本片笔记完全仿照【Flutter高级玩法-shape】Path在手,天下我有来学习的,感谢博主的分享。
平时在使用一些Widget的时候,有时候会碰到shape属性,但是完全没有用过,也只是在使用Card的时候看到过这个属性,今天偶然看到这个博客,想不到这个属性这么有用,所以就学习记录一下。
- 下面是一个完全没有使用
shape属性绘制出来的的一个Material控件:
Material(
color: Colors.orangeAccent,
elevation: 8.0,
child: Container(
alignment: Alignment.center,
padding: EdgeInsets.all(10.0),
constraints: BoxConstraints.expand(height:50.0),
child: Text("没有Shape的效果",style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),),
),
),
执行效果如下:

BoxBorder,BorderDirectional,Border
BoxBorder主要掌管边线方面的事,自身是一个abstract,不能直接使用。
BorderDirectional通过top,bottom,start,end分别控制上下左右的边线对象BorderSide。
下面使用BorderDirectional控制一个Material的边线:
Material(
color: Colors.pinkAccent,
elevation: 10.0,
shape: BorderDirectional(
top: BorderSide(color:Colors.redAccent,width: 5.0),
start: BorderSide(color: Colors.blueAccent,width: 10.0),
bottom: BorderSide(color: Colors.redAccent,width: 5.0),
end: BorderSide(color:Colors.blueAccent,width: 10.0),
),
child: Container(
alignment: Alignment.center,
constraints: BoxConstraints.expand(height: 50.0),
color: Colors.greenAccent,
child: Text("使用BorderDirectional控制边线",style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),),
),
),
最终的运行效果如下:

使用Border也可以达到上面的效果:
Material(
color: Colors.pinkAccent,
elevation: 10.0,
shape: Border(
top: BorderSide(color: Colors.redAccent, width: 5.0),
left: BorderSide(color: Colors.blueAccent, width: 10.0),
bottom: BorderSide(color: Colors.redAccent, width: 5.0),
right: BorderSide(color: Colors.blueAccent, width: 10.0),
),
child: Container(
constraints: BoxConstraints.expand(height: 50.0),
child: Text(
"使用Border控制边线",
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
),
alignment: Alignment.center,
),
),
从代码上来看,不管是BorderDirectional还是Border,内部都是使用BorderSide来设置边线的颜色和宽度的。
程序运行效果如下:

可以看到,和BorderDirectional运行效果是一致的。
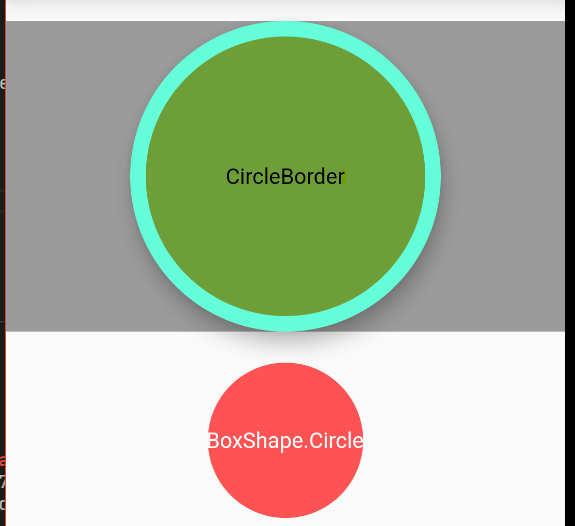
CircleBorder
CircleBorder会以min(width,height)为直径,裁切出一个圆形
//使用CircleBorder
Material(
color: Colors.lightGreenAccent,
elevation: 10.0,
shape: CircleBorder(side: BorderSide(color: Colors.tealAccent,width: 10.0)),
child: Container(
color: Colors.black38,
alignment: Alignment.center,
height: 200,
child: Text("CircleBorder",style: TextStyle(color: Colors.black),),
),
),
在Container中的decoration属性里面也可以指定shape的类型,现在将它指定为BoxShape.circle对比一下效果:
//对Container使用BorderShape.circle
Container(
alignment: Alignment.center,
margin: EdgeInsets.only(top: 20.0),
constraints: BoxConstraints.tightForFinite(height: 100.0),
child: Text("BoxShape.Circle",style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
shape: BoxShape.circle,
color: Colors.redAccent,
),
),
RoundedRectangleBorder和ContinuousRectangleBorder
圆角矩形:
Material(
color: Colors.limeAccent,
elevation: 10.0,
shape: RoundedRectangleBorder(
side: BorderSide(color: Colors.yellowAccent,width: 5.0),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.all(Radius.circular(5.0))
),
child: Container(
alignment: Alignment.center,
constraints: BoxConstraints.expand(height: 50.0),
color: Colors.black26,
child: Text("RoundedRectangleBorder圆角矩形",style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),),
),
),

