我们知道属性修饰词一般都用nonatomic,因为是修饰对象的,所以关于atomic的源码是在objc,我们打开objc源码,然后查找reallySetProperty方法
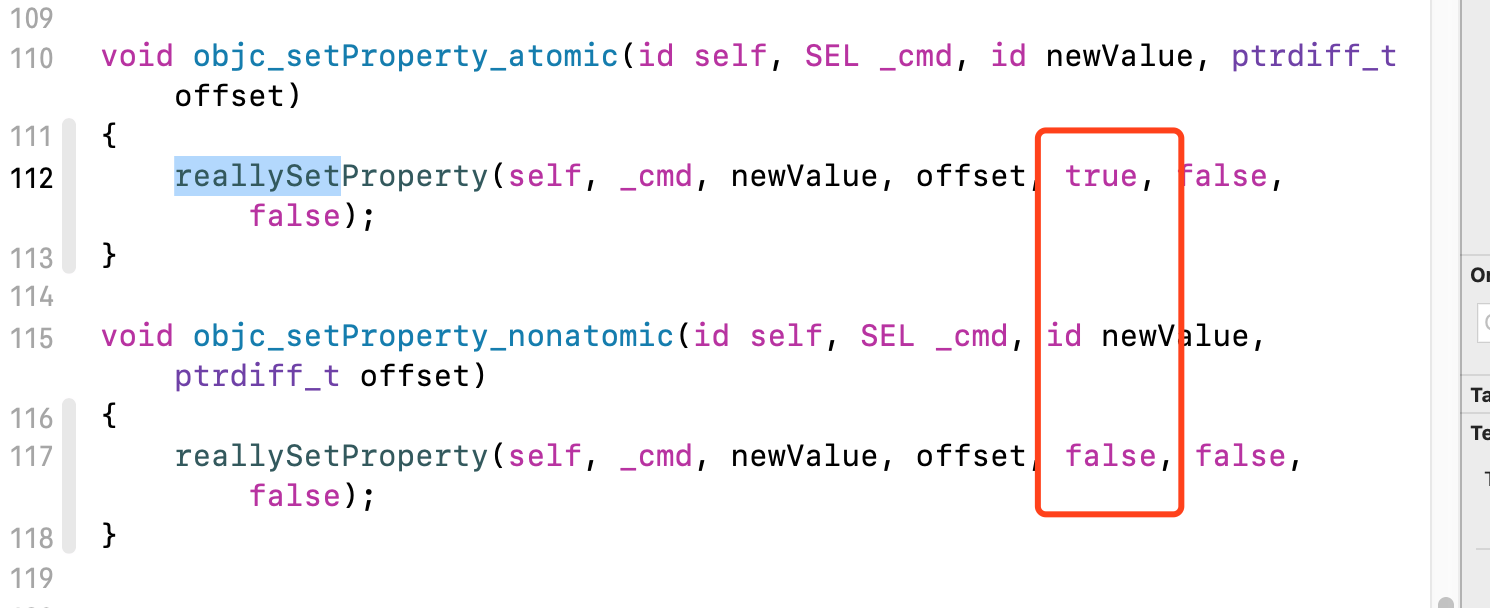
我们看到atomic和nonatomic只有第五个参数是不一样的,我们点进reallySetProperty看看
static inline void reallySetProperty(id self, SEL _cmd, id newValue, ptrdiff_t offset, bool atomic, bool copy, bool mutableCopy)
{
if (offset == 0) {
object_setClass(self, newValue);
return;
}
id oldValue;
id *slot = (id*) ((char*)self + offset);
if (copy) {
newValue = [newValue copyWithZone:nil];
} else if (mutableCopy) {
newValue = [newValue mutableCopyWithZone:nil];
} else {
if (*slot == newValue) return;
newValue = objc_retain(newValue);
}
//读写锁、自旋锁、互斥锁
if (!atomic) {
oldValue = *slot;
*slot = newValue;
} else {
//对slot进行加盐,避免哈希冲突
