一. 简介
最初的公钥方案是在 1977 年由 Ron Rivest、Adi Shamir 和Len Adleman 在 MIT 提出的,并且于 1978 年首次发表。 RSA 方案从那时起便占据了绝对的统治地位,成为最广泛接受和实现的通用公钥加密方法。 RSA 是分组密码,对于某个 m 它的明文和密文是 0〜n-1 之间的整数。
二. 用途
用于在开放的网络环境上保护电子通信,而不依赖于隐藏或隐蔽的通道,甚至用于密钥交换。开放的网络环境容易受到各种通信安全问题的影响,比如中间人攻击和欺骗。通信安全通常包括要求通信不得在运输途中可读(保存保密),通信在运输途中不能修改(保证沟通完整性),沟通必须来自一个确定原(发送方真实性),和收件人必须不能否定或拒绝接收的通信。将非对称加密与 Enveloped Public Key Encryption(EPKE)方法相结合,允许在开放的网络环境中安全发送通信。换句话说,即使密码分析者听了包括密钥交换在内的整个对话也无法解释对话。
公钥密码术中使用的区别技术是使用非对称密钥算法,其中一方用于执行加密的密钥与另一方用于解密的密钥不同。每个用户都有一对加密密钥——一个公共加密密钥和一个私有解密密钥。例如,用于数字签名的密钥对(包括一个私有签名密钥和一个公共验证密钥)。公钥可以广泛分发,而私钥只有其所有者知道。它们在数学上是相关的,但是选择参数是为了从公钥计算私钥是不可行的。
相反,对称密钥算法使用的是一个秘密密钥,它必须由发送方(用于加密)和接收方)用于解密)共享并保持私有。要使用对称加密方案,发送方和接收方必须事先安全地共享密钥。
由于对称密钥算法几乎总是比非对称密钥算法计算量小得多,所以通常使用密钥交换算法交换密钥,然后使用该密钥和对称密钥算法传输数据。PGP 和 SSL/TLS 方案家族使用这个过程,因此称为混合加密系统。综上非对称算法适用于
- 密钥交换
- 数字签名
- 与对称加密算法混合使用(PGP, SSL, TLS)
三. 原理
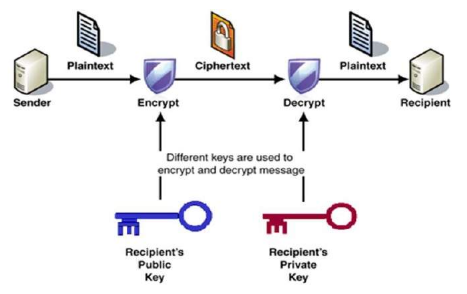
对于某一明文块M和密文块C,加密和解密有如下的形式:
发送方和接收方都必须知道 n 和 e 的值,并且只有接收者知道d的值。RSA 公钥密码算法的公钥KU=<e, n>, 私钥KR=<d, n>。为使该算法能够用于公钥加密,它必须满足下列要求:
- 可以找到 e、d、n 的值,使得对所有的 Medmod n = M 成立。
- 对所有满足 M < n 的值,计算 Me 和 Cd 相对容易。
- 给定 e 和 n 不可能推出 d
前两个要求很容易得到满足。当 e 和 n 取很大的值时,第三个要求也能够得到满足。下面的图 1 总结了 RSA 算法。
- 开始时选择两个素数 p 和 q,计算它们的积 n 作为加密和解密时的模。
- 接着需要计算 n 的欧拉函数值 φ(n)。φ(n) 表示小于 n 且与 n 互素的正整数的个数。
- 然后选择与 φ(n) 互素的整数 e,即 e 和 φ(n) 的最大公约数为 1。
- 最后,计算 e 关于模 φ(n) 的乘法逆元 d。d 和 e 具有所期望的属性。
假设用户 A 已经公布了他的公钥,且用户 B 希望给 A 发送消息 M。那么B计算 C = Me(mod n) 并且发送 C。当接收到密文时,用户 A 通过计算 M = Cd (mod n) 解密密文。
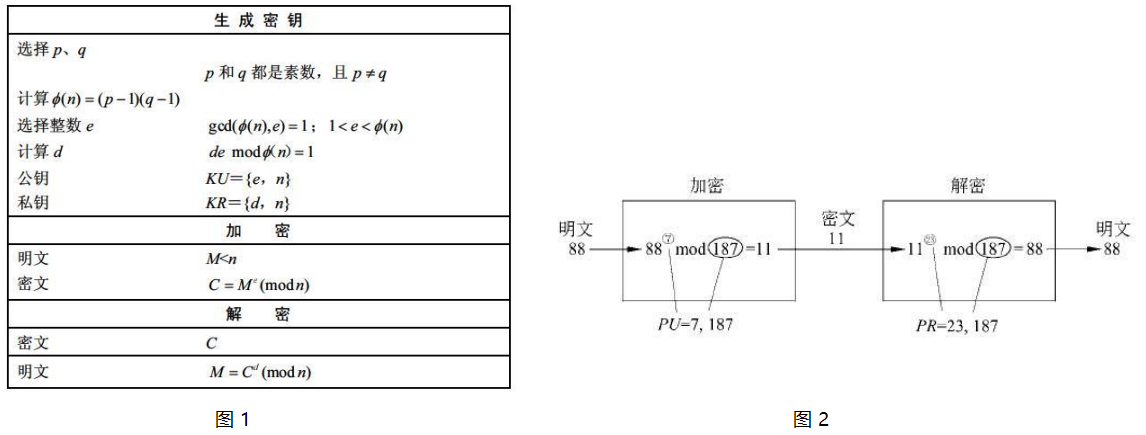
上面的图 2 显示一个例子。对于这个例子,按下列步骤生成密钥:
- 选择两个素数:p=17 和 q=11。
- 计算 n = pq = 17x11 = 187。
- 计算 φ(n) = (p-l)(q-l) = 16xl0 = 160。
- 选择 e,使得 e与φ(n) =160 互素且小于 φ(n):选择 e=7
- 计算 d,使得 de mod 160 = 1 且 d<160。 正确的值是 d=23 。这是因为 23x7 = 161 = 10x16 + 1。
这样就得到公钥PU = <7, 187>,私钥 PR = <23, 187>。下面的例子说明输入明文M= 88时密钥的使用情况。
对于加密,需要计算C = 887modl 87。利用模运算的性质,计算如下:
对于解密,计算M = 1123 mod 187:
四. 代码实现
说到这里,我们知道,要实现 RSA 算法,需要解决下面的数学问题:
- 如何产生素数?怎么进行素数测试?
