setuid u+s
setuid的定义:当一个可执行程序具有了setuid权限,当用户执行这个程序的时候(可执行程序可以理解为命令),将以这个程序的所有者的身份执行。
setgid g+s
setgid的权限,对应的数字是2。概念和setuid是一样的。当一个程序具有setgid的时候,当一个用户执行这个程序的时候会以这个程序所属组的身份去执行。
授予的命令是chmod g+s。或者chmod 2755。
o+t
粘着位,这一位的权限是1。如果一个目录有写权限,那么就可以对目录里面文件进行删除和创建。
下面是题目:
思考问题:如何使用SGID位实现对某个目录下文件的共享,即实现某个目录下文件对目录所属组内的用户的共享。尝试列出完成此任务的命令序列(一行一条命令)。
设置SetGID
chmod 2xxx
chmod g+s
取消SetGID
chmod xxx
chmod g-s
共享目录
根据setGID的特性,可以实现大范围地创建并共享文档。
先做准备工作
#创建一个分享组
[wenqiang@localhost ~]$ sudo groupadd shared

#添加当前用户到分享组
[wenqiang@localhost ~]$ sudo usermod -a wenqiang -G shared
#创建新用户,并添加到分享组,-M 不创建home目录
[wenqiang@localhost ~]$ sudo useradd -M person2share -G shared
#检查结果
[wenqiang@localhost ~]$ id person2share

[wenqiang@localhost ~]$ cat /etc/group | grep shared

共享目录
#创建共享目录
[wenqiang@localhost ~]$ mkdir shared_dir
[wenqiang@localhost ~]$ ls -lF

#修改目录组,设置SGID
[wenqiang@localhost ~]$ sudo chgrp shared shared_dir/
[wenqiang@localhost ~]$ sudo chmod g+s shared_dir
[wenqiang@localhost ~]$ ls -lF
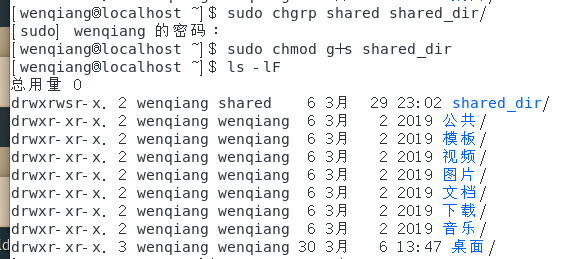
#注意到组权限x变为了s,设置SGID成功
#目录下新建一个文件,该文件所属组为目录组,文件执行权限为组权限。可能需要设置umask
[wenqiang@localhost ~]$ cd shared_dir
[wenqiang@localhost shared_dir]$ touch testfile
[wenqiang@localhost shared_dir]$ ls -lF
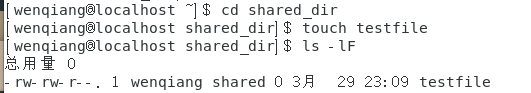
测试
#关闭属主权限
[wenqiang@localhost shared_dir]$ sudo chmod u-rw testfile
[wenqiang@localhost shared_dir]$ ls -lF
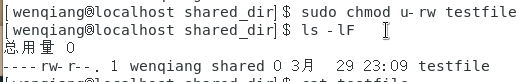
[wenqiang@localhost shared_dir]$ cat testfile

#切换用户进行尝试
[wenqiang@localhost shared_dir]$ su person2share
//这里因为用户是新建的,之前没有,所有不知道用户密码,得用root改用户密码。

[wenqiang@localhost shared_dir]$ su root
[root@localhost shared_dir]# passwd person2share
[root@localhost shared_dir]# su person2share
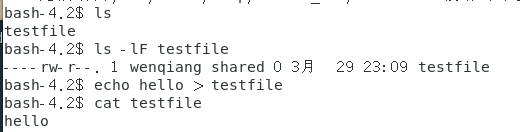
bash-4.2$ ls
bash-4.2$ ls -lF testfile
bash-4.2$ echo hello > testfile
bash-4.2$ cat testfile