前言
前面写完了 EventBus 的源码分析,现在可以构思分析一下 Cache 模块。这也是自己使用最多的工具。我们平时使用本地缓存的情况也会有,譬如存储一些数据量很小,但访问量很高的数据,或者 Redis 远程数据的带宽成为了瓶颈,则可以考虑把数据缓存做本地。
- 简单的Demo
关于 Gauva Cache 的用法,简单来说,其实就是一个本地缓存的,可以和 HashMap 比较,鉴于它是线程安全的,所以我们可以和 ConcurrentHashMap 进行比较。ConcurrentHashMap 的键值对是强应用的,不提供缓存失效策略,需要手动删除 K-V 对。相比下,Gauva 的 Cache 则会提供的功能,会更加贴合缓存需求,例如提供配置失效策略,加载回调,缓存stat监控等等。
同样,Cache 一如 EventBus 的那种风格,强大的功能+简单的API。
简单的demo
/**
* Cache
*/
@Slf4j
public class CacheTest {
LoadingCache<Integer, String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.recordStats() // 配置记录缓存的状态
.build(new CacheLoader<Integer, String>(){
@Override
public String load(Integer key) throws Exception {
log.info("load key:" + key);
return key + "";
}
});
@Test
public void testCache() {
System.out.println("Test 1");
log.info("first load");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// 第一次读取,都会执行 CacheLoader 的方法
String value = cache.getUnchecked(i);
}
log.info("load from cache");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// 第二次读取,会走 Cache 缓存
String value = cache.getUnchecked(i);
}
// 打印cache的工况
log.info("cache stats : " + cache.stats());
}
}
输出:
.huoji.h5.guava.cache.CacheTest - first load
14:37:09.326 [main] INFO com.huoji.h5.guava.cache.CacheTest - load key:0
...省略
14:37:09.331 [main] INFO com.huoji.h5.guava.cache.CacheTest - load key:9
14:37:09.331 [main] INFO com.huoji.h5.guava.cache.CacheTest - load from cache
14:37:09.333 [main] INFO com.huoji.h5.guava.cache.CacheTest - cache stats :
// 缓存的工况:命中10,不命中10,成功加载:10, 加载异常 0, 加载耗时:4012176 纳秒(1s的10E分之一),失效数量 0
CacheStats{hitCount=10, missCount=10, loadSuccessCount=10, loadExceptionCount=0, totalLoadTime=4012176, evictionCount=0}
Disconnected from the target
类图
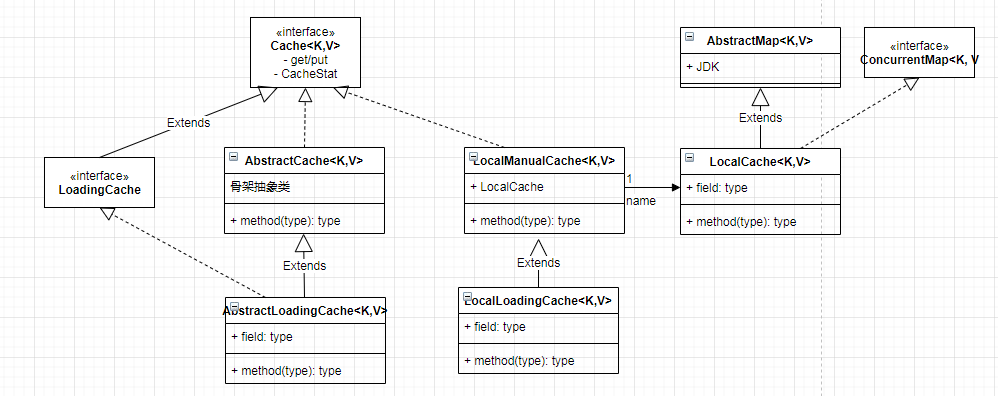
如上图,抛开一些组件和扩展, Guava 的 Cache 模块的类图还是比较简单的,这个类图也主要服务于 本地缓存,Guava 本省保留了一些关于缓存的接口定义,方便我们去扩展,如 ForwardingCache,这个后面研究好了再补充说明。
类图比较简单,大部分的功能都可以在接口命名中找到答案,就不一个个讨论了。对于 本地缓存 的源码中,LocalCache.java 这个类是最庞大的,连上注释大概4k行,里面也包含了很多特性的实现,例如:基于空间、时间、引用类型的回收方案的实现。这也是我自己希望从源码中获得答案的。
LocalCache 源码分析
LocalCache 从接口定义中,我们可以发现:
- 它是一个包权限的类,Guava 设计的风格,不希望客户端有太多的使用成本
- 它是一个线程安全的Map
这个类开始就写了一段注释,我认为比较重要,花了一点时间翻译了一下。大概是讲述整个Map的关于线程安全和Entry淘汰策略的实现思路。这对后面几千行代码的阅读是比较有用的。
LocalCache 字段
整体比较简单,就不翻译了。
分段存储的数据结构
类似 JDK1.7 的 ConcurrentHashMap 方式
/** The segments, each of which is a specialized hash table. */
final Segment<K, V>[] segments;
策略定义
/** Strategy for comparing keys. keys 比较策略 */
final Equivalence<Object> keyEquivalence;
/** Strategy for comparing values. values 比较策略*/
final Equivalence<Object> valueEquivalence;
/** Strategy for referencing keys. keys 引用策略 枚举*/
final Strength keyStrength;
/** Strategy for referencing values. values 应用策略 枚举 */
final Strength valueStrength;
时间相关设置
/** How long after the last access to an entry the map will retain that entry. */
final long expireAfterAccessNanos;
/** How long after the last write to an entry the map will retain that entry. */
final long expireAfterWriteNanos;
/** How long after the last write an entry becomes a candidate for refresh. */
final long refreshNanos;
回调队列
这个是缓存失效时,回调方法的保存位置。Q: 为什么用的是队列?
