一. 应用加载回顾
应用加载的步骤为:
- 系统调用 exec() 会我们的应用映射到新的地址空间
- 然后通过 dyld 进行加载、链接、初始化主程序和主程序所依赖的各种动态库
- 最后在 initializeMainExecutable 方法中经过一系列初始化调用 notifySingle 函数,该函数会执行一个 load_images 的回调
- 然后在 doModinitFuntions 函数内部会调用 attribute((constructor)) 的 c 函数
- 然后 dyld 返回主程序的入口函数,开始进入主程序的 main 函数
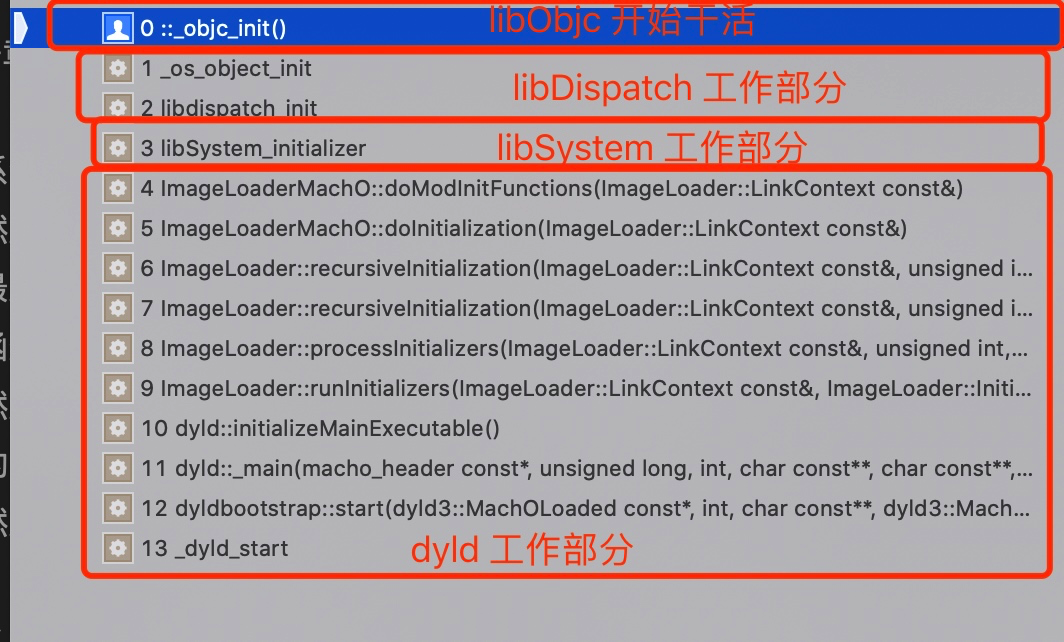
在 main 函数执行执行,其实 dyld 还会在流程中初始化 libSystem,而 libSystem 又会去初始化 libDispatch,在 libDispatch 初始化方法里面又会有一步 _os_object_init,在 _os_object_init 内部就会调起 _objc_init。
二. 探索_objc_init
先看下源码
/***********************************************************************
* _objc_init
* Bootstrap initialization. Registers our image notifier with dyld.
* Called by libSystem BEFORE library initialization time
**********************************************************************/
void _objc_init(void)
{
static bool initialized = false;
if (initialized) return;
initialized = true;
// fixme defer initialization until an objc-using image is found?
environ_init();
tls_init();
static_init();
lock_init();
exception_init();
// 保存 - libobjc - dyld
// C++ 怎么去做到通知
// 指针 - 回调 - 函数的地址
// 这里就是我们的数据 - images - objc lib
// dyld
_dyld_objc_notify_register(&map_images, load_images, unmap_image);
}
2.1 environ_init
/***********************************************************************
* environ_init
* Read environment variables that affect the runtime.
* Also print environment variable help, if requested.
**********************************************************************/
void environ_init(void)
{
if (issetugid()) {
// All environment variables are silently ignored when setuid or setgid
// This includes OBJC_HELP and OBJC_PRINT_OPTIONS themselves.
return;
}
bool PrintHelp = false;
bool PrintOptions = false;
bool maybeMallocDebugging = false;
// Scan environ[] directly instead of calling getenv() a lot.
