六、Webpack 底层原理及脚手架工具分析
1.如何编写一个Loader
css-loader、style-loader、 file-loader等 当我们打包一个类型文件或模块的时候,loader就会产生作用。
写完loaders之后,只要在module中配置好相应的规则,就可以使用了。
// index.js
console.log('hello fruit')
// wepack.config.js
module.exports = {
mode: "development",
entry: {
main: './src/index.js'
},
module: {
rules: [{
test: /\.js/,
use: [path.resolve(__dirname, './loaders/replaceLoader.js')] // 配置自己写的loader
}]
},
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: '[name].js'
}
}
// replaceLoader.js
module.exports = function (source) { // 不要用箭头函数,this指向会有问题
return source.replace('fruit', 'fruitBro')
}
// package.json
{
"name": "make-loader",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"devDependencies": {
"webpack": "^4.41.6",
"webpack-cli": "^3.3.11"
}
}
npm run build
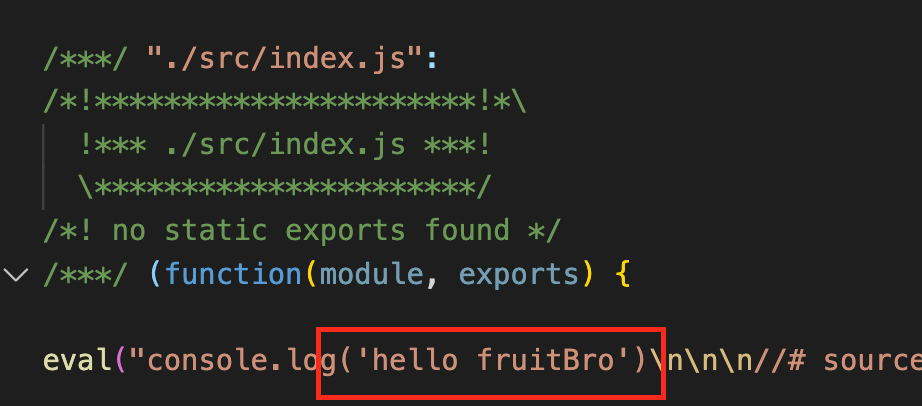
replaceLoader成功将fruit替换为fruitBro
继续优化:
// wepack.config.js
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [{
test: /\.js/,
use: [
{
loader: path.resolve(__dirname, './loaders/replaceLoader.js'),
options: {
name: 'Fruit'
}
}
],
}]
},
}
通过query参数可获取name参数,可通过以下方式打印:
// replaceLoader.js
module.exports = function (source) {
console.log("======",this.query) // { name: 'Fruit' }
return source.replace('fruit', 'fruitBro')
}
因此我们可以用上述方式进行替换
// replaceLoader.js
module.exports = function (source) {
return source.replace('fruit', this.query.name)
}
编译生成的代码如下:
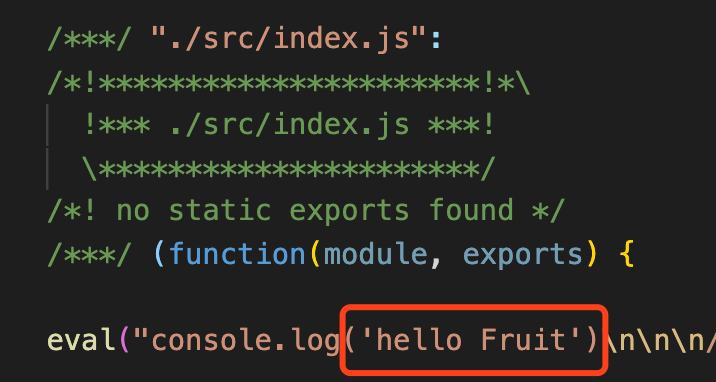
参考文档: webpack.docschina.org/api/loaders…
但是this.query.name的写法并不是很方便。因此官方提供了loader-utils模块,帮助我们分析内容。
参考文档: webpack.docschina.org/api/loaders…
npm install loader-utils --save-dev
写法改为如下:
const loaderUtils = require('loader-utils')
module.exports = function (source) {
const options = loaderUtils.getOptions(this) // 会将参数的所有内容都放到options中
return source.replace('fruit', options.name)
}
参考文档:webpack.docschina.org/api/loaders…
此时的loader只能return一个结果,额外的东西无法带出去,比如sourceMap,此时可以通过this.callback带出去
this.callback共四个参数
this.callback(
err: Error | null,
content: string | Buffer,
sourceMap?: SourceMap,
meta?: any
);
module.exports = function (source) {
const options = loaderUtils.getOptions(this)
const result = source.replace('fruit', options.name) // 通过loader解析后的新的源代码
// this.callback(null, result, sourceMap) // 共四个参数
this.callback(null, result) 这样写等价于return
}
在loader中做异步操作
参考文档:webpack.docschina.org/api/loaders…
this.async会告诉 loader-runner 这个 loader 将会异步地回调。返回 this.callback。和上述的this.callback一样,需要传入4个参数。
module.exports = function (source) {
const options = loaderUtils.getOptions(this)
const callback = this.async()
setTimeout(() => {
const result = source.replace('fruit', options.name)
callback(null, result)
}, 5000) // loader需要5秒才能执行完
}
以上就是一个异步loader的编写方法。
多个loader同时使用的写法,replaceLoaderAsync.js、replaceLoader.js。loader的使用顺序,从下到上,从右到左。
// replaceLoaderAsync.js
const loaderUtils = require('loader-utils')
module.exports = function (source) {
const options = loaderUtils.getOptions(this)
const callback = this.async()
setTimeout(() => {
const result = source.replace('fruit', options.name) // 先把fruit替换为Fruit,再把Fruit替换为Fruit Bro
callback(null, result)
}, 1000) // loader需要5秒才能执行完
}
// replaceLoader.js
module.exports = function (source) {
return source.replace('Fruit', 'Fruit Bro')
}
// wepack.config.js
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [{
test: /\.js/,
use: [
{
loader: path.resolve(__dirname, './loaders/replaceLoader.js'),
},
{
loader: path.resolve(__dirname, './loaders/replaceLoaderAsync.js'),
options: {
name: 'Fruit'
}
},
],
}]
},
}
可以把path.resolve(__dirname省略掉,借助resolveLoader,写法如下:
// wepack.config.js
module.exports = {
resolveLoader: {
modules: ['node_modules', './loaders']
},
module: {
rules: [{
test: /\.js/,
use: [
{
loader: 'replaceLoader',
},
{
loader: 'replaceLoaderAsync',
options: {
name: 'Fruit'
}
},
],
}]
},
}
以上就是自定义loader的常见语法.