/** Entries waiting to be consumed by the removal listener. */
// TODO(fry): define a new type which creates event objects and automates the clear logic
final Queue<RemovalNotification<K, V>> removalNotificationQueue;
加载器与统计器
这个是用于回调加载数据和统计缓存工况的组件
/**
* Accumulates global cache statistics. Note that there are also per-segments stats counters which
* must be aggregated to obtain a global stats view.
*/
final StatsCounter globalStatsCounter;
/** The default cache loader to use on loading operations. */
final @Nullable CacheLoader<? super K, V> defaultLoader;
LocalCache 的构造方法
一种典型的builder模式,构造方法主要是填充上面的配置。很多的注释可以通过CacheBuilder类进行了解。
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with the specified strategy, initial capacity and concurrency level.
*/
LocalCache(
CacheBuilder<? super K, ? super V> builder, @Nullable CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) {
// 设置并发级别,其用于决定应该初始化多少个 segment 。在Cache中,segment意味这锁的粒度,粒度越多支持的并发数会越大。
// CacheBuilder.java:362 有更详细的解释
concurrencyLevel = Math.min(builder.getConcurrencyLevel(), MAX_SEGMENTS);
// 设置引用策略
keyStrength = builder.getKeyStrength();
valueStrength = builder.getValueStrength();
// 设置比较策略
keyEquivalence = builder.getKeyEquivalence();
valueEquivalence = builder.getValueEquivalence();
maxWeight = builder.getMaximumWeight();
weigher = builder.getWeigher();
// 设置时间
expireAfterAccessNanos = builder.getExpireAfterAccessNanos();
expireAfterWriteNanos = builder.getExpireAfterWriteNanos();
refreshNanos = builder.getRefreshNanos();
// 设置回调,假如没设置回调监听,则用一个 discardingQueue 忽略所有的提交。否则使用ConcurrentLinkedQueue构建队列
removalListener = builder.getRemovalListener();
removalNotificationQueue =
(removalListener == NullListener.INSTANCE)
? LocalCache.<RemovalNotification<K, V>>discardingQueue()
: new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<RemovalNotification<K, V>>();
ticker = builder.getTicker(recordsTime());
// 根据策略构建工厂 工厂模式
entryFactory = EntryFactory.getFactory(keyStrength, usesAccessEntries(), usesWriteEntries());
// 构建统计器和加载器
globalStatsCounter = builder.getStatsCounterSupplier().get();
defaultLoader = loader;
// 设置 容量限制 的缓存
int initialCapacity = Math.min(builder.getInitialCapacity(), MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
if (evictsBySize() && !customWeigher()) {
initialCapacity = (int) Math.min(initialCapacity, maxWeight);
}
// Find the lowest power-of-two segmentCount that exceeds concurrencyLevel, unless
// maximumSize/Weight is specified in which case ensure that each segment gets at least 10
// entries. The special casing for size-based eviction is only necessary because that eviction
// happens per segment instead of globally, so too many segments compared to the maximum size
// will result in random eviction behavior.