// This optimizes the case where none are set.
for (char **p = *_NSGetEnviron(); *p != nil; p++) {
...
}
// Special case: enable some autorelease pool debugging
// when some malloc debugging is enabled
// and OBJC_DEBUG_POOL_ALLOCATION is not set to something other than NO.
if (maybeMallocDebugging) {
const char *insert = getenv("DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES");
const char *zombie = getenv("NSZombiesEnabled");
const char *pooldebug = getenv("OBJC_DEBUG_POOL_ALLOCATION");
if ((getenv("MallocStackLogging")
|| getenv("MallocStackLoggingNoCompact")
|| (zombie && (*zombie == 'Y' || *zombie == 'y'))
|| (insert && strstr(insert, "libgmalloc")))
&&
(!pooldebug || 0 == strcmp(pooldebug, "YES")))
{
DebugPoolAllocation = true;
}
}
// Print OBJC_HELP and OBJC_PRINT_OPTIONS output.
if (PrintHelp || PrintOptions) {
if (PrintHelp) {
_objc_inform("Objective-C runtime debugging. Set variable=YES to enable.");
_objc_inform("OBJC_HELP: describe available environment variables");
if (PrintOptions) {
_objc_inform("OBJC_HELP is set");
}
_objc_inform("OBJC_PRINT_OPTIONS: list which options are set");
}
if (PrintOptions) {
_objc_inform("OBJC_PRINT_OPTIONS is set");
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(Settings)/sizeof(Settings[0]); i++) {
const option_t *opt = &Settings[i];
if (PrintHelp) _objc_inform("%s: %s", opt->env, opt->help);
if (PrintOptions && *opt->var) _objc_inform("%s is set", opt->env);
}
}
}
这里主要是环境变量的设置工作。
2.2 tls_init
void tls_init(void)
{
#if SUPPORT_DIRECT_THREAD_KEYS
_objc_pthread_key = TLS_DIRECT_KEY;
pthread_key_init_np(TLS_DIRECT_KEY, &_objc_pthread_destroyspecific);
#else
_objc_pthread_key = tls_create(&_objc_pthread_destroyspecific);
#endif
}
这里主要是线程key的绑定。
2.3 static_init
/***********************************************************************
* static_init
* Run C++ static constructor functions.
* libc calls _objc_init() before dyld would call our static constructors,
* so we have to do it ourselves.
**********************************************************************/
static void static_init()
{
size_t count;
auto inits = getLibobjcInitializers(&_mh_dylib_header, &count);
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
inits[i]();
}
}
这里主要是c++静态函数的构造
2.4 lock_init
void lock_init(void)
{
}
2.5 exception_init
/***********************************************************************
* exception_init
* Initialize libobjc's exception handling system.
* Called by map_images().
**********************************************************************/
void exception_init(void)
{
old_terminate = std::set_terminate(&_objc_terminate);
}
这里主要做的是异常处理初始化。
2.6 _dyld_objc_notify_register
void _dyld_objc_notify_register(_dyld_objc_notify_mapped mapped,
_dyld_objc_notify_init init,
_dyld_objc_notify_unmapped unmapped)
{
dyld::registerObjCNotifiers(mapped, init, unmapped);
}
void registerObjCNotifiers(_dyld_objc_notify_mapped mapped, _dyld_objc_notify_init init, _dyld_objc_notify_unmapped unmapped)
{
// record functions to call
sNotifyObjCMapped = mapped;
sNotifyObjCInit = init;
sNotifyObjCUnmapped = unmapped;
// call 'mapped' function with all images mapped so far
try {
notifyBatchPartial(dyld_image_state_bound, true, NULL, false, true);
}
catch (const char* msg) {
// ignore request to abort during registration
}
// <rdar://problem/32209809> call 'init' function on all images already init'ed (below libSystem)
for (std::vector<ImageLoader*>::iterator it=sAllImages.begin(); it != sAllImages.end(); it++) {
ImageLoader* image = *it;
if ( (image->getState() == dyld_image_state_initialized) && image->notifyObjC() ) {
dyld3::ScopedTimer timer(DBG_DYLD_TIMING_OBJC_INIT, (uint64_t)image->machHeader(), 0, 0);
(*sNotifyObjCInit)(image->getRealPath(), image->machHeader());
}
}
}
通过注释我们看到,_dyld_objc_notify_register函数的作用,就是注册dyld加载成功后的通知回调函数。官方解释为
注意:仅供 objc 运行时使用 当 objc 镜像被映射(mapped)、**卸载(unmapped)和初始化(initialized)**的时候,注册的回调函数就会被调用。 这个方法是 dlyd 中声明的,一旦调用该方法,调用结果会作为该函数的参数回传回来。比如,当所有的 images 以及 section 为 objc-image-info 被加载之后会回调 mapped 方法。 load 方法也将在这个方法中被调用。
今天研究的就是mapped这个回调函数。也就是map_images
三. map_images
3.1 map_images
/***********************************************************************
* map_images
* Process the given images which are being mapped in by dyld.