重点:
loader这个函数一定要是声明式的定义function,而不能是箭头函数,loader中要用this方法,this的指向在箭头函数下可能会出错。loader分同步和异步。异步要先调用一下this.async()。
常用实例:
- 前端代码的异常捕获。
try catch,代码中出现function的时候就替换成try{function {} } catch(e),把所有的代码都放到try catch中执行,这样我们只需要写一个loader就能解决错误监控的问题了,就能异常捕获了。 - 国际化网站。在loader中进行中英文替换,通过占位符的方法来解决,写法如下:
if (Node全局变量 === '中文') {
source.replace('{{title}}', '中文标题')
} else {
source.replace('{{title}}', 'english title')
}
不过我们现在都用react-intl-universal来实现国际化。
2.如何编写一个Plugin
loader和plugin之间有什么区别呢?loader在文件执行的过程中修改文件,帮助我们处理模块;plugin在打包结束之后或某些具体时刻上,如在打包之前用CleanWebpackPlugin,在打包之后用htmlWebpackPlugin。在打包过程中的某些时刻,想做一些时间,可以用插件来实现。随着plugin越来越多,webpack能做的事情也越来越多。plugin是webpack的灵魂。plugin的核心设计模式:事件驱动、发布订阅的设计模式。代码之前的执行是通过事件来驱动的。
plugin(插件)的定义形式和loader的定义形式不同,loader是一个函数,plugin是一个class类。
为什么使用plugin的时候,要使用实例的方法new,因为plugin本质上是class,要创建一个实例才能使用它。
定义插件:
// copyright-webpack-plugin.js
class CopyRightWebpackPlugin {
constructor () {
console.log('plugin used')
}
apply(compiler) {
}
}
module.exports = CopyRightWebpackPlugin
使用插件:
// webpack.config.js
const path = require('path')
const CopyrightwebpackPlugin = require('./plugins/copyright-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
mode: 'development',
entry: {
main: './src/index.js'
},
plugins: [
new CopyrightwebpackPlugin()
