组成
-
所有Swift的“基本”类型都是值类型
- Int, Double, String,…
-
Swift的所有集合都是值类型
- 数组,集合,字典,…
-
包含值类型的Swift元组、结构和枚举是值类型
特点
变量独立
- Variables Are Logically Distinct
- Mutating one variable of some value type will never affect a different variable
//--变量独立
var a: Int = 5
var b = a
b = 10
//结果不同
print("a = \(a)", "b = \(b)") // a = 5, b = 10
//地址不同
var arryA = [1,2]
var arryB = arryA
withUnsafePointer(to: &arryA) {print($0)}
withUnsafePointer(to: &arryB) {print($0)}
可变性表达
- let 声明值不可改变
- var 声明值可变
//
let numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
//
var strings = [String]()
for x in numbers{
strings.append(String(x))
}
拷贝消耗小
-
Copying a low-level, fundamental type is constant time
- Int, Double, etc.
-
Copying a struct, enum, or tuple of value types is constant time
- CGPoint, etc.
-
Extensible data structures use copy-on-write
- Copying involves a fixed number of reference-counting operations
- String, Array, Set, Dictionary, etc.
值类型实践
绘制图像
协议抽象
类型结构和协议
struct Polygon {
var corners: [CGPoint] = []
init (corners: [CGPoint]){
self.corners = corners
}
}
struct Circle {
var center: CGPoint
var radius: CGFloat
init(center: CGPoint, radius: CGFloat) {
self.center = center
self.radius = radius
}
}
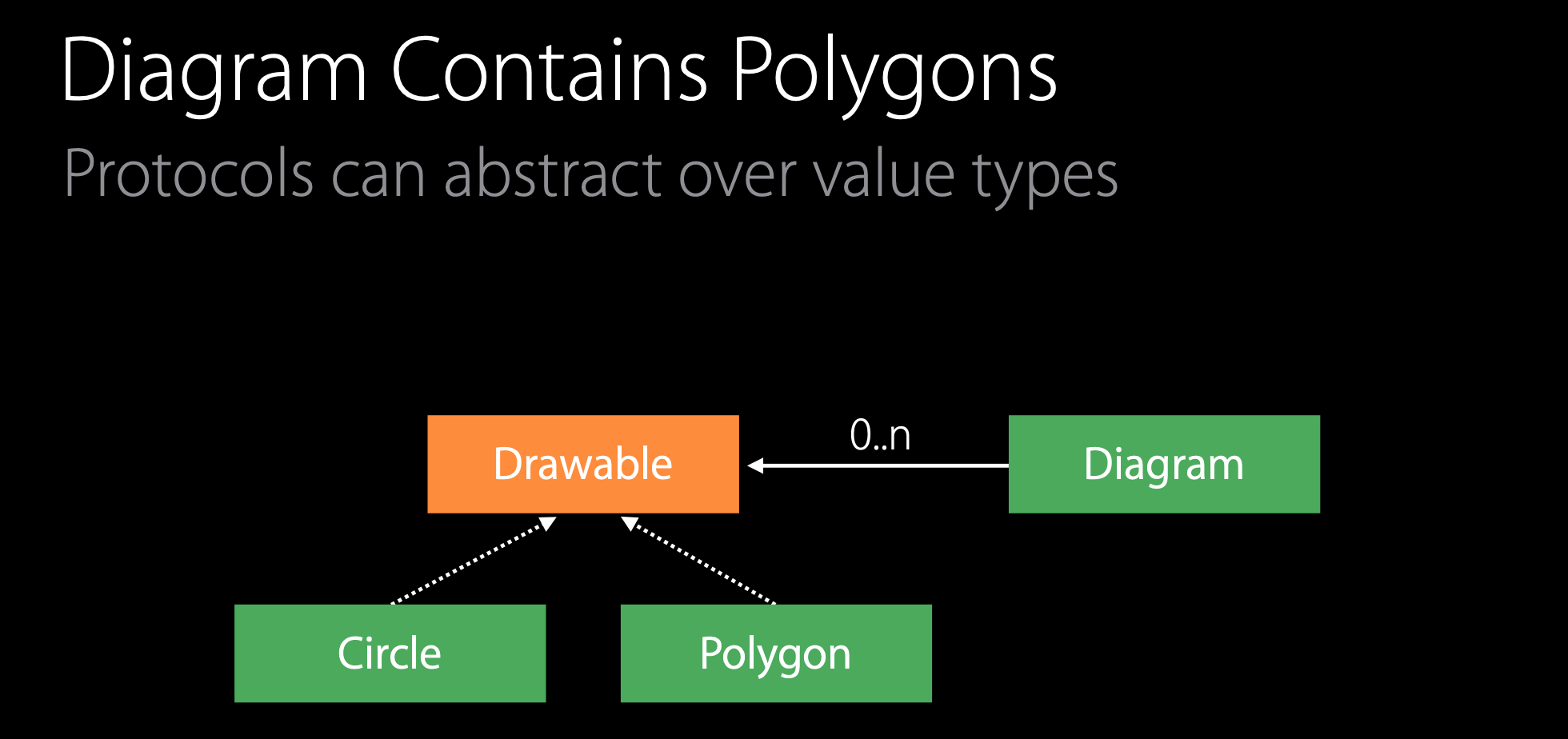
protocol Drawable {