- 怎么进行模幂运算,怎么实现快速模幂?
- 如何用欧几里得算法求最大公因子?
- 怎么用中国剩余定理(扩展欧几里得算法)求解 ax = b (mod m) ?
- 怎么构造一次同余方程,求乘法逆元?
1. 素数选择与素性测试
通过随机的方式生成大数,对这个大数进行一定轮数的素性测试。
素数又称质数,是在大于 1 的整数中,只能被 1 和其自身整除的数(如 2、3、5 等)。素性测试是检验一个给定的整数是否为素数的测试。常见的素性测试方法有:
- 试除法
- 概率性检验算法
- 费马小定理 (Fermat’s little theorem)
- 费马概率性检验 (Fermat primality test)
- 米勒-拉宾概率性检验 (Miller–Rabin primality test)
在这里不展开说了,感兴趣的朋友可以看看我的 这篇博客。下面PrimalityTester.isProbablePrime使用的是米勒-拉宾素性测试。
/**
* 随机生成一个可能是素数的数
* @param range 随机数产生范围
* @return 一个可能是素数的数
*/
public static long probablePrime(int range, int rounds) {
if (range > 0 && rounds > 0) {
ThreadLocalRandom random = ThreadLocalRandom.current();
while (true) {
int num = random.nextInt(range) + 2;
// 进行rounds轮素性测试
if (PrimalityTester.isProbablePrime(num, rounds))
return num;
}
}
return -1;
}
2. 实现模逆算法
欧几里得算法:利用辗转相除法求最大公约数。
public static long gcd(long m, long n) {
while(true){
if ((m = m % n) == 0)
return n;
if ((n = n % m) == 0)
return m;
}
}
使用实现非递归的扩展欧几里得算法求解ax + by = gcd(a,b)。
private static long extendedEuclid(long a, long b) {
long x = 0, y = 1, lastX = 1, lastY = 0, temp;
if (a < b) {
temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
while (b != 0) {
long q = a / b, r = a % b;
a = b;
b = r;
temp = x;
x = lastX - q * x;
lastX = temp;
temp = y;
y = lastY - q * y;
lastY = temp;
}
return lastY;
}
通过求解线性同余方程ax ≡ b(mod m)求解乘法逆元:
public static long linearCongruence(long a, long b, long m) {
if(b % gcd(a, m) != 0)
return - 1;
/*
通过扩展欧几里得算法求得x的逆元x'
x = kx', b = k(a, m)
所以要求地 x = (b / gcd(a, m)) * x'
*/
long result = (b / gcd(a, m)) * extendedEuclid(a, m);
if(result < 0)
result += m;
return result;
}
3. 实现快速模指运算
实现了模指运算的递归及非递归算法,因为是理论性实验,将实验数据控制在不会发生溢出的范围内,所以可以选用非递归的做法。modExpNonRec()实现了快速的运算算法,即反复平方乘算法。
实现了模指运算的递归及非递归算法,因为是理论性实验,将实验数据控制在不会发生溢出的范围内,所以可以选用非递归的做法。modExpNonRec()实现了快速的运算算法,即反复平方乘算法。
public static int exp(int x, int b, int n) {
if (b == 1) {
return x % n;
}
if ((b & 1)