// 1、参考 HashMap table 数组长度为 2的幂次方原则
// 2、这里的参数主要受限于两个配置:A 并发级别,B 容量限制(假如容量有限,就不能浪费segment)
int segmentShift = 0;
int segmentCount = 1;
while (segmentCount < concurrencyLevel && (!evictsBySize() || segmentCount * 20 <= maxWeight)) {
++segmentShift;
segmentCount <<= 1;
}
this.segmentShift = 32 - segmentShift;
// 设置掩码,用于对key值进行hash使用的。这个也类似于 hashMap 的 rehash 方法
segmentMask = segmentCount - 1;
// 设置 segments 数组
this.segments = newSegmentArray(segmentCount);
int segmentCapacity = initialCapacity / segmentCount;
if (segmentCapacity * segmentCount < initialCapacity) {
++segmentCapacity;
}
int segmentSize = 1;
while (segmentSize < segmentCapacity) {
segmentSize <<= 1;
}
// 注意这里的segmentSize,不是 this.segments.size(),而是单个 segmentSize
if (evictsBySize()) {
// Ensure sum of segment max weights = overall max weights
long maxSegmentWeight = maxWeight / segmentCount + 1;
long remainder = maxWeight % segmentCount;
for (int i = 0; i < this.segments.length; ++i) {
if (i == remainder) {
maxSegmentWeight--;
}
this.segments[i] =
createSegment(segmentSize, maxSegmentWeight, builder.getStatsCounterSupplier().get());
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < this.segments.length; ++i) {
//
this.segments[i] =
createSegment(segmentSize, UNSET_INT, builder.getStatsCounterSupplier().get());
}
}
}
- Q: weights initialCapacity maximumSize 这几个参数是什么区别,什么关系?
答:
- 在基于容量的回收策略中,LRU 虽然可以提供权重恒等的删除策略,但对于一些比较特别的Entry,例如占用空间很大于是不想被回收的,可以自定义自己的权重计算方法(接口:Weighter)
- maximunSize 表示容量最大值,initialCapacity 是初始化容量。设置两者相等,可以有效避免扩容带来的内存消耗,当然也会因此有些副作用。
翻译LocalCache的整体介绍:LocalCache.java line:104-128
The basic strategy is to subdivide the table among Segments, each of which itself is a concurrently readable hash table. The map supports non-blocking reads and concurrent writes across different segments.
(LocalCache 是一个线程安全的Map) 解决并发问题的基本策略就是通过 Segments 对 table 进行分割,每一个 Segments 本身就是支持并发读的 hash 表。这个 Map (LocalCache) 中的每一个 segment 支持非阻塞读和并发写。
If a maximum size is specified, a best-effort bounding is performed per segment, using a page-replacement algorithm to determine which entries to evict when the capacity has been exceeded.
假如指定了最大容量,我们可以使用 page-replacement(页替换) 算法在超出容量的时候,用来确定应该被排除的 entries。
The page replacement algorithm's data structures are kept casually consistent with the map. The ordering of writes to a segment is sequentially consistent. An update to the map and recording of reads may not be immediately reflected on the algorithm's data structures. These structures are guarded by a lock and operations are applied in batches to avoid lock contention. The penalty of applying the batches is spread across threads so that the amortized cost is slightly higher than performing just the operation without enforcing the capacity constraint.
页替换算法的数据结构应该和 map 保持一致。 数据对 sement 的写入顺序应该要保持一致的。一个更新操作或者读操作不需要立即映射到算法的数据上。这些数据结构是被锁保护起来的,所以这里操作可以先集合起来,通过批处理去避免锁竞争。应用批处理的成本会摊到每个线程上,因此,摊销成本比不执行容量约束的情况下稍微高一点。
This implementation uses a per-segment queue to record a memento of the additions, removals, and accesses that were performed on the map. The queue is drained on writes and when it exceeds its capacity threshold.
这个页算法的实现,是每一个 segment 都有一个队列用于记录添加、删除、读取等操作。当map超过容量阈值时,队列也会一起耗尽。(队列满)
The Least Recently Used page replacement algorithm was chosen due to its simplicity, high hit rate, and ability to be implemented with O(1) time complexity. The initial LRU implementation operates per-segment rather than globally for increased implementation simplicity. We expect the cache hit rate to be similar to that of a global LRU algorithm.
最少最近使用(LRU)页替换算法非常简单、命中率高,时间复杂度为 O(1) ,因此被选为 Map 淘汰策略,为了实现简单,最初(initial)的 LRU 实现是面向每一个段的,而不是全局。我们认为它的缓存命中率应该和全局 LRU 相差不大。
参考链接
后续
Cache 的模块主要核心代码和实现都集中在 LocalCache 类中,这个类很大,有接近5k行。这些先记录第一篇,后面会根据 LocalCache 的不同模块的划分,预计会写下如下两篇篇分析:
- 1、LocalCache Entry 的不同引用是如何实现的
- 2、LocalCache.Segment 的源码分析及淘汰策略的实现
同样,作为优质的源代码,会继续分析内部使用的数据结构和设计模式等技巧。