队列的概念
只允许在一端插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表;进行插入操作的一端称为队尾(入队列),进行删除操作的一端称为队头(出队列);队列具有先进先出(FIFO)的特性。
顺序存储结构实现队列
普通顺序队列
1)队头不动,出队列时队头后的所有元素向前移动
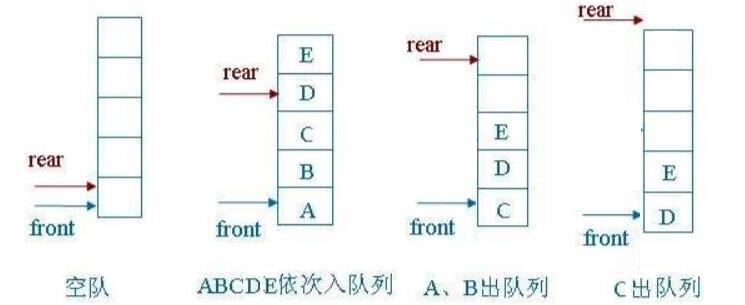
2) 队头移动,出队列时队头向后移动一个位置
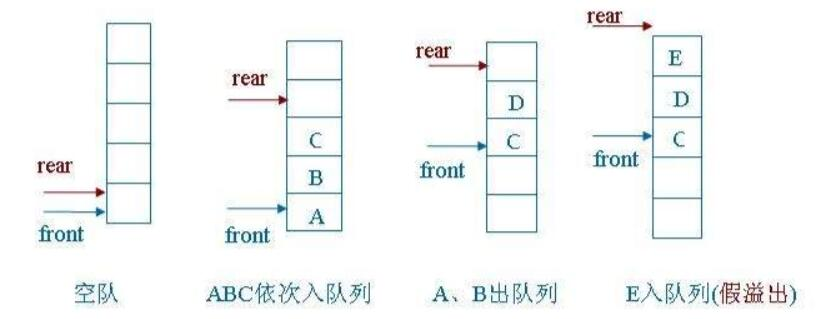
循环队列
基于普通顺序队列出现的问题,使用循环队列可以解决问题。
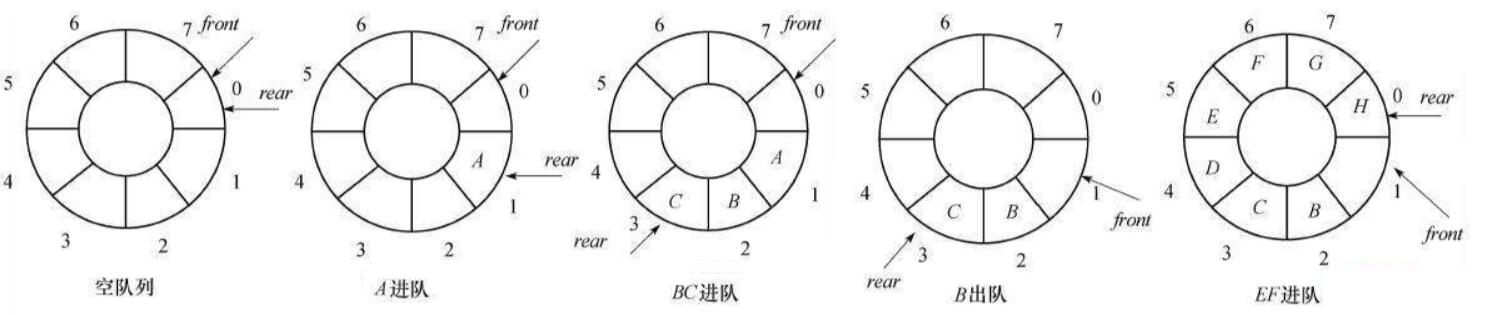
总结一下规律,
- rear的变化,当rear=7,如何让rear = 0呢?很显然 rear = (rear+1)%size;
- front同理也遵循这样的变化head=(head+1)%size.
如何判定队满呢?