L
/** Function to calculate (a ^ b) % c **/
public static long modExpNonRec(long a, long b, long c) {
long res = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) {
res *= a;
res %= c;
}
return res % c;
}
4. 编程实现 RSA 算法
基于上述的基础函数,可以写出RSA加解密算法,并进行封装。在加密时,因为当数值val超过2 << 16时,将val转换为char类型会发生溢出问题,所以将模逆结果值分割成两个字符表示,在解密时再进行还原。
package org.jordon.security.core.crypto.assymmetry;
import org.jordon.security.util.MathUtil;
import java.util.Base64;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
/**
* 原生RSA加解密算法实现
* @author Jrodon
* @since 2018/10
*/
public class RawRSACipherService {
// 密钥属性组
private long n, d, e;
// 素数的选择范围
private static final int RANGE = 2 << 10;
// 加密完得到的
private static final int SPLIT_POINT = 2 << 8;
// 素性测试轮数
private static final int PRIMALITY_TESTING_ROUNDS = 4;
// Base64编码工具
private static final Base64.Encoder encoder = Base64.getEncoder();
private static final Base64.Decoder decoder = Base64.getDecoder();
public RawRSACipherService() {
Random random = ThreadLocalRandom.current();
// 随机选择两个大素数
long p = MathUtil.probablePrime(RANGE, PRIMALITY_TESTING_ROUNDS), q;
do {
q = MathUtil.probablePrime(RANGE, PRIMALITY_TESTING_ROUNDS);
} while (p == q);
this.n = p * q;
long eulerVal = (p - 1) * (q - 1);
// 随机地取一个正整数e,1<e<φ(n)且(e,φ(n))=1,将e公开
do {
e = Math.abs(random.nextLong()) % eulerVal + 1;
}while (MathUtil.gcd(e, eulerVal) != 1);
// 根据ed = 1 (mod φ(n)),求出d,并对d保密
d = (MathUtil.linearCongruence(e, 1, eulerVal)) % eulerVal;
}
/**
* 加密函数,当数值val超过2 << 16时,将val转换为char类型会发生溢出问题
* 所以将模逆结果值分割成两个字符表示,在解密时再进行还原
* @param plaintext 明文
* @return 密文
*/
public String encrypt(String plaintext) {
int[] plaintextBytes = changeToInts(plaintext.toCharArray());
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
for (int plaintextByte : plaintextBytes) {
int modExpResult = (int) MathUtil.modExpNonRec(plaintextByte, e, n);
builder.append((char) (modExpResult / SPLIT_POINT)).