* Calls ABI-agnostic code after taking ABI-specific locks.
*
* Locking: write-locks runtimeLock
**********************************************************************/
void
map_images(unsigned count, const char * const paths[],
const struct mach_header * const mhdrs[])
{
mutex_locker_t lock(runtimeLock);
return map_images_nolock(count, paths, mhdrs);
}
3.2 map_images_nolock
我们继续跟踪map_images_nolock
void
map_images_nolock(unsigned mhCount, const char * const mhPaths[],
const struct mach_header * const mhdrs[])
{
static bool firstTime = YES;
header_info *hList[mhCount];
uint32_t hCount;
size_t selrefCount = 0;
...
// 主要是判断
if (hCount > 0) {
// 主要的读镜像的代码
_read_images(hList, hCount, totalClasses, unoptimizedTotalClasses);
}
firstTime = NO;
}
3.3 _read_images
/***********************************************************************
* _read_images
* Perform initial processing of the headers in the linked
* list beginning with headerList.
*
* Called by: map_images_nolock
*
* Locking: runtimeLock acquired by map_images
**********************************************************************/
void _read_images(header_info **hList, uint32_t hCount, int totalClasses, int unoptimizedTotalClasses)
{
...
}
官方的解释为:开始,对已经链接了的 Mach-O 镜像表中的头部进行初始化处理 由于这个函数比较多,我们分几段来分析
3.3.1 创建存储类的表
if (!doneOnce) {
doneOnce = YES;
......
// namedClasses
// Preoptimized classes don't go in this table.
// 4/3 is NXMapTable's load factor
int namedClassesSize =
(isPreoptimized() ? unoptimizedTotalClasses : totalClasses) * 4 / 3;
gdb_objc_realized_classes =
NXCreateMapTable(NXStrValueMapPrototype, namedClassesSize);
allocatedClasses = NXCreateHashTable(NXPtrPrototype, 0, nil);
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: first time tasks");
}
变量doneOnce控制了这段代码只会执行一次,首先创建了两张表,gdb_objc_realized_classes这张表存储了不在dyld共享缓存里的所有的类,包括已经实现的和没实现的,其容量是所有类数量的4/3。allocatedClasses这张表只存储已经初始化的类。这么做的目的猜测是在使用的时候只带着allocatedClasses这张小表就好了,效率也高
3.3.2 类的重映射
// Discover classes. Fix up unresolved future classes. Mark bundle classes.
for (EACH_HEADER) {
// 从编译后的类列表中取出所有类,获取到的是一个classref_t类型的指针
classref_t *classlist = _getObjc2ClassList(hi, &count);
if (! mustReadClasses(hi)) {
// Image is sufficiently optimized that we need not call readClass()
continue;
}
bool headerIsBundle = hi->isBundle();
bool headerIsPreoptimized = hi->isPreoptimized();
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
// 数组中会取出OS_dispatch_queue_concurrent、OS_xpc_object、NSRunloop等系统类,例如CF、Fundation、libdispatch中的类。以及自己创建的类
Class cls = (Class)classlist[i];
// 通过readClass函数获取处理后的新类,
Class newCls = readClass(cls, headerIsBundle, headerIsPreoptimized);
// 初始化所有懒加载的类需要的内存空间 - 现在数据没有加载到的 - 连类都没有初始化的
if (newCls != cls && newCls) {
// Class was moved but not deleted. Currently this occurs
// only when the new class resolved a future class.