func draw()
}
extension Polygon: Drawable {
func draw() {
let ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext()
ctx?.move(to: CGPoint.init(x: corners.last!.x, y: corners.last!.y))
for point in corners {
ctx?.addLine(to: CGPoint.init(x: point.x, y: point.y))
}
ctx?.closePath()
ctx?.strokePath()
}
}
extension Circle: Drawable {
func draw() {
let ctx = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext()
ctx?.addArc(center: CGPoint.init(x: center.x, y: center.y), radius: radius, startAngle: 0, endAngle: CGFloat.pi * 2, clockwise: true)
ctx?.closePath()
ctx?.strokePath()
}
}
struct Diagram {
var items: [Drawable] = []
mutating func addItem(item: Drawable) {
items.append(item)
}
func draw() {
for item in items {
item.draw()
}
}
}
绘图
//---绘图
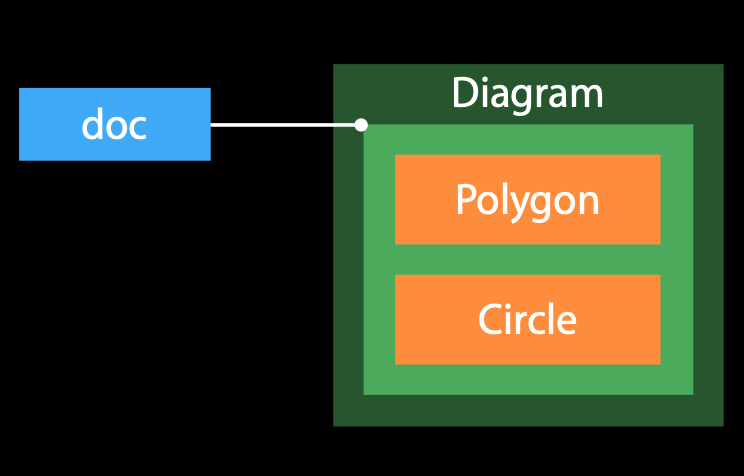
var doc = Diagram()
let corners = [
CGPoint.init(x: 0, y: 0),
CGPoint.init(x: 100, y: 0),
CGPoint.init(x: 100, y: 100),
CGPoint.init(x: 0, y: 100)
]
doc.addItem(item: Polygon.init(corners: corners))
doc.addItem(item: Circle.init(center: CGPoint.init(x: 50, y: 50), radius: 50))
doc.draw()
copy-on-write写时复制
为什么要使用写时复制
-
因为 Unrestricted mutation of referenced objects breaks value semantics 引用对象的不受限制的突变破坏了值语义. 案例: 值类型中有引用类型对象的属性.
-
高效, 只对突变的部分将引用对象独立拷贝一份,其它引用资源共享.