spinlock_t& slotlock = PropertyLocks[slot];
slotlock.lock();//加锁
oldValue = *slot;
*slot = newValue;
slotlock.unlock();
}
objc_release(oldValue);
}
我们看到。当不是atomic时候,setter方法是直接将值传递过去,当时atomic时候会加一把锁后再赋值。
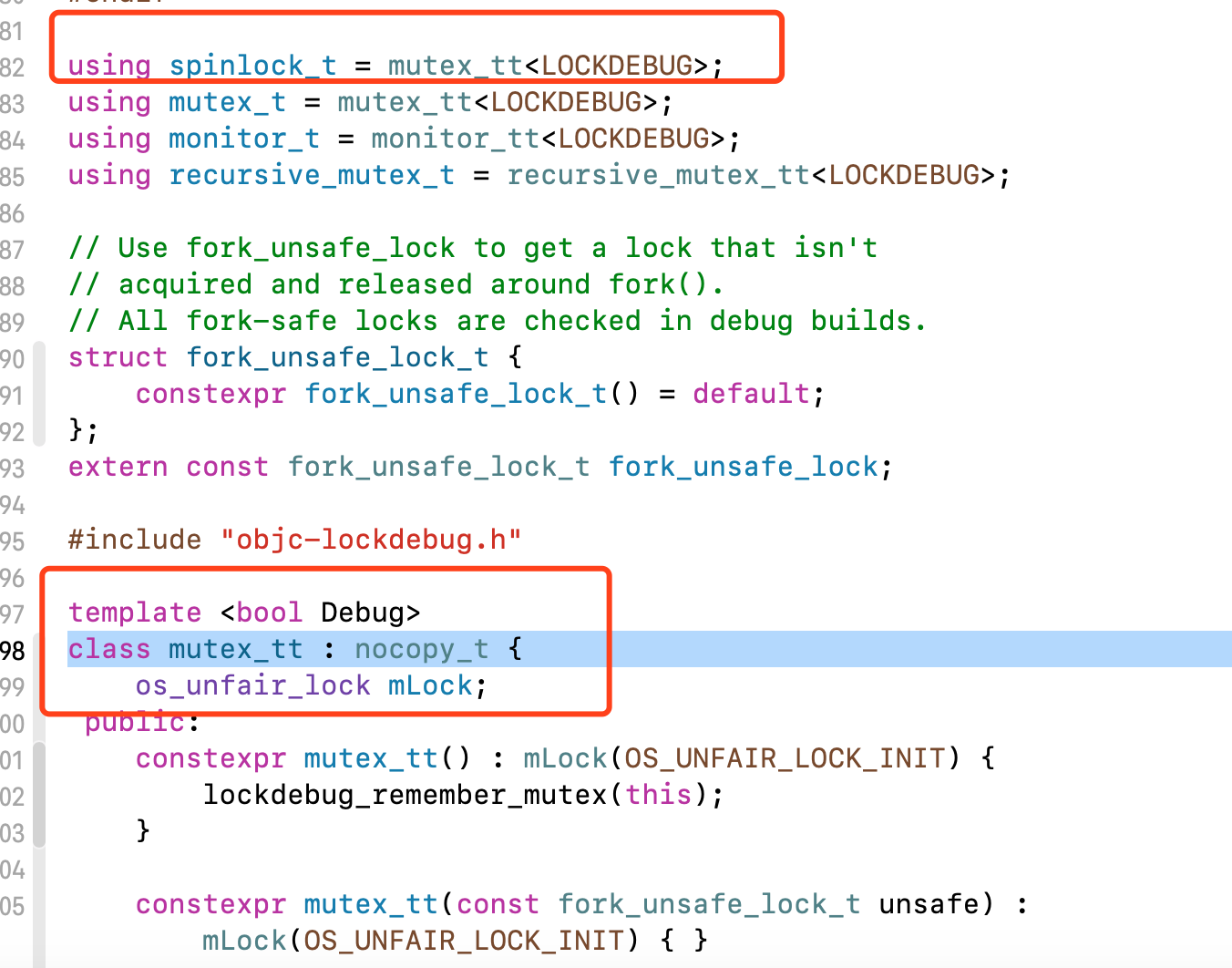
这个地方我们看到spinlock_t其实是做了一下转换,真正的锁是os_unfair_lock,
我们再看一下getter方法,搜一下getProperty
id objc_getProperty(id self, SEL _cmd, ptrdiff_t offset, BOOL atomic) {
if (offset == 0) {
return object_getClass(self);
}
// Retain release world
id *slot = (id*) ((char*)self + offset);
if (!atomic) return *slot;
// Atomic retain release world
spinlock_t& slotlock = PropertyLocks[slot];
slotlock.lock();
id value = objc_retain(*slot);
slotlock.unlock();
// for performance, we (safely) issue the autorelease OUTSIDE of the spinlock.
return objc_autoreleaseReturnValue(value);
}
我们看到get方法中如果不是atomic的话,直接返回属性里面的值,如果是atomic的话,也会加一个锁,然后将属性值retain一下得到一个新的变量,然后再将这个变量release一下return回去。
上面我们知道atomic会对set和get方法都加上自旋锁,但是因为要不断加锁解锁,所以会很消耗性能,但是是否加完锁就一定安全呢,我们做一下下面验证
- (void)lg_test_atomic2{
//Thread A
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i ++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
self.array = @[@"Hank", @"CC", @"Cooci"];
}
else {
self.array = @[@"Kody"];
}
NSLog(@"Thread A: %@\n", self.array);
}
});
//Thread B
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i ++) {
if (self.array.count >= 2) {
NSString* str = [self.array objectAtIndex:1];
}
NSLog(@"Thread B: %@\n",self.array);
}
});
}
上面代码运行崩了,因为atomic仅仅对set和get方法进行加密,但是无法控制外面的宏观线程,例如上面代码,由于是多线程set和get,在get方法哪里,有可能if判断完成后还没开始get时候又进行了一次set方法,所以无法保证get和set的安全,所以atomic只能保证自己本身的set和get安全,而无法保证外面宏观的线程问题
还有一个例子:
- (void)lg_test_atomic1{
//Thread A
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i ++) {
self.num = self.num+1;
NSLog(@"Thread A: %d\n", self.num);
}
});
//Thread B
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i ++) {
self.num = self.num+1;
NSLog(@"Thread b : %d\n", self.num);
}
});
}
08 13:37:29.917947+0800 005-atomic分析[61880:10355767] Thread A: 19989
2020-03-08 13:37:29.918004+0800 005-atomic分析[61880:10355767] Thread A: 19990
2020-03-08 13:37:29.918085+0800 005-atomic分析[61880:10355767] Thread A: 19991
2020-03-08 13:37:29.918149+0800 005-atomic分析[61880:10355767] Thread A: 19992
2020-03-08 13:37:29.918223+0800 005-atomic分析[61880:10355767] Thread A: 19993
2020-03-08 13:37:29.918309+0800 005-atomic分析[61880:10355767] Thread A: 19994
2020-03-08 13:37:29.918329+0800 005-atomic分析[61880:10355767] Thread A: 19995
2020-03-08 13:37:29.918382+0800 005-atomic分析[61880:10355767] Thread A: 19996
2020-03-08 13:37:29.918433+0800 005-atomic分析[61880:10355767] Thread A: 19997
2020-03-08 13:37:29.918532+0800 005-atomic分析[61880:10355767] Thread A: 19998
按道理最后应该是20000的,但实际上少了两个,进一步验证atomic并不安全,所以关于线程安全还是需要程序员自己去处理