从上面的效果图也可以看出,最好是就别给Container中再设置颜色了,否则圆角的效果就没有了。
ContinuousRectangleBorder的效果如下:
Material(
color: Colors.pinkAccent,
elevation: 10.0,
shape: ContinuousRectangleBorder(
side: BorderSide.none,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(20.0),
),
child: Container(
alignment: Alignment.center,
constraints: BoxConstraints.expand(height: 50.0),
child: Text("ContinuousRectangleBorder圆角矩形",style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),),
),
),

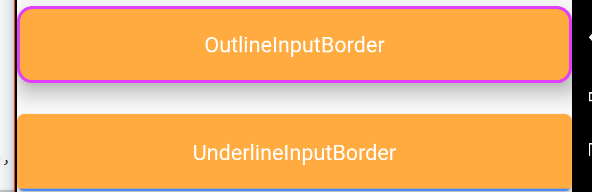
OutlineInputBorder和UnderlineInputBorder
这两个是常用的输入框的边线:
Material(
color: Colors.orangeAccent,
elevation: 10.0,
shape: OutlineInputBorder(
borderSide: BorderSide(color: Colors.purpleAccent,width: 2.0),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(10.0),
gapPadding: 10.0
),
child: Container(
alignment: Alignment.center,
height: 50.0,
child: Text("OutlineInputBorder",style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),),
),
),
Padding(padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 20.0)),
Material(
color: Colors.orangeAccent,
elevation: 2.0,
shape: UnderlineInputBorder(
borderSide: BorderSide(color: Colors.blueAccent,width: 3.0),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(5.0),
),
child: Container(
alignment: Alignment.center,
height: 50.0,
child: Text("UnderlineInputBorder",style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),),
),
),
自定义ShapeBorder
共有5个抽象方法:
class _MyShapeBorder extends ShapeBorder{
@override
// TODO: implement dimensions
EdgeInsetsGeometry get dimensions => null;
@override
Path getInnerPath(Rect rect, {TextDirection textDirection}) {
// TODO: implement getInnerPath
return null;
}
@override
Path getOuterPath(Rect rect, {TextDirection textDirection}) {
// TODO: implement getOuterPath
return null;
}
@override
void paint(Canvas canvas, Rect rect, {TextDirection textDirection}) {
// TODO: implement paint
}
@override
ShapeBorder scale(double t) {
// TODO: implement scale
return null;
}
}
可以看到有一个paint方法,在里面提供了Canvas和Rect,也就是可以在这个区域里面绘制,首先可以看一下这个Rect的参数:
shape rect is Rect.fromLTRB(0.0, 0.0, 360.0, 50.0)
可以看到直接拿到了可以绘制的区域。
首先在左上角绘制一个圆:
class _MyShapeBorder extends ShapeBorder {
//外部圆的paint
Paint _outPaint;
//内部圆的Paint
Paint _innerPaint;
_MyShapeBorder(){
_outPaint = Paint()
..color = Colors.deepOrangeAccent
..strokeWidth = 2.0
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke
..strokeJoin = StrokeJoin.round;
_innerPaint = Paint()
..color = Colors.black
..strokeWidth = 2.0
..style = PaintingStyle.fill
..strokeJoin = StrokeJoin.round;
}
@override
// TODO: implement dimensions
EdgeInsetsGeometry get dimensions => null;
@override
Path getInnerPath(Rect rect, {TextDirection textDirection}) {
// TODO: implement getInnerPath
return null;
}
@override
Path getOuterPath(Rect rect, {TextDirection textDirection}) {
// TODO: implement getOuterPath
return null;
}
@override
void paint(Canvas canvas, Rect rect, {TextDirection textDirection}) {
print("shape rect is${rect}");
double width = rect.width;
double height = rect.height;
canvas.drawCircle(Offset(0.1 * width, 0.3 * height), 0.1 * height, _outPaint);
canvas.drawCircle(Offset(0.1 * width, 0.3 * height), 0.05 * height, _innerPaint);
}
@override
ShapeBorder scale(double t) {
// TODO: implement scale
return null;
}
}
在Material中使用:
Material(
color: Colors.orangeAccent,
elevation: 2.0,
shape: _MyShapeBorder(),
child: Container(
alignment: Alignment.center,
height: 50.0,
child: Text(
"自定义ShapeBorder",
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
),
),
),
运行效果:

getOuterPath可以返回一个Path对象,也就是形状的裁剪,下面将上面的_MyShapeBorder裁剪为圆角矩形:
@override
Path getOuterPath(Rect rect, {TextDirection textDirection}) {
Path outerPath = Path();
outerPath.addRRect(RRect.fromRectAndRadius(rect, Radius.circular(10.0)));
return outerPath;
}

