1、数据结构
- 数组
- 数组可以分为队列、栈等
- 哈希表
- 用来存储 key-value 对
2、队列Queue
- 特点: 先进先出 的数组
- 进入:push(),出:shift()
- 代码:(吃饭叫号)
- 选择queue作为数据结构
- queue.push 为入队,queue.shift 为出队
题目: 请实现一个餐厅叫号网页
- 点击「取号」按钮生成一个号码
- 点击「叫号」按钮显示请X号就餐
手写队列Queue
- 首先选择队列Queue作为数据结构
- queue.push()为入队,queue.shift()为出队
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./style.css" />
</head>
<style>
#screen {
border: 1px solid black;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="screen"></div>
<div class="actions">
<button id="createNumber">取号</button>
<button id="callNumber">叫号</button>
</div>
<div>当前号码 <span id="newNumber"></span></div>
<div>当前队列 <span id="queue"></span></div>
<script src="./main.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
const divScreen = document.querySelector("#screen");
const btnCreateNumber = document.querySelector("#createNumber");
const btnCallNumber = document.querySelector("#callNumber");
const spanNewNumber = document.querySelector("#newNumber");
const spanQueue = document.querySelector("#queue");
let n = 0;
let queue = [];
btnCreateNumber.onclick = () => {
n += 1;
queue.push.call(queue, n); //queue.push(n)
spanNewNumber.innerHTML = n;
spanQueue.innerHTML = JSON.stringify(queue);
};
btnCallNumber.onclick = () => {
if (queue.length === 0) {
divScreen.innerText = "没有客人了";
return;
}
const m = queue.shift.call(queue); //const m = queue.shift()
divScreen.innerHTML = `请 ${m} 号就餐`;
spanQueue.innerHTML = JSON.stringify(queue);
};
3、栈Stack
- 特点:后进先出 的数组
- 压栈:push(),弹栈:pop()
- JS函数的调用栈 call stack 就是一个栈
- 假设 f1 调用了 f2,f2 又调用了 f3
- 那么 f3 结束后应该回到 f2,f2 结束后应该回到 f1
4、链表 Linked List
const createList = (value) => {
return {
data: value,
next: null,
};
};
const appendList = (list, value) => {
const node = {
data: value,
next: null,
};
let x = list;
while (x.next) {
x = x.next;
}
//x.next ===null //x是最后一个节点
x.next = node;
return node;
};
const removeFromList = (list, node) => {
let x = list;
let p = null;
while (x !== node) {
p = x;
x = x.next;
}
p.next = x.next;
};
<!-- 删除节点的整体思路 -->
<!--const removeFromList = (list, node)=>{-->
<!-- // 遍历-->
<!-- if(list === node){-->
<!-- // 如果删除的是第1个节点-->
<!-- list = node.next-->
<!-- // 第一个节点 自动被回收-->
<!-- }else{-->
<!-- // 如果删除的是第2个节点-->
<!-- // 就让第1个节点.next = 第2个节点.next-->
<!-- if(list.next === node){-->
<!-- list.next = node.next-->
<!-- // 第2个节点 自动被回收-->
<!-- }else{-->
<!-- // 开始递归了-->
<!-- // 如果删除的是第3个节点-->
<!-- // 就让第2个节点.next = 第3个节点.next-->
<!-- if(list.next.next === node){-->
<!-- (list.next).next = node.next-->
<!-- }-->
<!-- }-->
<!-- }-->
<!--}-->
const travelList = (list, fn) => {
let x = list;
while (x !== null) {
fn(x);
x = x.next;
}
};
const list = createList(10);
const node2 = appendList(list, 20);
console.log(node2);
const node3 = appendList(list, 30);
const node4 = appendList(list, 40);
const node5 = appendList(list, 50);
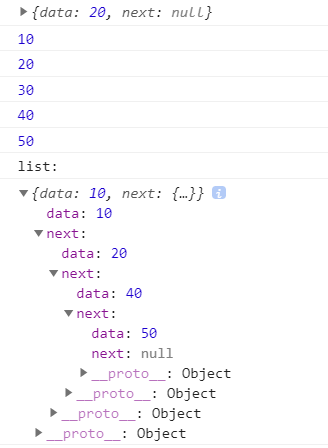
travelList(list, (node) => {
console.log(node.data);
});
const node = list;
removeFromList(list, node3);
console.log("list:");
console.log(list);
输出:
const list = createList(10);
const node = list // node 就是 list 的第一个节点
removeFromList(list, node) // list 没有任何变化
const newList = removeFromList(list, node) // 就算获取返回值也没有用,因为根本就没返回新 list
正确的实现方法为:
const removeFromList = (list, node) => {
let x = list;
let p = node; // 课堂里将 p 初始化为 null,这里改为 node
while (x !== node && x !== null) { // 课堂里忘了对 null 进行处理,如果 node 不在 list 中,x 就可能为 null
p = x;
x = x.next;
}
if(x === null){ // 若 x 为 null,则不需要删除,直接 return, false 表示无法删除不在list里的节点
return false
}else if(x === p){ // 这说明要删除的节点是第一个节点
p = x.next
return p // 如果删除的是第一个节点,那么就要把新 list 的头节点 p 返回给外面,即 newList = removeFromList(list, list)
}else{
p.next = x.next;
return list // 如果删除的不是第一个节点,返回原来的 list 即可
}
};
const list = createList(10);
const node = list // node 就是 list 的第一个节点了现在
const newList = removeFromList(list, node) // 必须用 newList 获取返回值才能拿到删除了第一个节点的新 list
- 链表
- 双向链表:每个节点有一个 previous 指向上一个节点
- 循环链表:最后一个节点的 next 指向头节点
5、哈希表 hashTable
- 场景
- 假设哈希表 hash 里有一万对 key-value
- 比如 name: 'wbh' , age: 18 ,p1: 'property1' .....
- 如何使得读取 hash['xxx'] 速度最快
- 解决办法
- 不做任何优化,hash['xxx'] 需要遍历所有 key , 算数复杂度为 O(n)
- 对 key 排序,使用二分查找, 复杂度为 O(log2n)
- 用字符串对应的 ASCII 数字做索引, 对索引做除法取余数,O(1),冲突了怎么办,冲突了就顺延
6、树Tree(一个链多个)
- 实际使用
- 中国的省市区,可以看成一棵树
- 公司的层级结构,可以看成一棵树
- 网页中的节点,可以看成一棵树
let createTree = (value) => {
return {
data: value,
children: null,
parent: null,
};
};
const addChild = (node, value) => {
const newNode = {
data: value,
children: null,
parent: node,
};
node.children = node.children || []; //node.children 不为空,则等于自身,为空就是一个空数组[]
node.children.push(newNode);
return newNode;
};
const travel = (tree, fn) => {
fn(tree);
if (!tree.children) {
//如果children为空,直接返回
return false;
}
for (let i = 0; i < tree.children.length; i++) {
travel(tree.children[i], fn);
}
};
const removeNode = (tree, node) => {
const siblings = node.parent.children;
let index = 0;
for (let i = 1; i < siblings.length; i++) {
if (node === siblings[i]) {
index = i;
}
}
siblings.splice(index, 1);
};
const tree = createTree(10);
const node2 = addChild(tree, 20);
const node3 = addChild(tree, 30);
const node4 = addChild(tree, 40);
addChild(tree, 50);
const node21 = addChild(node2, 201);
const node22 = addChild(node2, 202);
addChild(node2, 203);
addChild(node2, 204);
travel(tree, (node) => {
console.log(node.data);
});
removeNode(tree, node22);
console.log(tree);
输出:
