,用于侦听器option.watch时 user为true,其他基本为false
this.lazy = !!options.lazy // 惰性求值,当属于计算属性option.computed时为true
this.sync = !!options.sync // 标记为同步计算
} else {
this.deep = this.user = this.lazy = this.sync = false
}
// 回调,多用于侦听器option.watch,其他大部分为空函数
this.cb = cb
this.id = ++uid // uid for batching
this.active = true
this.dirty = this.lazy // for lazy watchers
this.deps = []
this.newDeps = []
this.depIds = new Set()
this.newDepIds = new Set()
this.expression = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'
? expOrFn.toString()
: ''
if (typeof expOrFn === 'function') {
this.getter = expOrFn
} else {
this.getter = parsePath(expOrFn)
if (!this.getter) {
this.getter = function () { }
}
}
this.value = this.lazy
? undefined
: this.get()
}
...
get () { ... }
addDep () { ... }
cleanupDeps () { ... }
update () { ... }
run () { ... }
evaluate () { ... }
depend () { ... }
teardown () { ... }
}
这里着重看一下expOrFn和cb参数
- 当用于
render-watcher时,expOrFn是updateComponent,cb为空函数 - 当用于
computed-watcher时,expOrFn是计算属性的计算方法,cb为computed.get或 空函数 - 当用于
normal-watcher时,expOrFn是watch属性的名字,cb为watch.handler属性
- 对于渲染watcher和计算watcher来说,expOrFn的值是一个函数,可以直接设置getter
- 对于侦听器option.watch来说,expOrFn是watch属性的名字,会使用parsePath函数解析路径,获取组件上该属性的值(运行getter)
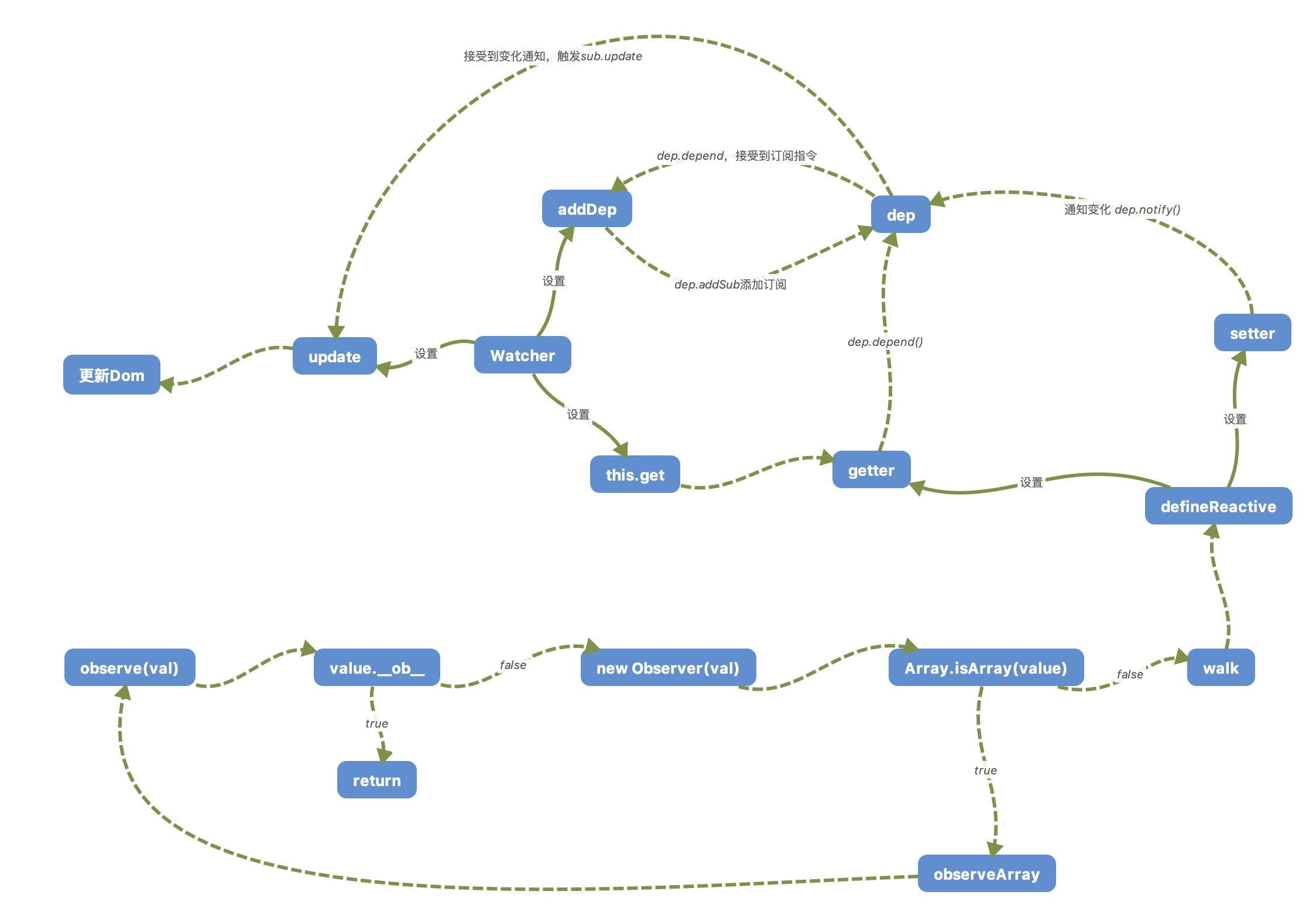
依赖(订阅目标)更新,执行update,会进行取值操作,运行watcher.getter,也就是expOrFn函数
constructor最后,会调用this.get --> this.getter,来获取当前的value。并通过判断this.deep,来调用traverse,对一个对象做深层递归遍历,而遍历过程中就是对一个子对象的访问,会触发它们的 getter ,这样就可以收集到依赖,也就是订阅它们变化的 watcher。
...