append((char) (modExpResult % SPLIT_POINT));
}
return encoder.encodeToString(builder.toString().getBytes());
}
/**
* 解密函数
* @param cipher 密文
* @return 明文
*/
public String decrypt(String cipher) {
// 获取解码后的字符串的字符数组
char[] cipherChars = new String(decoder.decode(cipher)).toCharArray();
// 将相邻两个字符合并,用一个整型数表示,得到原加密结果数组
int[] cipherInts = new int[cipherChars.length / 2];
for(int i = 0; i < cipherInts.length; i++)
cipherInts[i] = (int)cipherChars[i * 2] * SPLIT_POINT
+ (int)cipherChars[i * 2 + 1];
// 解密
int[] plaintextInts = new int[cipherInts.length];
for(int i = 0; i < cipherInts.length; i++)
plaintextInts[i] = (int)MathUtil.modExpNonRec(cipherInts[i], d, n);
StringBuilder plainText = new StringBuilder();
for (int plaintextInt : plaintextInts)
plainText.append((char) plaintextInt);
return plainText.toString();
}
/**
* 考虑到Java的字符编码问题和扩展性,将字符数组转化为int数组
* 而不用字节表示
* @param chars 字符数组
* @return int数组
*/
private int[] changeToInts(char[] chars) {
if (chars != null && chars.length > 0) {
int[] result = new int[chars.length];
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
result[i] = chars[i];
}
return result;
}
return null;
}
}
5. 利用 RSA 进行数据加解密
使用 JUnit 编写测试代码,为了便于查看,随机生成可打印的明文样例的进行 n 轮测试。为了便于查看,将素数选择范围调到 100,明文长度调到 20 个以内。
package org.jordon.security.core.crypto.assymmetry;
import org.jordon.security.util.ArrayUtil;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
public class RawRSACipherServiceTest {
private Random random = ThreadLocalRandom.current();
@Test
public void test() {
RawRSACipherService service = new RawRSACipherService();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // 进行30次测试
String example = genPlaintext();
ArrayUtil.printInfo("example", example, false);
String cipher = service.encrypt(example);
ArrayUtil.printInfo("cipher", cipher, false);
String plaintext = service.decrypt(cipher);
ArrayUtil.printInfo("plaintext", plaintext, true);
}
}
// 随机生成明文样例
private String genPlaintext() {
// 随机生成含有[1, 50]个可打印字符的字符串
int count = random.nextInt(20) + 1;
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
// 在可打印字符范围内随机获取
int val = random.nextInt(126 -33) + 33;
builder.append((char) val);
}
return builder.toString();
}
}
测试结果
example PQ?j+fMFCVcql`Q!W"Ca
cipher AMKeAC8ASQDCjAArAMKIAE0AJABDAMKJAFgAfQDCtQAoAC8AIQBXACIAQwAF
plaintext PQ?j+fMFCVcql`Q!W"Ca
example qX(zN0"X
cipher AH0AYwBgAMKFAMKxAAMAIgBj
plaintext qX(zN0"X
example \QWD6XO*=k?D6
cipher AMKSAC8AVwARAEEAYwAGAF0AGAAdAEkAEQBB
plaintext \QWD6XO*=k?D6
example abXluHtY}37j5
cipher AAUAYgBjAMK1AMKXAHsAwpwAWQBxAFUANwDCjABo
plaintext abXluHtY}37j5
6. 实现对大数据进行加密
为了实现对大数据进行加密,可以将上述过程中的数据类型从 long 改成 BigInteger,因为BigInteger中提供一系列专门用于 RSA 设计的方法
- 大素数产生: BigInteger.probablePrime (内置两重素性检验)
- 模幂运算:modPow()
- 模逆云散:modInverse()
所以很容易就能写出相应的 RSA 算法:
package org.jordon.security.core.crypto.assymmetry;
import lombok.Getter;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
@Getter
public class RSACipherService {
private final static BigInteger one = new BigInteger("1");
private final static SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
private BigInteger privateKey;
private BigInteger publicKey;
private BigInteger modulus;
// generate an N-bit (roughly) public and private key
public RSACipherService(int N) {
// 随机选取选取素数p,q
BigInteger p = BigInteger.probablePrime(N / 2, random);
BigInteger q = BigInteger.probablePrime(N / 2, random);