// Non-lazily realize the class below.
// 将懒加载的类添加到数组中
resolvedFutureClasses = (Class *)
realloc(resolvedFutureClasses,
(resolvedFutureClassCount+1) * sizeof(Class));
resolvedFutureClasses[resolvedFutureClassCount++] = newCls;
}
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: discover classes");
这里的重点在于readClass这个函数,在这个函数中可以看到如下代码:
Class replacing = nil;
if (Class newCls = popFutureNamedClass(mangledName)) {
// This name was previously allocated as a future class.
// Copy objc_class to future class's struct.
// Preserve future's rw data block.
if (newCls->isAnySwift()) {
_objc_fatal("Can’t complete future class request for '%s' "
"because the real class is too big.",
cls->nameForLogging());
}
class_rw_t *rw = newCls->data();
const class_ro_t *old_ro = rw->ro;
memcpy(newCls, cls, sizeof(objc_class));
rw->ro = (class_ro_t *)newCls->data();
newCls->setData(rw);
freeIfMutable((char *)old_ro->name);
free((void *)old_ro);
addRemappedClass(cls, newCls);
replacing = cls;
cls = newCls;
}
乍一看好像在这里会进行ro的读取和rw的赋值,但其实如果我们这个判断条件上打个断点会发现程序跟不会走到这里,也就是说一般的系统类和自定义类并不会走这里,只有符合popFutureNamedClass条件的类才会走这里。接着往下看:
addNamedClass(cls, mangledName, replacing);
addClassTableEntry(cls);
/***********************************************************************
* addNamedClass
* Adds name => cls to the named non-meta class map.
* Warns about duplicate class names and keeps the old mapping.
* Locking: runtimeLock must be held by the caller
**********************************************************************/
static void addNamedClass(Class cls, const char *name, Class replacing = nil)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
Class old;
if ((old = getClassExceptSomeSwift(name)) && old != replacing) {
inform_duplicate(name, old, cls);
// getMaybeUnrealizedNonMetaClass uses name lookups.
// Classes not found by name lookup must be in the
// secondary meta->nonmeta table.
addNonMetaClass(cls);
} else {
NXMapInsert(gdb_objc_realized_classes, name, cls);
}
assert(!(cls->data()->flags & RO_META));
// wrong: constructed classes are already realized when they get here
// assert(!cls->isRealized());
}
addNamedClass作用是将当前类插入到总表gdb_objc_realized_classes中。
/***********************************************************************
* addClassTableEntry
* Add a class to the table of all classes. If addMeta is true,
* automatically adds the metaclass of the class as well.
* Locking: runtimeLock must be held by the caller.
**********************************************************************/
static void addClassTableEntry(Class cls, bool addMeta = true) {
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
// This class is allowed to be a known class via the shared cache or via
// data segments, but it is not allowed to be in the dynamic table already.
assert(!NXHashMember(allocatedClasses, cls));
if (!isKnownClass(cls))
NXHashInsert(allocatedClasses, cls);
if (addMeta)
addClassTableEntry(cls->ISA(), false);
}
addClassTableEntry作用是将当前类插入到allocatedClasses这张表中。 接下来是修复重映射,不过一般走不进来,暂时也不用过多关注。
// 主要是修复重映射 - 一般走不进来
// 将未映射Class和Super Class重映射,被remap的类都是非懒加载的类
if (!noClassesRemapped()) {
for (EACH_HEADER) {
// 重映射Class,注意是从_getObjc2ClassRefs函数中取出类的引用
Class *classrefs = _getObjc2ClassRefs(hi, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
remapClassRef(&classrefs[i]);
}
// fixme why doesn’t test future1 catch the absence of this?
