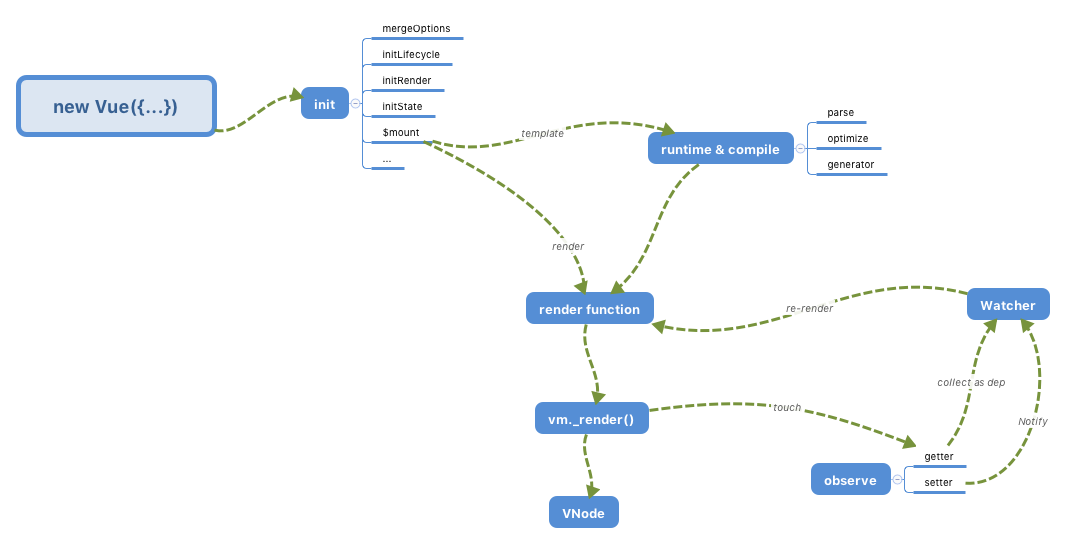
据说在很久很久以前,天地混沌一体,万物都在其中。没有声音,没有光,漆黑一片。有个名叫盘古的巨人,在混沌里孕育和成长。经过18,000年,盘古突然苏醒,当他睁开双眼之时,周围漆黑一片,他不知从哪里抓来一把斧子,挥动了一下,一声巨响过后,混沌就被劈开了。轻而清的上浮而为天,重而浊的下沉而为地。这便是世间万物的起源,来自于盘古的开天辟地。Vue的起源,源于一次Vue的实例化:
new Vue({
el: ...,
data: ...,
....
})
那么在这次new的过程中,究竟发生了什么事情?让我们来一探究竟。打开Vue的源码文件,其核心代码在src/core目录下。下面我们从入口文件index.js开始进入:
// src/core/index.js
// 这里应该是我们 Vue 核心方法
import Vue from './instance/index'
// 应该可以猜出这里是初始化一些全局API
import { initGlobalAPI } from './global-api/index'
// 应该是获取一个Boolean类型的变量,来判断是不是ssr
import { isServerRendering } from 'core/util/env'
// 开始执行初始化全局变量
initGlobalAPI(Vue)
// 为Vue原型定义属性$isServer
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$isServer', {
get: isServerRendering
})
// 为Vue原型定义属性$ssrContext
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$ssrContext', {
get () {
/* istanbul ignore next */
return this.$vnode && this.$vnode.ssrContext
}
})
Vue.version = '__VERSION__'
export default Vue
根据index.js中的指引,首先找到core/instance/index文件,可以清晰的看到:
import { initMixin } from './init'
import { stateMixin } from './state'
import { renderMixin } from './render'
import { eventsMixin } from './events'
import { lifecycleMixin } from './lifecycle'
import { warn } from '../util/index'
// 为什么不使用ES6 class???
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)
}
initMixin(Vue)// 定义_init方法
stateMixin(Vue)// 定义数据相关的方法$set,$delete,$watch方法
eventsMixin(Vue)// 定义事件相关的方法$on,$once,$off,$emit
lifecycleMixin(Vue)// 定义_update,及生命周期相关的$forceUpdate和$destroy
renderMixin(Vue)// 定义$nextTick,_render将render函数转为vnode
export default Vue
顺便一说:在
vue的内部,_符号开头定义的变量是供内部私有使用的,而$符号定义的变量是供用户使用的,而且用户自定义的变量不能以_或$开头,以防止内部冲突。
为什么不采用ES6的class来定义,原因是这样可以方便的把vue的功能拆分到不同的目录中去维护,将vue的构造函数传入到以下方法内
好了,接下来,我们接聊聊initGlobalAPI这个东西,其实在Vue官网上,就已经为我们说明了Vue的全局属性

// core/global-api/index
...
export function initGlobalAPI (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
// config
const configDef = {}
configDef.get = () => config
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
configDef.set = () => {
warn(
'Do not replace the Vue.config object, set individual fields instead.'
)
}
}
Object.defineProperty(Vue, 'config', configDef)
// 各种工具函数 这些工具方法不视作全局API的一部分,除非你已经意识到某些风险,否则不要去依赖他们
Vue.util = {
warn,
extend,
mergeOptions,
defineReactive
}
// 这里定义全局属性
Vue.set = set
Vue.delete = del
Vue.nextTick = nextTick
Vue.options = Object.create(null)
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => {
Vue.options[type + 's'] = Object.create(null)
})
Vue.options._base = Vue
extend(Vue.options.components, builtInComponents)
// 定义全局方法
initUse(Vue)// Vue.use
initMixin(Vue)// Vue.mixin
initExtend(Vue)// Vue.extend
initAssetRegisters(Vue)
}
接下来便是提供给ssr使用的全局变量$isServer 和 $ssrContext
欲知后事如何,且听下回分解!
事后三件事:
- 多动手
- 点个赞关个注评个论