从上面的规律来看,我们可以发现 (rear+1)%size == head 的时候,队列就满了,但是rear指向的位置实际上是没有数据的,这就意味这循环队列浪费了一个存储空间,以空间换取时间。
代码实现
这里主要是以循环队列为主。
- 定义数据
#define ERROR 0
#define OK 1
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAXSIZE 20
typedef int QElemType;
typedef int Status;
typedef struct Queue{
QElemType data[MAXSIZE];
int front;
int rear;
}ZJQueue;
- 初始化
/*
初始化 队列 头和尾都为0
*/
Status InitQueue(ZJQueue* Q){
Q->front = 0;
Q->rear = 0;
return OK;
}
- 清空队列
/**
清空队列
*/
Status ClearQueue(ZJQueue* Q){
Q->front = 0;
Q->rear = 0;
return OK;
}
- 判断是否为空
/*
判断队列是否为空 对头==队尾
**/
Status QueueEmpty(ZJQueue Q){
if (Q.front == Q.rear) {
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
- 队列是否已满
/*
队列是否已满
**/
Status QueueFull(ZJQueue Q){
if ((Q.rear + 1)%MAXSIZE == Q.front) {
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
- 队列长度
/**
队列长度
*/
int QueueLength(ZJQueue Q){
return ( Q.rear + MAXSIZE - Q.front)%MAXSIZE;
}
- 队列头部数据
/**
队列的头部数据
*/
Status GetHead(ZJQueue Q, QElemType* e){
if (QueueEmpty(Q)) {
return ERROR;
}
*e = Q.data[Q.front];
return OK;
}
- 入队
/*
入队
**/
Status EnQueue(ZJQueue *Q, QElemType e){
if (QueueFull(*Q)) {
return ERROR;
}
Q->data[Q->rear] = e;
// 对尾部位置进行更跟新
Q->rear = (Q->rear + 1)%MAXSIZE;
return OK;
}
- 出队
/***
出对
*/
Status DeQueue(ZJQueue *Q, QElemType *e){
if (QueueEmpty(*Q)) {
return ERROR;
}
*e = Q->data[Q->front];
// 对头部位置进行更新
Q->front = (Q->front + 1)%MAXSIZE;
return OK;
}
- 遍历队列
/**
遍历
*/
Status QueueTraverse(ZJQueue Q){
if (QueueEmpty(Q)) {
return ERROR;
}
int i = 0;
int index = Q.front;
while (index != Q.rear) {
printf(" %d", Q.data[index]);
i++;
index = (Q.front + i + MAXSIZE)%MAXSIZE;
}
printf("\n");
return OK;
}
链式存储结构实现队列
链式存储结构
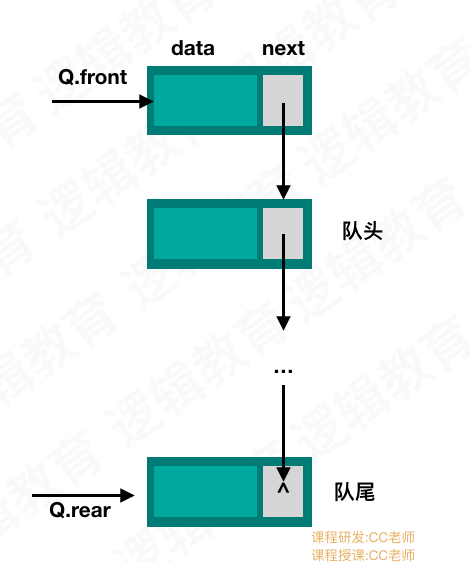
代码实现
- 定义数据
typedef int QElemType;
typedef int Status;
/// 定义节点结构
typedef struct QNode{
QElemType data;
struct QNode *next;
}QNode, *QueuePtr;
/// 定义队列结构
typedef struct LinkQueue{
QueuePtr front, rear;
}ZLinkQueue;
- 初始化
Status InitQueue(ZLinkQueue* Q){
// 头尾都指向新的节点
Q->front = Q->rear = (QueuePtr)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
// 如果生成失败,返回错误
if (!Q->front) {
return ERROR;
}
// 头节点的指针区域为空
Q->rear->next = NULL;
return OK;
}
- 清空队列
Status ClearQueue(ZLinkQueue* Q){
QueuePtr p = Q->front->next;
while (p) {
Q->rear = p->next;
free(p);
p = Q->rear;
}
Q->rear = Q->front;
Q->front->next = NULL;
return OK;
}
- 判断是否为空
Status QueueEmpty(ZLinkQueue Q){
if (Q.front == Q.rear) {
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
- 队列长度
int QueueLength(ZLinkQueue Q){
int length = 0;
if (QueueEmpty(Q)) {
return length;
}
QueuePtr p = Q.front->next;
while (p != Q.rear) {
length++;
p = p->next;
}
return length;
}
- 获取头部数据
Status GetHead(ZLinkQueue Q, QElemType* e){
if (QueueEmpty(Q)) {
return ERROR;
}
*e = Q.front->next->data;
return OK;
}
- 入队
Status EnQueue(ZLinkQueue *Q, QElemType e){
QueuePtr p = (QueuePtr)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (!p) {
return ERROR;
}
p->next = NULL;
p->data = e;
Q->rear->next = p;
Q->rear = p;
return OK;
}
- 出队
Status DeQueue(ZLinkQueue *Q, QElemType *e){
if (QueueEmpty(*Q)) {
return ERROR;
}
QueuePtr p = Q->front->next;
*e = p->data;
Q->front->next = p->next;
if (p == Q->rear) {
Q->rear = Q->front;
}
free(p);
// 对头部位置进行更新
return OK;
}
- 遍历
Status QueueTraverse(ZLinkQueue Q){
if (QueueEmpty(Q)) {
return ERROR;
}
QueuePtr p = Q.front->next;
while (p != Q.rear) {
printf(" %d", p->data);
p=p->next;
}
printf("\n");
return OK;
}
总结
在开发中,队列应用还是比较广泛,比如处理多任务的时候,使用队列如串形队列并行队列等,所以要掌握原理很有帮助。