classrefs = _getObjc2SuperRefs(hi, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
remapClassRef(&classrefs[i]);
}
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: remap classes");
3.3.3 将SEL添加到namedSelectors表中
// 将所有SEL都注册到哈希表中,是另外一张哈希表
// Fix up @selector references
static size_t UnfixedSelectors;
{
mutex_locker_t lock(selLock);
for (EACH_HEADER) {
if (hi->isPreoptimized()) continue;
bool isBundle = hi->isBundle();
SEL *sels = _getObjc2SelectorRefs(hi, &count);
UnfixedSelectors += count;
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
const char *name = sel_cname(sels[i]);
// 注册SEL的操作
sels[i] = sel_registerNameNoLock(name, isBundle);
}
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: fix up selector references");
再来看一下sel_registerNameNoLock
static SEL __sel_registerName(const char *name, bool shouldLock, bool copy)
{
SEL result = 0;
if (shouldLock) selLock.assertUnlocked();
else selLock.assertLocked();
if (!name) return (SEL)0;
result = search_builtins(name);
if (result) return result;
conditional_mutex_locker_t lock(selLock, shouldLock);
if (namedSelectors) {
result = (SEL)NXMapGet(namedSelectors, name);
}
if (result) return result;
// No match. Insert.
if (!namedSelectors) {
namedSelectors = NXCreateMapTable(NXStrValueMapPrototype,
(unsigned)SelrefCount);
}
if (!result) {
result = sel_alloc(name, copy);
// fixme choose a better container (hash not map for starters)
NXMapInsert(namedSelectors, sel_getName(result), result);
}
return result;
}
这部分代码比较好懂,其实就是从Macho文件的数据段中读出所有的SEL,再将所有SEL插入到namedSelectors表中。
3.3.4 修复旧的函数指针调用遗留
// Fix up old objc_msgSend_fixup call sites
// 修复旧的函数指针调用遗留
for (EACH_HEADER) {
message_ref_t *refs = _getObjc2MessageRefs(hi, &count);
if (count == 0) continue;
if (PrintVtables) {
_objc_inform("VTABLES: repairing %zu unsupported vtable dispatch "
"call sites in %s", count, hi->fname());
}
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
// 内部将常用的alloc、objc_msgSend等函数指针进行注册,并fix为新的函数指针
fixupMessageRef(refs+i);
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: fix up objc_msgSend_fixup");
3.3.5 将所有协议添加到protocol_map表中
// Discover protocols. Fix up protocol refs.
// 遍历所有协议列表,并且将协议列表加载到Protocol的哈希表中
for (EACH_HEADER) {
extern objc_class OBJC_CLASS_$_Protocol;
// cls = Protocol类,所有协议和对象的结构体都类似,isa都对应Protocol类
Class cls = (Class)&OBJC_CLASS_$_Protocol;
assert(cls);
// 获取protocol哈希表
NXMapTable *protocol_map = protocols();
bool isPreoptimized = hi->isPreoptimized();
bool isBundle = hi->isBundle();
// 从编译器中读取并初始化Protocol
protocol_t **protolist = _getObjc2ProtocolList(hi, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
readProtocol(protolist[i], cls, protocol_map,
isPreoptimized, isBundle);
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: discover protocols");
// Fix up @protocol references
// Preoptimized images may have the right
// answer already but we don’t know for sure.
// 修复协议列表引用,优化后的images可能是正确的,但是并不确定
for (EACH_HEADER) {
// 需要注意到是,下面的函数是_getObjc2ProtocolRefs,和上面的_getObjc2ProtocolList不一样
protocol_t **protolist = _getObjc2ProtocolRefs(hi, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
remapProtocolRef(&protolist[i]);
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: fix up @protocol references");
这一部分是将所有的协议都添加到protocol_map表中。然后会对协议列表的协议引用进行修复
3.3.6 初始化所有的非懒加载类
首先我们要知道懒加载类与非懒加载类的区别,根据苹果官方文档的解释: 两者之间的主要区别在于是否实现了+load方法,实现了+load方法则为非懒加载类,没有实现则为懒加载类。 接下来会遍历调用realizeClassWithoutSwift来实现所有非懒加载的类
- 读取类的数据
ro = (const class_ro_t *)cls->data();
if (ro->flags & RO_FUTURE) {
// This was a future class. rw data is already allocated.