解决方法
引用对象的变异操作必须先拷贝
案例值类型结构
struct BezierPath{
private var _path = UIBezierPath()
var pathForReading: UIBezierPath{
return _path
}
var pathForWriting: UIBezierPath{
mutating get{
_path = _path.copy() as! UIBezierPath
return _path
}
}
}
extension BezierPath{
var isEmpty: Bool{
return pathForReading.isEmpty
}
mutating func addLineToPoint(point: CGPoint){
pathForWriting.addLine(to: point)
}
}
案例测试
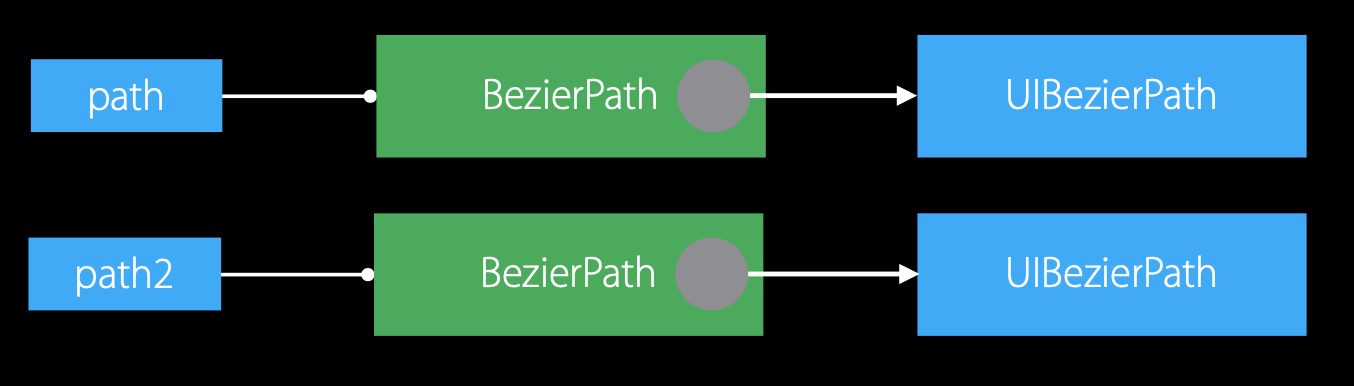
1.未引发写时复制
var path = BezierPath()
var path2 = path
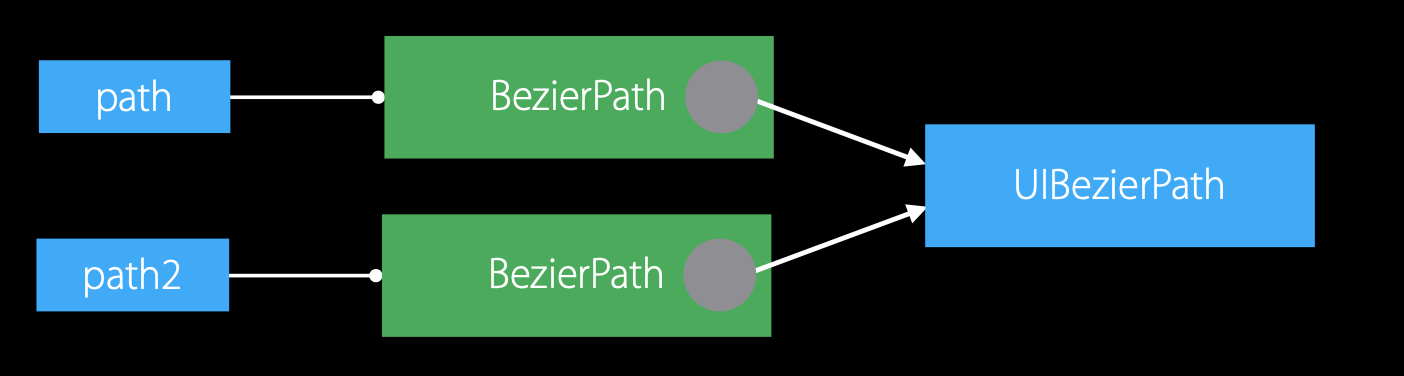
2.写时复制
var path = BezierPath()
var path2 = path
path.addLineToPoint(point: CGPoint(x: 10, y: 20))