// 计算欧拉函数值
BigInteger phi = (p.subtract(one)).multiply(q.subtract(one));
modulus = p.multiply(q);
// 在实际应用中公钥通常为2^16 + 1
publicKey = new BigInteger("65537");
// 模逆运算
privateKey = publicKey.modInverse(phi);
}
// 加密
public BigInteger encrypt(BigInteger message) {
return message.modPow(publicKey, modulus);
}
// 解密
public BigInteger decrypt(BigInteger encrypted) {
return encrypted.modPow(privateKey, modulus);
}
public String toString() {
String s = "";
s += "public = " + publicKey + "\n";
s += "private = " + privateKey + "\n";
s += "modulus = " + modulus;
return s;
}
}
添加单元测试
package org.jordon.security.core.crypto.assymmetry;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
public class RSACipherServiceTest {
private RSACipherService service = new RSACipherService(2 << 10);
private final static SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
@Test
public void test() {
int N = 1024;
RSACipherService key = new RSACipherService(N);
System.out.println(key);
// create random message, encrypt and decrypt
BigInteger message = new BigInteger(N - 1, random);
BigInteger encrypt = key.encrypt(message);
BigInteger decrypt = key.decrypt(encrypt);
System.out.println("message = " + message);
System.out.println("encrypted = " + encrypt);
System.out.println("decrypted = " + decrypt);
}
}
测试结果
public = 65537
private = 78525902072320391608737916884640910364505357174525590710167120993759405509547140594627878863225003441361395545158796231923361941968429447718551660867382833237960574251865474859924434185132857131903215178186236747385107077061523018585463899345444036005905759639826169641884190715470009961170662302049779058113
modulus = 111123511057904247384303352454411628574852901907645613196843638982726078745879922118460167927517210453802508633681810948599960519752655050853574023973606618611715320478128088434295076817222464874390543837050033282496413714543565095232472865740444355218882825770580971590396819382161816782243359703760806220343
message = 64817416795314078589627041975736817397997584028795185521897274181295008592767171589585106415811184609379911184733318659651706555695848036601359747359521829105599014520845612387012461222627857364612289243289267763784602632108473742072081572298228631598483984218130386362800051626492833278994468945333676583030
encrypted = 67902482420062658281496748456690089583528632570276215918392904236166977373756787220355016586353876542515948791235556706391024025337777674873358863284240161449718904162441130678507273673627624342258514489584294519298979557329482563284543751683385911800817642057923152429340572932972532657573862337149437977501
decrypted = 64817416795314078589627041975736817397997584028795185521897274181295008592767171589585106415811184609379911184733318659651706555695848036601359747359521829105599014520845612387012461222627857364612289243289267763784602632108473742072081572298228631598483984218130386362800051626492833278994468945333676583030
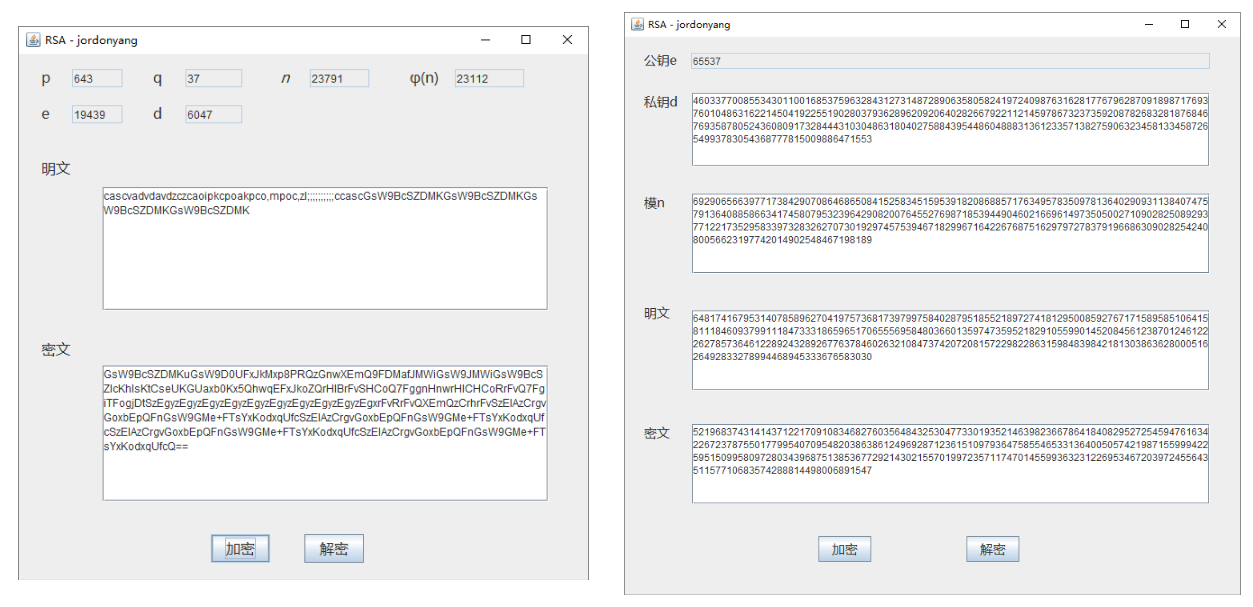
7. 实现简单的 GUI 界面
实现了普通 RSA 加解密界面 RSAView 和对大数据进行加解密的界面 RSABigIntegerView ,代码很长不贴了。
8. 分析总结
- RSA 算法是基于大合数难分解的数学事实实现的,只要 n 选的足够大,密码是很难被攻破的。
- 在确定密码参数情况下,解密时使用不同的d,不能还原明文。
- 在大素数产生环节,需要确定较可靠的素性检验算法,并进行足够多轮的测试验证。
- 随机数产生环节应考虑使用较安全的随机数生成算法,如对种子进行哈希等。
- 模幂运算是 RSA 的核心运算,在设计 RSA 实现时应该考虑使用更加高效的模幂算法,以提高 RSA 加解密的速度。
另外,本文涉及的代码片段已经上传到 Github,感兴趣的朋友可以去看看,如果对你有帮助,希望能点个 star 或 fork 支持一下。