剑指offer部分
链表
合并两个排序的链表
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null){
return list2;
}
if(list2 == null){
return list1;
}
if(list1.val <= list2.val){
list1.next = Merge(list1.next,list2);
return list1;
}
else {
list2.next = Merge(list1,list2.next);
return list2;
}
}
}
复制复杂的链表
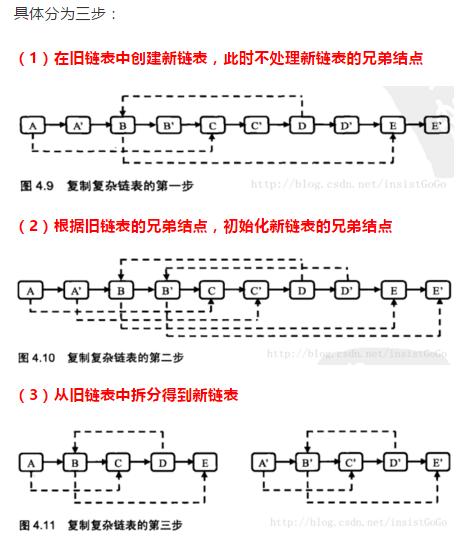
/*
public class RandomListNode {
int label;
RandomListNode next = null;
RandomListNode random = null;
RandomListNode(int label) {
this.label = label;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead)
{
if(pHead == null){
return null;
}
//复制结点,如复制A结点得到A1,将A1插入到A结点后面
RandomListNode curNode = pHead;
while(curNode != null){
RandomListNode cloneNode = new RandomListNode(curNode.label);
cloneNode.next = curNode.next;
curNode.next = cloneNode;
curNode = curNode.next.next;
}
//重新遍历链表,复制老结点的随机指针给新结点
curNode = pHead;
while(curNode != null){
// RandomListNode nextNode = new RandomListNode(curNode.label);
// nextNode = curNode.next;
curNode.next.random = curNode.random == null?null:curNode.random.next;
curNode = curNode.next.next;
}
//拆分链表,将链表拆分成复制后的链表和原链表
curNode = pHead;
RandomListNode pclone = curNode.next;
while(curNode !=null){
RandomListNode cloneNode = curNode.next;
curNode.next = cloneNode.next;
cloneNode.next = cloneNode.next==null?null:cloneNode.next.next;
curNode=curNode.next;
}
return pclone;
}
}
数组
顺时针打印数组
思路为:先归纳外圈打印规律为4个方向,然后可以归纳内圈与外圈打印的相似点
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix(int [][] matrix) {
ArrayList<Integer> printList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(matrix==null || matrix.length==0){
return printList;
}
int rlen = matrix.length-1;
int clen = matrix[0].length-1;//这个地方要注意
printMatrix(0,0,rlen,clen,printList,matrix);
return printList;
}
public void printMatrix(int startrow,int startcol,int endrow,int endcol,ArrayList<Integer> printList,int[][] matrix){
if(startrow < endrow && startcol <endcol){
//打印的时候最好自己先想清楚打印逻辑,其实可以边写边想思路,不是很复杂的题目可以一边打规律一遍想特点
for(int j=startcol;j<=endcol;j++) printList.add(matrix[startrow][j]);//右
for(int i=startrow+1;i<=endrow-1;i++) printList.add(matrix[i][endcol]);//下
for(int j=endcol;j>=startcol;j--) printList.add(matrix[endrow][j]);//左
for(int i=endrow-1;i>=startrow+1;i--) printList.add(matrix[i][startcol]);//上
printMatrix(startrow+1,startcol+1,endrow-1,endcol-1,printList,matrix);
}
else if(startrow == endrow && startcol<endcol){
for(int j=startcol;j<=endcol;j++)printList.add(matrix[startrow][j]);
}
else if(startrow<endrow && startcol==endcol){
for(int i=startrow;i<=endrow;i++)printList.add(matrix[i][startcol]);
}
else if(startrow == endrow && startcol == endcol){
printList.add(matrix[startrow][startcol]);
}
else {
return;
}
}
}
/*
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
*/
栈
包含min函数的栈
有两种方法,一种是借用辅助栈保持栈顶元素始终为最小的数,一种是维护一个记录最小值的变量
- 维护一个记录最小值的变量
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Solution {
//以下数字标注为自己白板写的时候编译错误
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>();//1
public void push(int node) {
s.push(node);
}
public void pop() {
s.pop();
}
public int top() {
return s.peek();
}
public int min() {
int min=s.peek();
int tmp=0;
Iterator<Integer> it = s.iterator();//2
while(it.hasNext()){//3
tmp=it.next();
if(min>tmp){
min=tmp;
}
}
return min;
}
}
- 借助辅助栈
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> minStack = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
if(minStack.empty() || node < minStack.peek())
minStack.push(node);
}
public void pop() {
if(stack1.peek() == minStack.peek()) //因为minStack维护的是stack1的最小值,当stack1不存在该最小值时,minStack也应该弹出该元素
minStack.pop();
stack1.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stack1.peek();
}
public int min() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
栈的压入,弹出序列
思路:通过实际的栈操作来模拟栈的弹出,压入
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public boolean IsPopOrder(int [] pushA,int [] popA) {
//3 4 5 2 1
if(pushA==null || popA == null || pushA.length==0||popA.length==0||pushA.length!=popA.length){
return false;
}
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>();
int i=0,j=0;
s.push(pushA[i++]);
while(j<=popA.length-1){
while(popA[j]!=s.peek()){
if(i == pushA.length) return false;
s.push(pushA[i++]);
}
s.pop();
j++;
}
return true;
}
}
队列
从上往下打印二叉树
思路:使用队列来实现二叉树的广度遍历,这里可以直接借助ArrayList模拟
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null){
return result;
}
queue.add(root);
while(queue.size()!=0){
TreeNode tmp = queue.remove(0);
if(tmp.left !=null){
queue.add(tmp.left);
}
if(tmp.right !=null){
queue.add(tmp.right);
}
result.add(tmp.val);
}
return result;
}
}