还可以做一些其它效果,比如在右边打个洞,具体实现就是将圆角矩形和圆形两个路径叠加,使用奇偶环绕来处理路径:
@override
Path getOuterPath(Rect rect, {TextDirection textDirection}) {
Path outerPath = Path();
outerPath.addRRect(RRect.fromRectAndRadius(rect, Radius.circular(10.0)));
var width = rect.width;
var height = rect.height;
//圆的直径
var radius = 0.2 * (min(width, height));
//计算圆所在的矩形的点
var pl = 0.1 * width;
var pt = 0.1 * height;
var left = width - radius - pl;
var top = pt;
var right = left + radius;
var bottom = top + radius;
outerPath.addOval(Rect.fromLTRB(left, top, right, bottom));
outerPath.fillType = PathFillType.evenOdd;
return outerPath;
}
运行效果如下:

上面已经做了在右上角添加一个洞,相应的,也可以抽象出一个类来在指定的位置添加一个洞:
//在指定位置打洞的ShapeBorder
class HoleShapeBorder extends ShapeBorder {
//指定圆角的大小
final Radius radius;
//洞的直径
final double diameter;
//指定偏移量
final Offset offset;
//可以不指定偏移量,指定宽度和高度的位置百分比
final double widthPercentage;
final double heightPercentage;
HoleShapeBorder(this.radius,
{this.offset,
this.widthPercentage = 0.0,
this.heightPercentage = 0,
this.diameter = 20})
: assert(
!(offset == null && (widthPercentage == 0 && heightPercentage == 0))),
assert(widthPercentage <= 1 && heightPercentage <= 1);
@override
EdgeInsetsGeometry get dimensions => null;
@override
Path getInnerPath(Rect rect, {TextDirection textDirection}) {
// TODO: implement getInnerPath
return null;
}
@override
Path getOuterPath(Rect rect, {TextDirection textDirection}) {
//首先根据指定的Radius在外边绘制一个圆角
Path path = Path();
path.addRRect(RRect.fromRectAndRadius(rect, radius));
var width = rect.width;
var height = rect.height;
//定义坐标
var left;
var top;
var right;
var bottom;
//距离左边的距离
var pl;
//距离上边的距离
var pt;
//判断offset是否为空
if (offset == null) {
pl = width * widthPercentage - diameter / 2;
pt = height * heightPercentage - diameter / 2;
} else {
//指定的偏移量大于可用的宽度
if (offset.dx > width)
pl = width - diameter;
else
pl = offset.dx;
//指定的偏移量大于可用的高度
if (offset.dy > height)
pt = height - diameter;
else
pt = offset.dy;
}
left = pl;
right = left + diameter;
top = pt;
bottom = top + diameter;
path.addOval(Rect.fromLTRB(left, top, right, bottom));
path.fillType = PathFillType.evenOdd;
return path;
}
@override
void paint(Canvas canvas, Rect rect, {TextDirection textDirection}) {
// TODO: implement paint
}
@override
ShapeBorder scale(double t) {
// TODO: implement scale
return null;
}
}
在上面的代码中,可以通过指定Offset(dx,dy)来设置打洞的位置,也可以通过设置洞的宽高比来设置所在的位置,如:
//自定义ShapeBorder -- 打洞
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 20.0, left: 20.0, right: 20.0),
child: Material(
color: Colors.orangeAccent,
elevation: 5.0,
shape: HoleShapeBorder(
Radius.circular(10.0),
widthPercentage: 0.5,
heightPercentage: 0.5,
),
child: Container(
constraints: BoxConstraints.expand(height: 60.0),
child: Text(
"自定义Shaper -- 打洞",
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white, fontSize: 16.0),
),
alignment: Alignment.center,
),
),
),
这里将指定的位置设置中间,执行效果如下:

根据指定偏移量打洞,下面根据Offset(20,20)打洞:
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 20.0, left: 20.0, right: 20.0),
child: Material(
color: Colors.orangeAccent,
elevation: 5.0,
shape: HoleShapeBorder(
Radius.circular(10.0),
offset: Offset(20, 20),
),
child: Container(
constraints: BoxConstraints.expand(height: 60.0),
child: Text(
"自定义Shaper -- 打洞",
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white, fontSize: 16.0),
),
alignment: Alignment.center,
),
),
),
运行效果如下:

