了解Prop
基本用法
<!-- 在 HTML 中是 kebab-case 的 -->
<blog-post post-title="hello!"></blog-post>
Vue.component('blog-post', {
// 在 JavaScript 中是 camelCase 的
props: ['postTitle'],
template: '<h3>{{ postTitle }}</h3>'
})
常见类型
字符串数组的形式
props: ['title', 'likes', 'isPublished', 'commentIds', 'author']
对象的形式
props: {
title: String,
likes: Number,
isPublished: Boolean,
commentIds: Array,
author: Object,
callback: Function,
contactsPromise: Promise // or any other constructor
}
汇总
整体来说可以分为传递静态的值 和通过v-bind 传递动态的值
- 传递一个数字
- 传递一个布尔值
- 传入一个数组
- 传入一个对象
- 传入一个对象的所有的属性
post: {
id: 1,
title: 'My Journey with Vue'
}
以下两种方式是等价的
<blog-post v-bind="post"></blog-post>
<blog-post
v-bind:id="post.id"
v-bind:title="post.title"
></blog-post>
在 Vue 中,子组件为何不可以修改父组件传递的 Prop ?
尝试修改会发生什么事情
首先创建一个文件来演示props 传值(父组件的数据传递给子组件)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Vue-prop</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{ message }}
<hr />
<ol>
<!-- 创建一个 todo-item 组件的实例 -->
<todo-item todo="学习"></todo-item>
</ol>
</div>
<script src="./vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 组件本质上是一个拥有预定义选项的一个 Vue 实例
// 注册一个TODO组件
Vue.component("todo-item", {
template: `
<div>
<li>{{todo}}</li>
<button @click = "changeProps">尝试改变父组件传来的prop</button></div>`,
props: ["todo"],
methods: {
changeProps() {
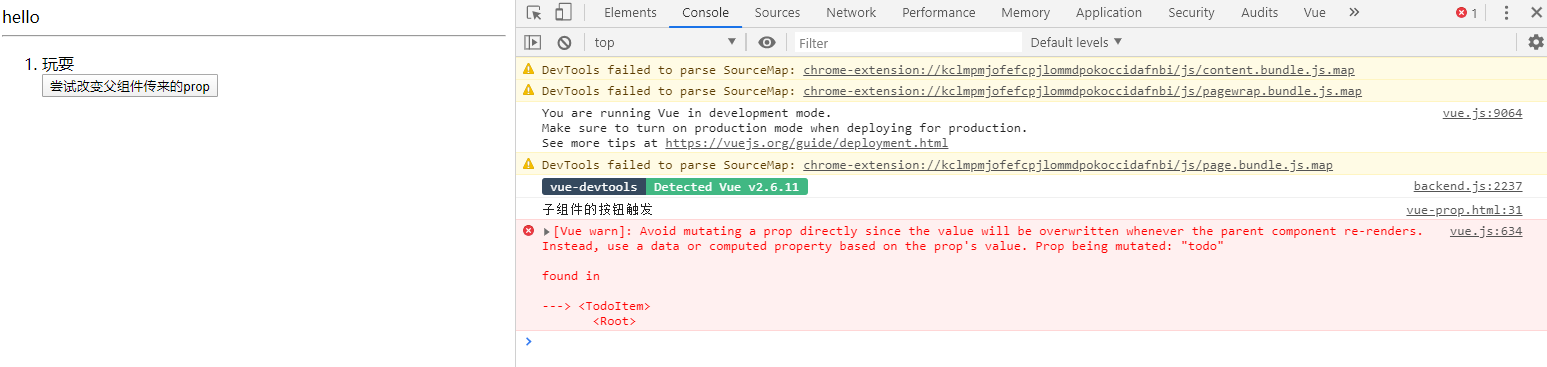
console.log(`子组件的按钮触发`);
this.todo = "玩耍";
}
}
});
var vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data() {
return {
message: "hello"
};
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
结果是什么,数据也是可以修改成功的,但是控制台会报一个警告
vue.js:634 [Vue warn]: Avoid mutating a prop directly since the value will be overwritten whenever the parent component re-renders. Instead, use a data or computed property based on the prop's value. Prop being mutated: "todo"
单向数据流
所有的 prop 都使得其父子 prop 之间形成了一个单向下行绑定:父级 prop 的更新会向下流动到子组件中,但是反过来则不行。这样会防止从子组件意外改变父级组件的状态,从而导致你的应用的数据流向难以理解。
额外的,每次父级组件发生更新时,子组件中所有的 prop 都将会刷新为最新的值。这意味着你不应该在一个子组件内部改变 prop。如果你这样做了,Vue 会在浏览器的控制台中发出警告。
简单的来说,vue这样处理从父组件来的数据,是为了方便监测数据的流动,如果一旦出现的错误,可以更为迅速的定位到错误的位置,
什么情况下,我们会改变这个prop
props: ['initialCounter'],
data: function () {
return {
counter: this.initialCounter
}
}
- 第一种情况:这个 prop 用来传递一个初始值;这个子组件接下来希望将其作为一个本地的 prop 数据来使用。在这种情况下,最好定义一个本地的 data 属性并将这个 prop 用作其初始值。
借助data
props: ['size'],
computed: {
normalizedSize: function () {
return this.size.trim().toLowerCase()
}
}
- 第二种情况这个 prop 以一种原始的值传入且需要进行转换。在这种情况下,最好使用这个 prop 的值来定义一个计算属性
借助计算属性
如果修改了,Vue 是如何监控到属性的修改并给出警告的
这里我们可以去源码里找答案,毕竟真实的警告暗示是vue来给出的
src>core>instance>state.js // 源码的位置
function initProps (vm: Component, propsOptions: Object) {
const propsData = vm.$options.propsData || {}
const props = vm._props = {}
// cache prop keys so that future props updates can iterate using Array
// instead of dynamic object key enumeration.
// 缓存prop的keys 为了是将来更新的props可以使用数组进行迭代,而不是动态的对象枚举
const keys = vm.$options._propKeys = []
const isRoot = !vm.$parent
// root instance props should be converted
// 不是root根组件
if (!isRoot) {
toggleObserving(false)
}
for (const key in propsOptions) {
keys.push(key)
const value = validateProp(key, propsOptions, propsData, vm)
/* istanbul ignore else */
// 通过判断是否在开发环境
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
const hyphenatedKey = hyphenate(key)
if (isReservedAttribute(hyphenatedKey) ||
config.isReservedAttr(hyphenatedKey)) {
warn(
`"${hyphenatedKey}" is a reserved attribute and cannot be used as component prop.`,
vm
)
}
// 如果不是,说明此修改来自子组件,触发warning提示
/**
* 传入的第4个函数是自定义的set函数,当props被修改的时候就会触发第四个参数的函数
*/
defineReactive(props, key, value, () => {
if (!isRoot && !isUpdatingChildComponent) {
warn(
`Avoid mutating a prop directly since the value will be ` +
`overwritten whenever the parent component re-renders. ` +
`Instead, use a data or computed property based on the prop's ` +
`value. Prop being mutated: "${key}"`,
vm
)
}
})
} else {
// 如果是开发环境,会在触发Set的时候判断是否此key是否处于updatingChildren中被修改
defineReactive(props, key, value)
}
// static props are already proxied on the component's prototype
// during Vue.extend(). We only need to proxy props defined at
// instantiation here.
if (!(key in vm)) {
proxy(vm, `_props`, key)
}
}
toggleObserving(true)
}
src>core>observer>index.js
/**
* Define a reactive property on an Object.
*/
export function defineReactive (
obj: Object,
key: string,
val: any,
customSetter?: ?Function,
shallow?: boolean
) {
const dep = new Dep()
const property = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, key)
if (property && property.configurable === false) {
return
}
// cater for pre-defined getter/setters
const getter = property && property.get
const setter = property && property.set
if ((!getter || setter) && arguments.length === 2) {
val = obj[key]
}
let childOb = !shallow && observe(val)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter () {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend()
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend()
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value)
}
}
}
return value
},
set: function reactiveSetter (newVal) {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val
/* eslint-disable no-self-compare */
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return
}
/* eslint-enable no-self-compare */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) {
customSetter()
}
// #7981: for accessor properties without setter
if (getter && !setter) return
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal)
} else {
val = newVal
}
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal)
dep.notify()
}
})
}
思考
如果是传入的是引用的数据类型,控制台会警告嘛?
<todo-item todo="学习" :todolist="todolist"></todo-item>
var vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data() {
return {
message: "hello",
todolist: [
{
id: "1",
todo: "吃饭"
}
]
};
}
});
最后
如有自己的理解也可以在评论区一块学习,如有错误也请指出,感谢你读到这里~~