],
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: '[name].js',
}
}
插件接收参数的方式:
// 传递参数
new CopyrightwebpackPlugin({
name: 'Fruit'
})
// 接收参数 options,使用constructor来接收参数
constructor (options) {
console.log('plugin', options)
}
compiler-hooks
参考文档: webpack.docschina.org/api/compile…
钩子:就是在某一时刻会自动执行的一个函数
webpack.docschina.org/api/compile…
本次目的:在dist文件夹中新增一个copyright.txt
compilation.assets的打印结果如下图:
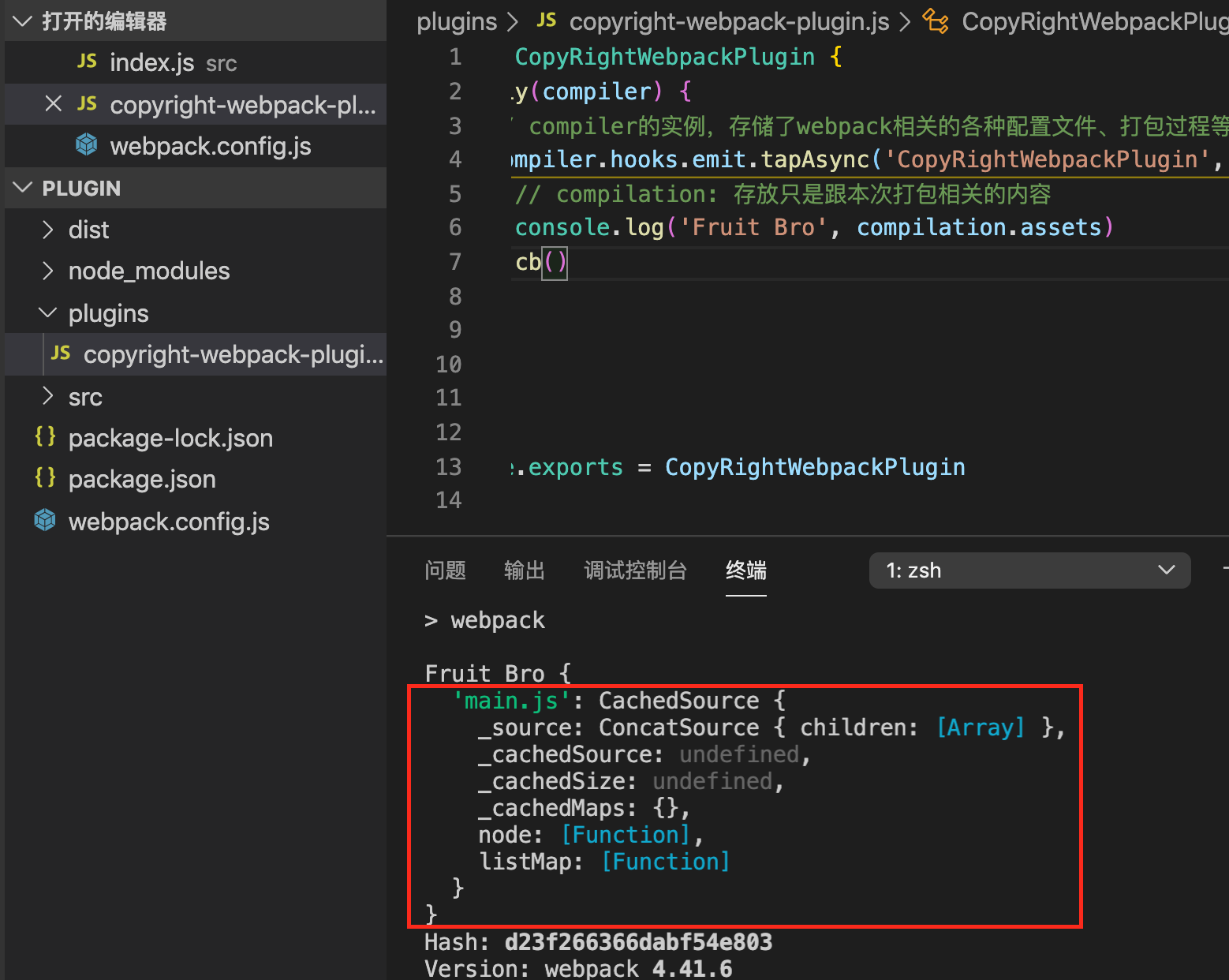
// copyright-webpack-plugin.js
class CopyRightWebpackPlugin {
apply(compiler) {
// compiler的实例,存储了webpack相关的各种配置文件、打包过程等一系列内容
compiler.hooks.emit.tapAsync('CopyRightWebpackPlugin', (compilation, cb) => {
// compilation: 存放只是跟本次打包相关的内容
// compilation.assets : 打包生成的内容是放在assets中的
console.log('Fruit Bro', compilation.assets)
// 有mian.js的key值,我们在新增一个'copyright.txt'的key值
compilation.assets['copyright.txt'] = {
source: function () {
return 'copyright by FruitBro'
},
size: function () {
return 21
}
}
cb()
})
}
}
module.exports = CopyRightWebpackPlugin
上述插件的作用:在即将把代码放到dist目录之前,往代码中增加了一个copyright.txt文件。下图打印结果,使用了emit时刻。
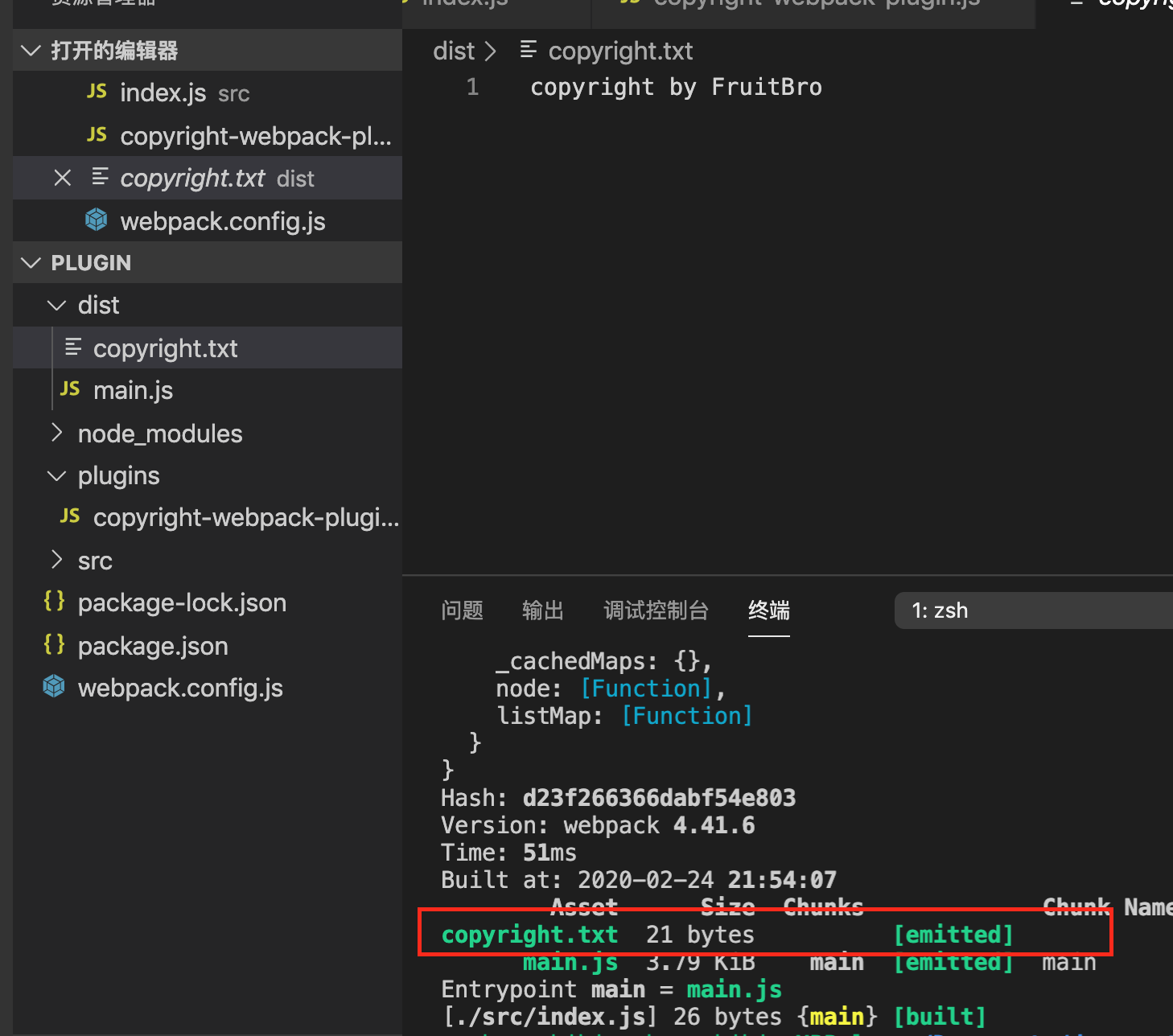
compilation还有很多时刻
// package.json 调试命令
{
"scripts": {
"debug": "node --inspect --inspect-brk node_modules/webpack/bin/webpack.js",
"build": "webpack"