打多个洞
在上面我们抽象出一些属性来做了一个简单继承的打洞的Shape,下面继续学习打多个洞:
//打多个洞的Shape
class MutilHoldShapeBorder extends ShapeBorder{
@override
// TODO: implement dimensions
EdgeInsetsGeometry get dimensions => null;
@override
Path getInnerPath(Rect rect, {TextDirection textDirection}) {
// TODO: implement getInnerPath
return null;
}
@override
Path getOuterPath(Rect rect, {TextDirection textDirection}) {
Path path = Path();
//首先仍然是绘制一个圆角
path.addRRect(RRect.fromRectAndRadius(rect, Radius.circular(10.0)));
//设置要绘制的洞的直径
double diameter = 20;
//洞之间的间距
double holePadding = 10;
//允许打洞的数量
int holeNum = rect.width ~/ (diameter + holePadding);
path.fillType = PathFillType.evenOdd;
//for循环打出每一个洞
int i = 0;
//距离左边的距离
var pl = holePadding;
//距离上边的距离
var pt = rect.height * 0.1;
double left = pl;
double top = pt;
for(i; i < holeNum; i++){
path.addOval(Rect.fromLTRB(left, top, left + diameter, top + diameter));
left += (holePadding + diameter);
}
return path;
}
@override
void paint(Canvas canvas, Rect rect, {TextDirection textDirection}) {
// TODO: implement paint
}
@override
ShapeBorder scale(double t) {
// TODO: implement scale
return null;
}
}
运行上面的代码,执行效果如下:

优惠券相关
使用Path也可以绘制出优惠券的背景,如下:
@override
Path getOuterPath(Rect rect, {TextDirection textDirection}) {
Path path = Path();
path.addRect(rect);
path.fillType = PathFillType.evenOdd;
//设置直径为30
var diameter = 30.0;
//上边缺口
//距离左边为0.7 * width
var gapTopPl = 0.7 * rect.width;
var gapTopPt = 0.0;
//首先在优惠券靠近右边的地方上下个绘制一个半圆
path.addArc(Rect.fromLTRB(gapTopPl, -diameter / 2, gapTopPl + diameter,diameter / 2 ),0,pi);
//下边缺口
var gapBottomPt = rect.height - diameter / 2;
path.addArc(Rect.fromLTRB(gapTopPl, gapBottomPt, gapTopPl + diameter, gapBottomPt + diameter),0,-pi);
return path;
}
需要注意的是,此时由于我们需要绘制的是半圆,所以这里使用path.addArc(Rect,startAngle,sweepAngle)来设置半圆的弧度。运行上面的代码,效果如下:

之后我们就需要切出左右两边的效果了,这个直径看起来有点大,可以小一点.
//优惠券左右两边的缺口
var gapPadding = 10.0;
//距离上边的偏移量
var gapLeftPt = gapPadding;
//计算可以切出的个数
var gapNum = (rect.height - gapPadding) ~/ (gapPadding + diameter);
print("可绘制的个数$gapNum");
for(int i = 0; i < gapNum; i++){
//绘制左边的缺口
path.addArc(Rect.fromLTRB(-diameter / 2 , gapLeftPt, diameter / 2 , gapLeftPt + diameter),-0.5 * pi, pi);
//绘制右边的缺口
path.addArc(Rect.fromLTRB(rect.width - (diameter / 2), gapLeftPt, rect.width + diameter / 2 , gapLeftPt + diameter), -0.5 * pi, -pi);
gapLeftPt += (gapPadding + diameter);
}

接着就是在上下两个缺口的位置绘制一条虚线:
@override
void paint(Canvas canvas, Rect rect, {TextDirection textDirection}) {
//绘制一条白色的虚线
var enableHeight = rect.height - diameter;
//虚线的高度为5,间隔为5
int dashNum = enableHeight ~/ 10;
var dashTop = diameter / 2;
var dashleft = rect.width * 0.7 + diameter / 2;
for(int i = 0; i < dashNum; i++){
if(dashTop + 5 > rect.height - diameter)
dashTop = rect.height - diameter;
canvas.drawLine(Offset(dashleft, dashTop), Offset(dashleft, dashTop + 5), _paint);
dashTop += 15;
}
}
运行效果如下:

ClipPath和Card
上面的示例都是在Material中使用,在ClipPath中也可以使用:
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 20.0, left: 20.0, right: 20.0),
child: ClipPath(
child: Image.asset(
"image/test.jpg",
fit: BoxFit.cover,
),
clipper: ShapeBorderClipper(shape: CouponShapeBorder()),
),
),

在Card中使用:
Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 20.0, left: 20.0, right: 20.0),
child: Card(
shape: MutilHoldShapeBorder(),
color: Colors.orangeAccent,
child: _ContentWidget("在Card中使用自定义Path"),
elevation: 5.0,
),
),
运行效果如下:

最后,再次感谢博主的分享,笔记中绘制的效果还有很多不尽如人意的地方,不满意可以查看原博主的文章:【Flutter高级玩法-shape】Path在手,天下我有