get () {
// 将Dep的target添加到targetStack,同时Dep的target赋值为当前watcher对象
pushTarget(this)
let value
const vm = this.vm
...
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
...
if (this.deep) {
traverse(value)
}
...
// update执行完成后,又将Dep.target从targetStack弹出。
popTarget()
this.cleanupDeps()
...
return value
}
...
如果数据被重新赋值了, 调用 Dep 的 notify 方法, 遍历dep.subs, 通知所有的 Watcher,并调用watcher.update,来更新数据。update中,根据不同情况来调用watcher.run来对数据进行更新操作,并在run中执行this.cb,将更新前后当值返回。
// 当一个依赖改变的时候,通知它update
update () {
/* istanbul ignore else */
// 只有计算属性 watcher的lazy设置了true,表示启用惰性求值
if (this.lazy) {
this.dirty = true
} else if (this.sync) {
this.run()
} else {
// 将watcher推入观察者队列中,下一个tick时调用。
// 也就是数据变化不是立即就去更新的,而是异步批量去更新的
// 最终调用 watcher.run 来执行更新操作
queueWatcher(this)
}
}
run () {
if (this.active) {
const value = this.get()
if (
value !== this.value ||
// Deep watchers and watchers on Object/Arrays should fire even
// when the value is the same, because the value may
// have mutated.
isObject(value) ||
this.deep
) {
// set new value
const oldValue = this.value
this.value = value
...
// 运行 cb 函数,这个函数就是之前传入的watch中的handler回调函数
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue)
...
}
}
}
}
vue数据相应中,Dep起到了一个桥梁的作用,用来连接Observer和Watcher。当getter执行当时候,会调用dep.depend(),其中,Dep.target则指向当前active当Watcher,并调用Dep.target.addDep,即watcher.addDep方法,将闭包中当dep添加到watcher.deps列表中,并在addDep中调用dep.addSub,将当前当watcher添加到dep.subs列表中。当setter执行当时候,会遍历dep.subs列表,依次执行watcher.update,来进行更新操作。
addDep (dep: Dep) {
const id = dep.id
if (!this.newDepIds.has(id)) {
this.newDepIds.add(id)
this.newDeps.push(dep)
if (!this.depIds.has(id)) {
dep.addSub(this)
}
}
}
// 把 newDepIds 的值赋给 depIds,然后把 newDepIds 清空。
cleanupDeps () {
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
const dep = this.deps[i]
if (!this.newDepIds.has(dep.id)) {
dep.removeSub(this)
}
}
let tmp = this.depIds
this.depIds = this.newDepIds
this.newDepIds = tmp
this.newDepIds.clear()
tmp = this.deps
this.deps = this.newDeps
this.newDeps = tmp
this.newDeps.length = 0
}
/**
* 对于计算属性,当取值计算属性时,发现计算属性的watcher的dirty是true
* 说明数据不是最新的了,需要重新计算,这里就是重新计算计算属性的值。
*/
evaluate () {
this.value = this.get()
this.dirty = false
}
/**
* 收集依赖
* 见 src/core/instance/state.js 中的 createComputedGetter
*/
depend () {
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].depend()
}
}
/**
* 取消订阅,清空dep.subs
* 见
* src/core/instance/lifecycle.js 中的 Vue.prototype.$destroy
* src/core/instance/state.js 中的 Vue.prototype.$watch
*/
teardown () {
if (this.active) {
// remove self from vm's watcher list
// this is a somewhat expensive operation so we skip it
// if the vm is being destroyed.
if (!this.vm._isBeingDestroyed) {
remove(this.vm._watchers, this)
}
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
this.deps[i].removeSub(this)
}
this.active = false
}
}
捋一下响应式的调用关系