},
}
- 在要调试的地方加入
debugger
class CopyRightWebpackPlugin {
apply(compiler) {
compiler.hooks.compile.tap('CopyRightWebpackPlugin', (compilation) => {
console.log('compiler')
})
compiler.hooks.emit.tapAsync('CopyRightWebpackPlugin', (compilation, cb) => {
debugger // 调试
compilation.assets['copyright.txt'] = {
source: function () {
return 'copyright by FruitBro'
},
size: function () {
return 21
}
}
cb()
})
}
}
module.exports = CopyRightWebpackPlugin
2.运行npm run debug
npm run debug
-
打开
devtool,点击左上角的node按钮
-
在
watch处添加compilation
-
这样即可看到
compilation中包含的所有方法
总结:
- 学会写一个类class
- 写apply方法
- 学会如何使用node调试工具进行插件调试
3. Bundler源码编写(模块分析)
手写简单类似webpack的Bundler
打印index.js的文件内容如下:
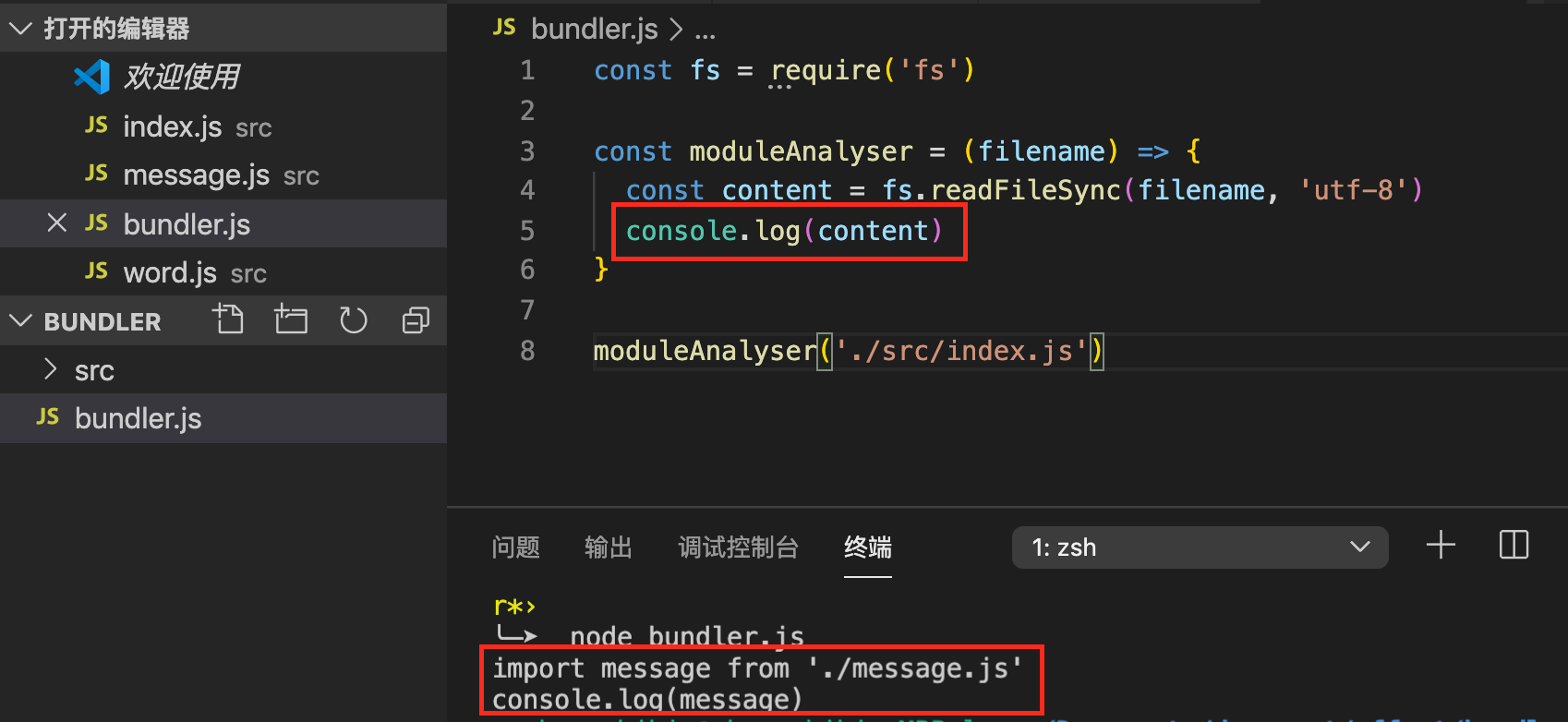
npm install cli-highlight -g
安装完成后,打印的内容可以部分高亮
node bundler.js | highlight
npm install @babel/parser // 帮助分析源代码
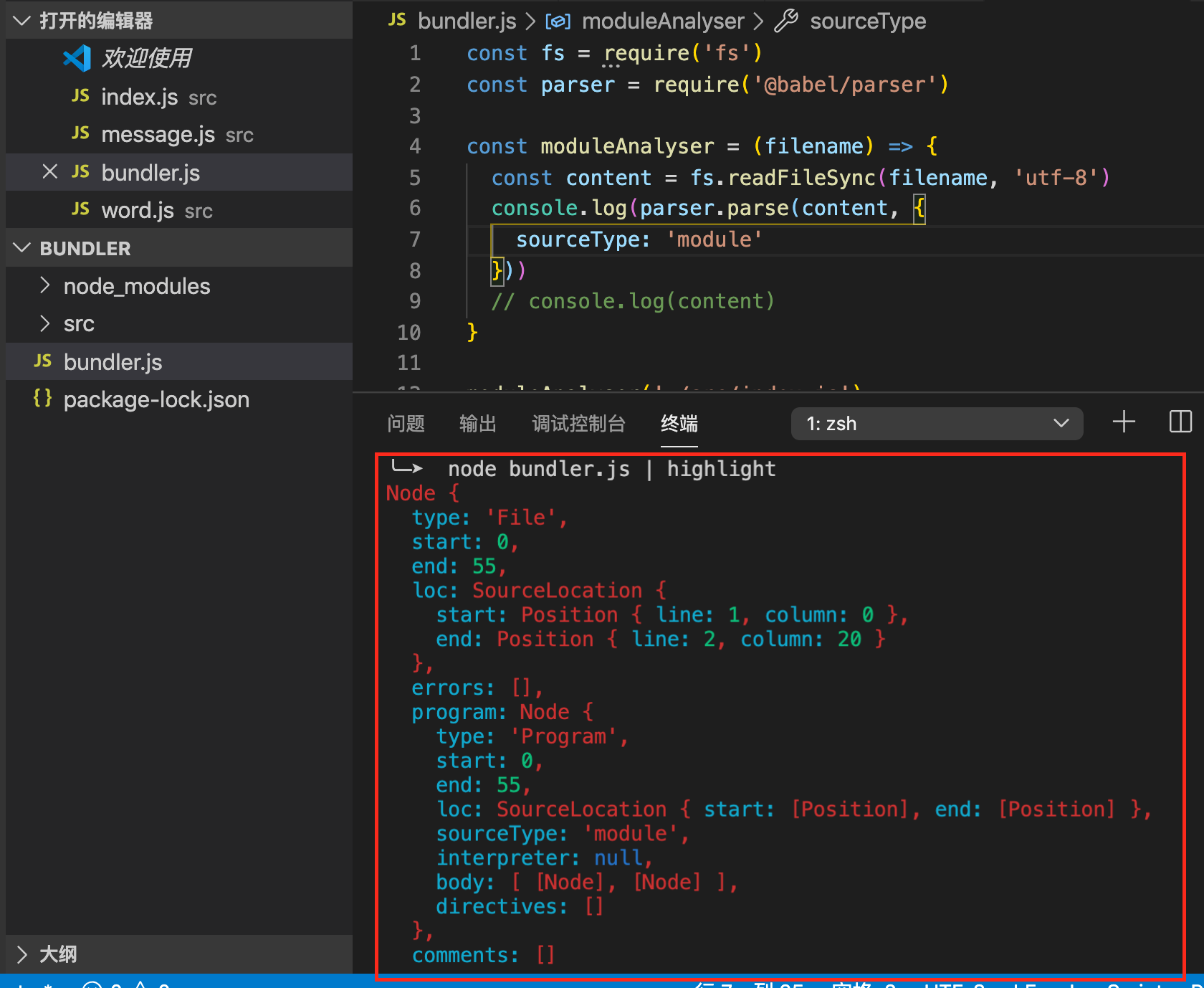
AST,可以很好的表述当前的代码。
program:代表当前运行的程序,其中body字段
const fs = require('fs')
const parser = require('@babel/parser')
const moduleAnalyser = (filename) => {
const content = fs.readFileSync(filename, 'utf-8')
const ast = parser.parse(content, {
sourceType: 'module'
})
console.log(ast.program.body)
}
moduleAnalyser('./src/index.js')
打印结果如下:
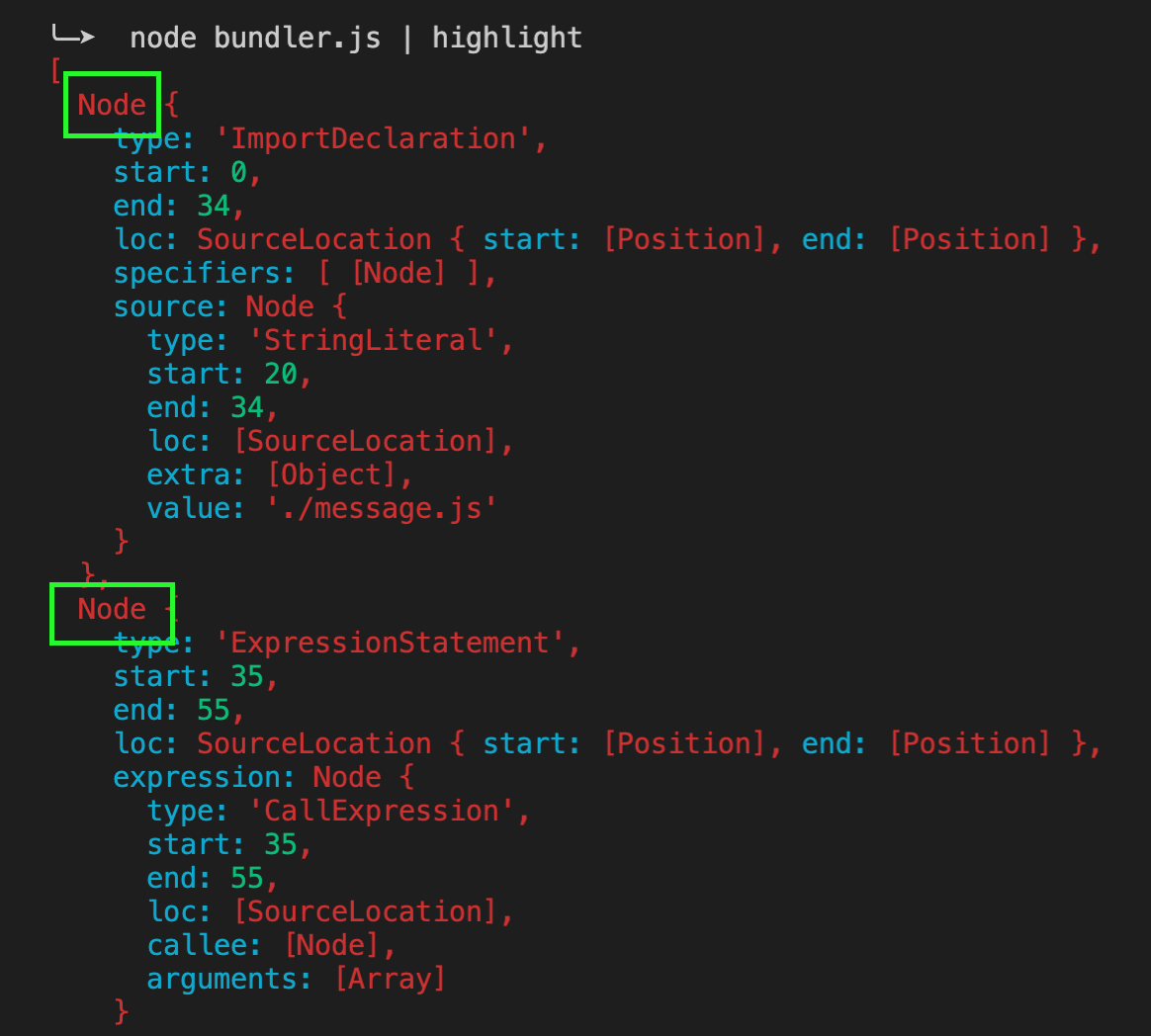
ImportDeclaration: 代表引入语法,对应 import message from './message.js'
ExpressionStatement: 代表表达式,对应 console.log(message)
通过抽象语法书AST,就可以找到声明的语句,找到对应的依赖关系,将我们的js代码转化为js对象。这样就拿到了代码里所有的依赖关系。
babel提供了工具帮助我们快速找到import节点。@babel/traverse
npm install @babel/traverse --save
const fs = require('fs')
const parser = require('@babel/parser')
const traverse = require('@babel/traverse').default //默认导出的es module
const moduleAnalyser = (filename) => {
const content = fs.readFileSync(filename, 'utf-8')
const ast = parser.parse(content, {
sourceType: 'module'
})
traverse(ast, {
ImportDeclaration({ node }) {
console.log(node)
}
})
}
moduleAnalyser('./src/index.js')
通过traverse分析出代码里的依赖。
traverse(ast, {
ImportDeclaration({ node }) { // 只要语法书ast中包含ImportDeclaration这样的引入语句时,就会走这个函数
console.log(node.source.value)
}
})
对入口文件的依赖分析
const moduleAnalyser = (filename) => {
const content = fs.readFileSync(filename, 'utf-8')
const ast = parser.parse(content, {
sourceType: 'module'
})
const dependencies = [] // 依赖,对入口文件的依赖分析
traverse(ast, {
ImportDeclaration({ node }) { // 只要语法书ast中包含ImportDeclaration这样的引入语句时,就会走这个函数
dependencies.push(node.source.value)
}
})
console.log(dependencies)
}
运行结果如下:
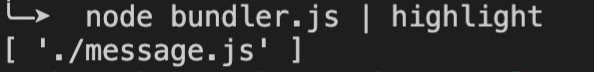
src/index.js入口文件。但是我们要是用的相对于根目录的路径。
以对象的方式存储依赖.
对引入的模块的原始代码打包编译成在浏览器上能够运行的代码,因此我们还要借助babel进行代码转化。
npm install @babel/core --save
参考文档:
npm install --save-dev @babel/preset-env
const fs = require('fs')
const path = require('path')
const parser = require('@babel/parser')
const traverse = require('@babel/traverse').default //默认导出的es module,用export default的内容,需要用.default方法。
const babel = require('@babel/core')
const moduleAnalyser = (filename) => {
const content = fs.readFileSync(filename, 'utf-8')
const ast = parser.parse(content, {
sourceType: 'module'
})
const dependencies = {} // 依赖,对入口文件的依赖分析
traverse(ast, {
ImportDeclaration({ node }) { // 只要语法书ast中包含ImportDeclaration这样的引入语句时,就会走这个函数
const dirname = path.dirname(filename)
const newFile = './' + path.join(dirname, node.source.value)
dependencies[node.source.value] = newFile
// console.log(newFile)
}
})
const { code } = babel.transformFromAst(ast, null, {
presets: ["@babel/preset-env"]
}) // code就是编译生成的可以在浏览器上运行的模块的代码
console.log(code)
return {
filename,
dependencies,
}
// console.log(dependencies)
}
moduleAnalyser('./src/index.js')
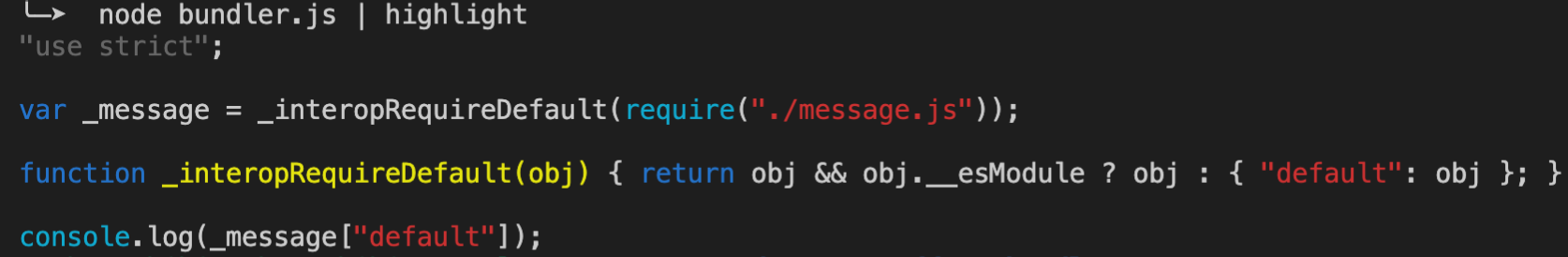
运行,打印结果如下:
const fs = require('fs')
const path = require('path')
const parser = require('@babel/parser')
const traverse = require('@babel/traverse').default //默认导出的es module,用export default的内容,需要用.default方法。
const babel = require('@babel/core')
const moduleAnalyser = (filename) => {
const content = fs.readFileSync(filename, 'utf-8')
const ast = parser.parse(content, {
sourceType: 'module'
})
const dependencies = {} // 依赖,对入口文件的依赖分析
traverse(ast, {
ImportDeclaration({ node }) { // 只要语法书ast中包含ImportDeclaration这样的引入语句时,就会走这个函数
const dirname = path.dirname(filename)
const newFile = './' + path.join(dirname, node.source.value)
dependencies[node.source.value] = newFile
// console.log(newFile)
}
})
const { code } = babel.transformFromAst(ast, null, {
presets: ["@babel/preset-env"]
}) // code就是编译生成的可以在浏览器上运行的模块的代码
// console.log(code)
return {
filename,
dependencies,
code,
}
// console.log(dependencies)
}
const moduleInfo = moduleAnalyser('./src/index.js')
console.log(moduleInfo)
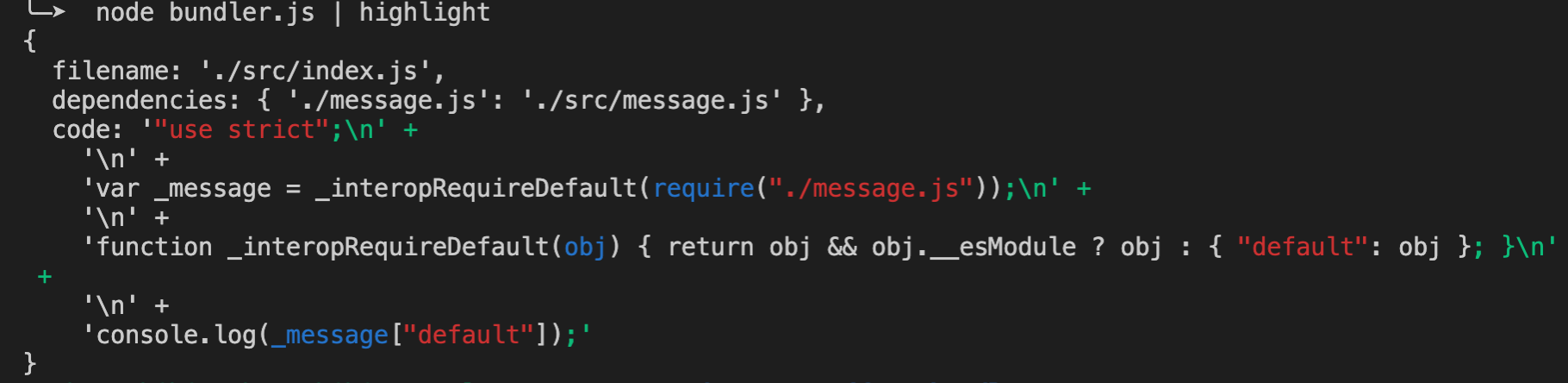
filename对应的文件路径为./src/index.js.
依赖dependencies了./message.js真正的路径为./src/message.js
对应的代码被翻译过后,要在浏览器中运行的部分为code.
抽象:当我们去做项目打包的时候,首先要对项目中的模块做分析。目前我们只对入口文件做了分析。
总结:
- 为了分析入口文件我们写了
moduleAnalyser函数, - 通过传入的文件名,用
fs.readFileSync读出了文件中的内容 - 再通过
parser.parse将读出的代码转化为js对象,即AST抽象语法树。 - 通过
ImportDeclaration分析声明都在哪些地方,找到import语句对应的内容,分析依赖,并拼装为js对象dependencies,以键值对的方式存入。 - 借助
babel.transformFromAst对源代码进行编译,转化为浏览器可以执行的代码,存入{ code }中 - 最终返回入口文件名字
filename、依赖关系dependencies、编译后的代码code
4.bundle源码编写(Dependencies Graph)
想要实现把所有模块都分析出来,我们还需要写一个函数。生成依赖图谱。通过递归实现。如下:
const fs = require('fs')
const path = require('path')
const parser = require('@babel/parser')
const traverse = require('@babel/traverse').default //默认导出的es module,用export default的内容,需要用.default方法。
const babel = require('@babel/core')
const moduleAnalyser = (filename) => {
const content = fs.readFileSync(filename, 'utf-8')
const ast = parser.parse(content, {
sourceType: 'module'
})
const dependencies = {} // 依赖,对入口文件的依赖分析
traverse(ast, {
ImportDeclaration({ node }) { // 只要语法书ast中包含ImportDeclaration这样的引入语句时,就会走这个函数
const dirname = path.dirname(filename)
const newFile = './' + path.join(dirname, node.source.value)
dependencies[node.source.value] = newFile
// console.log(newFile)
}
})
const { code } = babel.transformFromAst(ast, null, {
presets: ["@babel/preset-env"]
}) // code就是编译生成的可以在浏览器上运行的模块的代码
// console.log(code)
return {
filename,
dependencies,
code,
}
// console.log(dependencies)
}
const makeDependenciesGraph = (entry) => {
const entryModule = moduleAnalyser(entry)
const graphArr = [ entryModule ]
for (let i = 0; i < graphArr.length; i++) {
const item = graphArr[i]
const { dependencies } = item
if (dependencies) {
for (const j in dependencies) {
graphArr.push(
moduleAnalyser(dependencies[j])
) // 对每一个依赖的内容进行分析
}
}
}
console.log(graphArr)
// console.log('entryModule', entryModule)
// 对数组做格式上的转化
const graph = {}
graphArr.forEach(item => {
graph[item.filename] = {
dependencies: item.dependencies,
code: item.code,
}
})
// 转化为对象
return graph
}
const graphInfo = makeDependenciesGraph('./src/index.js')
console.log(graphInfo)
5.bundle源码编写(生成代码)
从上面的代码我们可以拿到所有模块代码分析生成的结果(Dependencies Graph),接下来就让我们用(Dependencies Graph)生成真正可以在浏览器上运行的代码。
需要用到闭包。
const fs = require('fs')
const path = require('path')
const parser = require('@babel/parser')
const traverse = require('@babel/traverse').default //默认导出的es module,用export default的内容,需要用.default方法。
const babel = require('@babel/core')
const moduleAnalyser = (filename) => {
const content = fs.readFileSync(filename, 'utf-8')
const ast = parser.parse(content, {
sourceType: 'module'
})
const dependencies = {} // 依赖,对入口文件的依赖分析
traverse(ast, {
ImportDeclaration({ node }) { // 只要语法书ast中包含ImportDeclaration这样的引入语句时,就会走这个函数
const dirname = path.dirname(filename)
const newFile = './' + path.join(dirname, node.source.value)
dependencies[node.source.value] = newFile
// console.log(newFile)
}
})
const { code } = babel.transformFromAst(ast, null, {
presets: ["@babel/preset-env"]
}) // code就是编译生成的可以在浏览器上运行的模块的代码
// console.log(code)
return {
filename,
dependencies,
code,
}
// console.log(dependencies)
}
const makeDependenciesGraph = (entry) => {
const entryModule = moduleAnalyser(entry)
const graphArr = [ entryModule ]
for (let i = 0; i < graphArr.length; i++) {
const item = graphArr[i]
const { dependencies } = item
if (dependencies) {
for (const j in dependencies) {
graphArr.push(
moduleAnalyser(dependencies[j])
) // 对每一个依赖的内容进行分析
}
}
}
// console.log(graphArr)
// console.log('entryModule', entryModule)
// 对数组做格式上的转化
const graph = {}
graphArr.forEach(item => {
graph[item.filename] = {
dependencies: item.dependencies,
code: item.code,
}
})
return graph
}
const generateCode = (entry) => {
const graph = JSON.stringify(makeDependenciesGraph(entry))
// 生成的代码为闭包,避免污染全局环境
return `
(function(graph) {
function require(module) {
function localRequire(relativePath) {
return require(graph[module].dependencies[relativePath]) // 返回真实路径
}
var exports = {}; // 需要加;,否则编译后的代码执行会报错
(function(require, exports, code) {
eval(code)
})(localRequire, exports, graph[module].code)
return exports;
};
require('${entry}')
})(${graph});
`
}
const code = generateCode('./src/index.js')
console.log(code)
编译后的代码如下:
(function(graph) {
function require(module) {
function localRequire(relativePath) {
return require(graph[module].dependencies[relativePath]) // 返回真实路径
}
var exports = {};
(function(require, exports, code) {
eval(code)
})(localRequire, exports, graph[module].code)
return exports;
};
require('./src/index.js')
})({"./src/index.js":{"dependencies":{"./message.js":"./src/message.js"},"code":"\"use strict\";\n\nvar _message = _interopRequireDefault(require(\"./message.js\"));\n\nfunction _interopRequireDefault(obj) { return obj && obj.__esModule ? obj : { \"default\": obj }; }\n\nconsole.log(_message[\"default\"]);"},"./src/message.js":{"dependencies":{"./word.js":"./src/word.js"},"code":"\"use strict\";\n\nObject.defineProperty(exports, \"__esModule\", {\n value: true\n});\nexports[\"default\"] = void 0;\n\nvar _word = require(\"./word.js\");\n\nvar message = \"say \".concat(_word.word);\nvar _default = message;\nexports[\"default\"] = _default;"},"./src/word.js":{"dependencies":{},"code":"\"use strict\";\n\nObject.defineProperty(exports, \"__esModule\", {\n value: true\n});\nexports.word = void 0;\nvar word = 'hello';\nexports.word = word;"}});
可以反复尝试写一下。
在创建打包工具的过程中,我们会使用到 babel、node、闭包、递归等知识点。
七、Creact-React-App 和 Vue-Cli 3.0脚手架工具配置分析
1. 通过CreacteReactApp深入学习webpack配置
通过阅读别人的配置文件来提升自己的配置能力。
create-react-app脚手架工具。
npx create-react-app my-app
脚手架工具会尽可能的让我们的开发更简单。
// package.json
{
"scripts": {
"start": "react-scripts start",
"build": "react-scripts build",
"test": "react-scripts test",
"eject": "react-scripts eject",
}
}
npm run eject此命令可以把隐藏的webpack配置项展示出来。执行完之后会多出./config和./scripts文件夹。
// package.json
{
"scripts": {
"start": "node scripts/start.js",
"build": "node scripts/build.js",
"test": "node scripts/test.js",
}
}
遇到不会的就去搜,去解决。
// webpack.config.js
bail: isEnvProduction // 代表一旦打包的过程中出错就及时停止,不再继续打包。
output: {
path: 打包路径,
pathinfo:把引入的信息输出,
filename: 输出文件名,
chunkFileName: ,
publicPath: ,
devtoolModuleFilenameTemplate: sourcemap依赖文件在硬盘中的真正位置,
optimization: 优化、代码压缩,
},
resolve: { // 当引入其他模块的时候,就会走resolve,用里面plugins对应的插件.
modules: 根据你的配置生成数组,
extensions: 找一个模块项的后缀对应的文件是否存在,
alias: 别名,
plugins: 插件,
},
resolveLoader: { 只有引入一些loader的时候,里面的plugin才会执行。resolve是全集,resolveLoader是只有在引入loader的时候才会执行。
plugins: [
]
},
module: {
strictExportPresence: true, // 引入的模块必须明确export导出自己的内容
rules: [
{
parser: {requireEnsure: false} // 不允许用require语法,必须用import进行异步代码的加载
}
]
}
WorkboxWebpackPlugin: pwa相关配置
./config/paths.js存放的都是打包文件要用到的一些路径信息。
./config/env.js是帮助我们初始化项目运行环境。
webpackDevServer.config.js对应的配置内容。
主要文件作用:
./scripts/build.js和./scripts/start.js为打包和开发对应的编译文件。webpack.config.js是整个webpack打包的核心.webpackDevServer.config.js是开发环境的配置项.
2. Vue CLI3的配置方法
参考文档:cli.vuejs.org/zh/
npm install -g @vue/cli
// 创建项目
vue create my-project
// 启动项目
cd my-project
npm run serve
理念:
vue: 让用户配置起来更简单
react:让使用配置起来更灵活
npm run build // 生成dist目录
想要改变生成目录dist等内容,不需要改变webpack.config.js,只需要创建vue.config.js,vue提供了一套配置文件
参考文档:https://cli.vuejs.org/zh/config/
cli.vuejs.org/zh/config/#… 修改输出目录 在底层再转化为webpack配置,配置大量精简。
// webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
outputDir: 'fruit', // 将dist改为fruit目录
pages: {
index: {
// page 的入口
entry: 'src/index/main.js',
// 模板来源
template: 'public/index.html',
// 在 dist/index.html 的输出
filename: 'index.html',
// 当使用 title 选项时,
// template 中的 title 标签需要是 <title><%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %></title>
title: 'Index Page',
// 在这个页面中包含的块,默认情况下会包含
// 提取出来的通用 chunk 和 vendor chunk。
chunks: ['chunk-vendors', 'chunk-common', 'index']
},
list: {
entry: 'src/index/main.js',
template: 'public/index.html',
filename: 'index.html',
title: 'Index Page',
chunks: ['chunk-vendors', 'chunk-common', 'index']
}
},
css: {
modules: true // 以css的module形式引入css,防止组件间的影响。
}
}
// webpack
module.exports = {
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'fruit') // webpack中需要这样配置
}
}
多页配置参考文档: cli.vuejs.org/zh/config/#…
参考文档:
- webpack.docschina.org/guides/ 找webpack解决方案
- webpack.docschina.org/concepts/ 核心概念
- webpack.docschina.org/configurati… 非常精确的配置项
- webpack.docschina.org/api/ Loader和Plugin的API
- webpack.docschina.org/loaders/ 官方推荐的Loader及其作用
- webpack.docschina.org/plugins/ 官方推荐的Plugin及其作用