有时需要测试一下某个功能的并发性能,又不要想借助于其他工具,索性就自己的开发语言,来一个并发请求就最方便了。
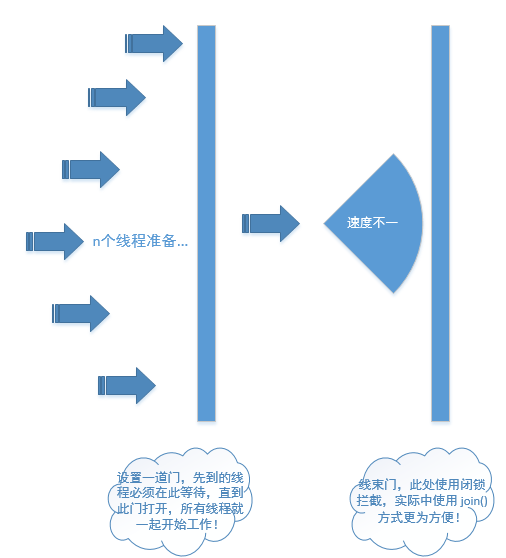
java中模拟并发请求,自然是很方便的,只要多开几个线程,发起请求就好了。但是,这种请求,一般会存在启动的先后顺序了,算不得真正的同时并发!怎么样才能做到真正的同时并发呢?是本文想说的点,java中提供了闭锁 CountDownLatch, 刚好就用来做这种事就最合适了。
只需要:
-
开启n个线程,加一个闭锁,开启所有线程;
-
待所有线程都准备好后,按下开启按钮,就可以真正的发起并发请求了。
LatchTest.java
package com.gp.user;
import com.gp.user.utils.HttpUtils;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @Author: GP3
* @Description: 并发请求测试
* @Date: Created in 10:16 2020/4/17
* @Modified By:
*/
public class LatchTest {
private static final int NUM = 1000; //并发数
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable taskTemp = new Runnable() {
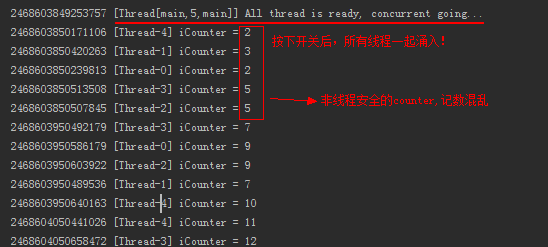
// 注意,此处是非线程安全的,留坑
private int iCounter;
@Override
public void run() {
// for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// 发起请求
HttpUtils.sendPost("http://172.16.7.206:8085/a/actApi/integrationTodoList",
"userName=gaopeng&pageNum=1&pageSize=15");
iCounter++;
System.out.println(System.nanoTime() + " [" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "] iCounter = " + iCounter);
try {
Thread.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// }
}
};
LatchTest latchTest = new LatchTest();
latchTest.startTaskAllInOnce(NUM, taskTemp);
}
public long startTaskAllInOnce(int threadNums, final Runnable task) throws InterruptedException {
final CountDownLatch startGate = new CountDownLatch(1);
final CountDownLatch endGate = new CountDownLatch(threadNums);
for(int i = 0; i < threadNums; i++) {
Thread t = new Thread() {
public void run() {
try {
// 使线程在此等待,当开始门打开时,一起涌入门中
startGate.await();
try {
task.run();
} finally {
// 将结束门减1,减到0时,就可以开启结束门了
endGate.countDown();
}
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
ie.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
t.start();
}
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println(startTime + " [" + Thread.currentThread() + "] All thread is ready, concurrent going...");
// 因开启门只需一个开关,所以立马就开启开始门
startGate.countDown();
// 等等结束门开启
endGate.await();
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println(endTime + " [" + Thread.currentThread() + "] All thread is completed.");
System.err.println("=====执行时间:" + TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(endTime - startTime) + "豪秒");
return endTime - startTime;
}
}
HttpUtils.java
package com.gp.user.utils;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLConnection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author: GP3
* @Description: http请求
* @Date: Created in 10:10 2020/4/17
* @Modified By:
*/
public class HttpUtils {
public HttpUtils() {
}
/**
* 向指定URL发送POST请求
* @param url
* @param paramMap
* @return 响应结果
*/
public static String sendPost(String url, Map<String, String> paramMap) {
PrintWriter out = null;
BufferedReader in = null;
String result = "";
try {
URL realUrl = new URL(url);
// 打开和URL之间的连接
URLConnection conn = realUrl.openConnection();
// 设置通用的请求属性
conn.setRequestProperty("accept", "*/*");
conn.setRequestProperty("connection", "Keep-Alive");
conn.setRequestProperty("user-agent","Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1;SV1)");
// conn.setRequestProperty("Charset", "UTF-8");
// 发送POST请求必须设置如下两行
conn.setDoOutput(true);
conn.setDoInput(true);
// 获取URLConnection对象对应的输出流
out = new PrintWriter(conn.getOutputStream());
// 设置请求属性
String param = "";
if (paramMap != null && paramMap.size() > 0) {
Iterator<String> ite = paramMap.keySet().iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
String key = ite.next();// key
String value = paramMap.get(key);
param += key + "=" + value + "&";
}
param = param.substring(0, param.length() - 1);
}
// 发送请求参数
out.print(param);
// flush输出流的缓冲
out.flush();
// 定义BufferedReader输入流来读取URL的响应
in = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream()));
String line;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
result += line;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("发送 POST 请求出现异常!" + e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 使用finally块来关闭输出流、输入流
finally {
try {
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
if (in != null) {
in.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 向指定 URL 发送POST方法的请求
*
* @param url
* 发送请求的 URL
* @param param
* 请求参数,请求参数应该是 name1=value1&name2=value2 的形式。
* @return 所代表远程资源的响应结果
*/
public static String sendPost(String url, String param) {
PrintWriter out = null;
BufferedReader in = null;
String result = "";
try {
URL realUrl = new URL(url);
// 打开和URL之间的连接
URLConnection conn = realUrl.openConnection();
// 设置通用的请求属性
// conn.setRequestProperty("Accept", "application/json"); // 设置接收数据的格式
// conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/json");
conn.setRequestProperty("accept", "*/*");
// conn.setRequestProperty("connection", "Keep-Alive");
// conn.setRequestProperty("user-agent","Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0;
// Windows NT 5.1;SV1)");
// 发送POST请求必须设置如下两行
conn.setDoOutput(true);
conn.setDoInput(true);
// 获取URLConnection对象对应的输出流
out = new PrintWriter(conn.getOutputStream());
// 发送请求参数
out.print(param);
// flush输出流的缓冲
out.flush();
// 定义BufferedReader输入流来读取URL的响应
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream(), "UTF-8"));
String line;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
result += line;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("发送 POST 请求出现异常!" + e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 使用finally块来关闭输出流、输入流
finally {
try {
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
if (in != null) {
in.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
return result;
}
}
执行结果如下:
并发请求操作流程示意图如下: