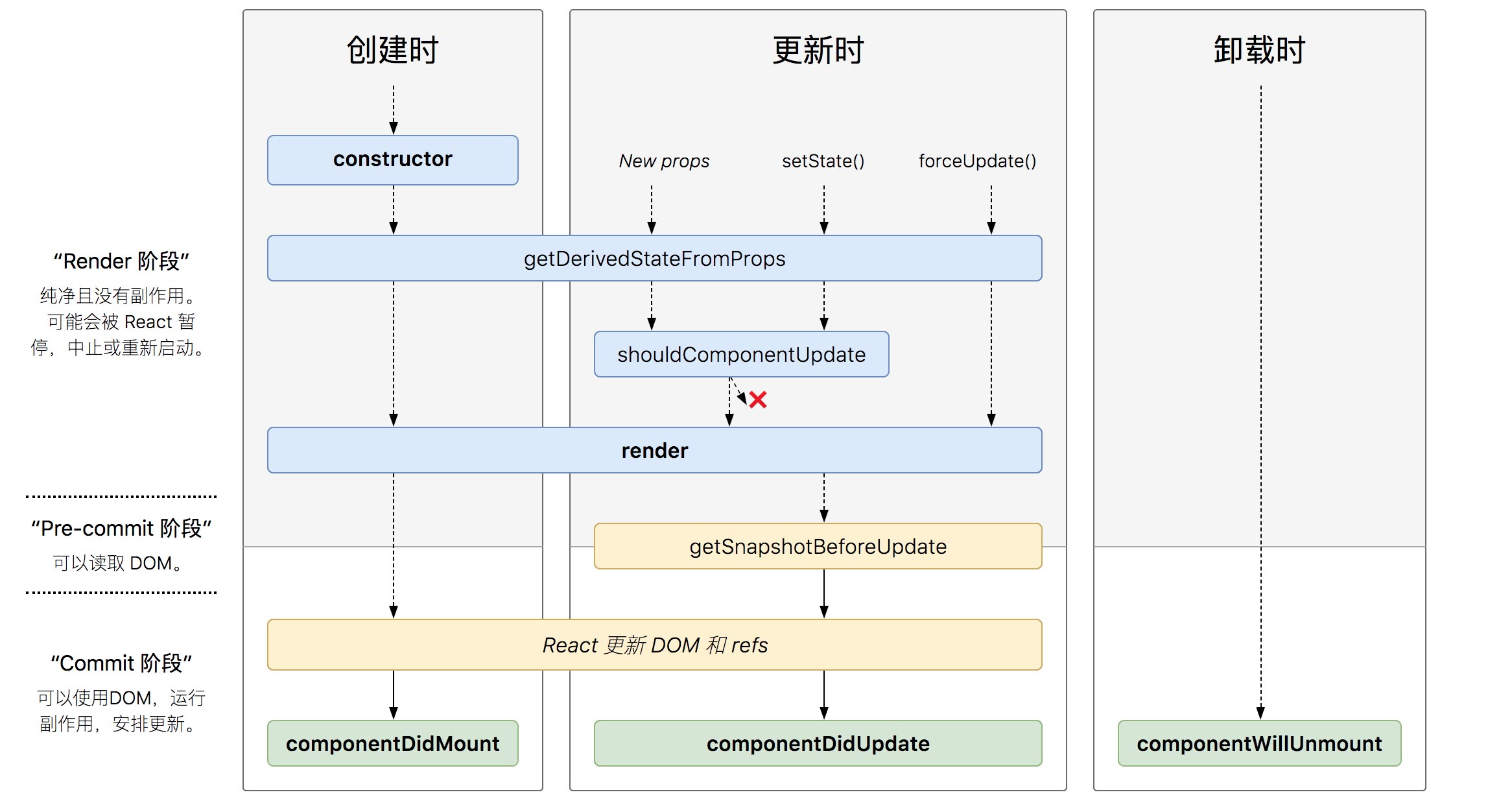
React的基础已经快更新完了,接下来这一篇我记录的是生命周期(只有类组件才有这个概念)相关的知识点,这个也是面试必问的点。
-
在开始之前先提醒一下,HTTP请求数据要放在
componentDidMount生命周期中。有人可能会问为什么不放在componentWillMount生命周期中,这个里面也不是不能发送HTTP请求指示在这个生命周期发送会有可能反复多次执行(这个react设计上的锅)。但是在新版生命周期里面,已经将它弃用所以也就没有了这个问题。 -
旧版生命周期:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
interface Props { }
interface State { number: number }
class Counter extends React.Component<Props, State> { // 他会比较两个状态相等就不会刷新视图 PureComponent是浅比较
static defaultProps = {
name: 'name'
};
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { number: 0 }
console.log('1.constructor构造函数')
}
componentWillMount() { // 取本地的数据 同步的方式:采用渲染之前获取数据,只渲染一次
console.log('2.组件将要加载 componentWillMount');
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('4.组件挂载完成 componentDidMount');
}
handleClick = () => {
this.setState({ number: this.state.number + 1 });
};
// react可以shouldComponentUpdate方法中优化 PureComponent 可以帮我们做这件事
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState): boolean { // 代表的是下一次的属性 和 下一次的状态
console.log('5.组件是否更新 shouldComponentUpdate');
return nextState.number % 2 == 0;
// return nextState.number!==this.state.number; //如果此函数种返回了false 就不会调用render方法了
} //不要随便用setState 可能会死循环
componentWillUpdate() {
console.log('6.组件将要更新 componentWillUpdate');
}
componentDidUpdate() {
console.log('7.组件完成更新 componentDidUpdate');
}
render() {
console.log('3.render');
return (
<div>
<p>{this.state.number}</p>
{this.state.number > 3 ? null : <ChildCounter n={this.state.number} />}
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>+</button>
</div>
)
}
}
class ChildCounter extends Component<{ n: number }> {
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('组件将要卸载componentWillUnmount')
}
componentWillMount() {
console.log('child componentWillMount')
}
render() {
console.log('child-render')
return (<div>
{this.props.n}
</div>)
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('child componentDidMount')
}
componentWillReceiveProps(newProps) { //第一次不会执行,之后属性更新时才会执行
console.log('child componentWillReceiveProps')
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
return nextProps.n % 3 == 0; //子组件判断接收的属性 是否满足更新条件 为true则更新
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Counter />, document.getElementById('root'));
// defaultProps
// constructor
// componentWillMount
// render
// componentDidMount
// 状态更新会触发的
// shouldComponentUpdate nextProps,nextState=>boolean
// componentWillUpdate
// componentDidUpdate
// 属性更新
// componentWillReceiveProps newProps
// 卸载
// componentWillUnmount
-
新版生命周期:
static``getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state)这个生命周期的功能实际上就是将传入的props映射到state上面import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'; interface Props { } interface State { number: number } class Counter extends React.Component<Props, State> { static defaultProps = { name: 'name' }; constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { number: 0 } } handleClick = () => { this.setState({ number: this.state.number + 1 }); }; render() { console.log('3.render'); return ( <div> <p>{this.state.number}</p> <ChildCounter number={this.state.number} /> <button onClick={this.handleClick}>+</button> </div> ) } } class ChildCounter extends React.Component<{ number: number }, { number: number }> { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { number: 0 }; } static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState) { const { number } = nextProps; // 当传入的type发生变化的时候,更新state if (number % 2 == 0) { return { number: number * 2 }; } else { return { number: number * 3 }; } // 否则,对于state不进行任何操作 return null; } render() { console.log('child-render', this.state) return (<div> {this.state.number} </div>) } } ReactDOM.render( <Counter />, document.getElementById('root') );getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()被调用于render之后,可以读取但无法使用DOM的时候。它使您的组件可以在可能更改之前从DOM捕获一些信息(例如滚动位置)。此生命周期返回的任何值都将作为参数传递给componentDidUpdate()import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'; interface Props { } interface State { messages: Array<string> } class ScrollingList extends React.Component<Props, State> { wrapper timeID constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { messages: [] } this.wrapper = React.createRef(); } addMessage() { this.setState(state => ({ messages: [`${state.messages.length}`, ...state.messages], })) } componentDidMount() { this.timeID = window.setInterval(() => {//设置定时器 this.addMessage(); }, 1000) } componentWillUnmount() {//清除定时器 window.clearInterval(this.timeID); } getSnapshotBeforeUpdate() { //很关键的,我们获取当前rootNode的scrollHeight,传到componentDidUpdate 的参数perScrollHeight return this.wrapper.current.scrollHeight; } componentDidUpdate(pervProps, pervState, prevScrollHeight) { const curScrollTop = this.wrapper.current.scrollTop;//当前向上卷去的高度 //当前向上卷去的高度加上增加的内容高度 this.wrapper.current.scrollTop = curScrollTop + (this.wrapper.current.scrollHeight - prevScrollHeight); } render() { let style = { height: '100px', width: '200px', border: '1px solid red', overflow: 'auto' } return ( <div style={style} ref={this.wrapper} > {this.state.messages.map((message, index) => ( <div key={index}>{message} </div> ))} </div> ); } }
ReactDOM.render( , document.getElementById('root') ); ```