rw = cls->data();
ro = cls->data()->ro;
cls->changeInfo(RW_REALIZED|RW_REALIZING, RW_FUTURE);
} else {
// Normal class. Allocate writeable class data.
rw = (class_rw_t *)calloc(sizeof(class_rw_t), 1);
rw->ro = ro;
rw->flags = RW_REALIZED|RW_REALIZING;
cls->setData(rw);
}
首先程序会读取类的data信息获取到ro,ro是一个只读的结构,在编译期就已经赋值了,主要存储了类的实例变量、属性列表、方法列表和协议列表等信息,在这一步rw只是进行了初始化,还并未有赋值操作。
- 递归实现父类和元类
// Realize superclass and metaclass, if they aren’t already.
// This needs to be done after RW_REALIZED is set above, for root classes.
// This needs to be done after class index is chosen, for root metaclasses.
// This assumes that none of those classes have Swift contents,
// or that Swift’s initializers have already been called.
// fixme that assumption will be wrong if we add support
// for ObjC subclasses of Swift classes.
supercls = realizeClassWithoutSwift(remapClass(cls->superclass));
metacls = realizeClassWithoutSwift(remapClass(cls->ISA()));
之前我们在探索类的结构时讲过,类结构中包含isa和superclass,这里正是利用这一点去递归实现类的元类和父类,以保证类的继承链的完整性。至于递归的出口,我们知道所有类的基类是NSObject,而NSObject的父类是nil,所以递归到nil就会跳出去。而元类不同,类通过isa会找到元类,接着找到根元类,而根元类的元类指向自己,这样会进入死循环,不过苹果肯定是做的很完善的,在remapClass中其实做了判断:
/***********************************************************************
* remapClass
* Returns the live class pointer for cls, which may be pointing to
* a class struct that has been reallocated.
* Returns nil if cls is ignored because of weak linking.
* Locking: runtimeLock must be read- or write-locked by the caller
**********************************************************************/
static Class remapClass(Class cls)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
Class c2;
if (!cls) return nil;
NXMapTable *map = remappedClasses(NO);
if (!map || NXMapMember(map, cls, (void**)&c2) == NX_MAPNOTAKEY) {
return cls;
} else {
return c2;
}
}
这里其实是类的查找,如果在表里已经存在该类就会返回c2,其实也就是nil,从而跳出元类的递归实现。
- 将此类连接到其父类的子类列表
// Connect this class to its superclass’s subclass lists
if (supercls) {
addSubclass(supercls, cls);
} else {
addRootClass(cls);
}
这一步的目的将当前类添加到其父类的子类列表中,使得子类与父类形成一个类似于双向链表的结构。
- 对rw进行赋值 经过一系列处理在函数的最后会调用methodizeClass,这个函数中会对rw进行赋值,将类的方法、属性、协议从ro中读取出来存到rw中,同时也会添加类的分类。
// Install methods and properties that the class implements itself.
method_list_t *list = ro->baseMethods();
if (list) {
prepareMethodLists(cls, &list, 1, YES, isBundleClass(cls));
rw->methods.attachLists(&list, 1);
}
property_list_t *proplist = ro->baseProperties;
if (proplist) {
rw->properties.attachLists(&proplist, 1);
}
protocol_list_t *protolist = ro->baseProtocols;
if (protolist) {
rw->protocols.attachLists(&protolist, 1);
}
// Root classes get bonus method implementations if they don’t have
// them already. These apply before category replacements.
if (cls->isRootMetaclass()) {
// root metaclass
addMethod(cls, SEL_initialize, (IMP)&objc_noop_imp, "", NO);
}
// Attach categories.
category_list *cats = unattachedCategoriesForClass(cls, true /*realizing*/);
attachCategories(cls, cats, false /*don’t flush caches*/);
我们可以看到不管是方法、属性还是协议都是通过attachLists来装载到rw中的,那么我们就有必要来看一下attachLists中是如何操作的:
void attachLists(List* const * addedLists, uint32_t addedCount) {
if (addedCount == 0) return;
if (hasArray()) {
// many lists -> many lists
// 原来有复数个元素并且新增元素个数为复数
// 拿到原本列表里的元素个数
uint32_t oldCount = array()->count;
// 旧的元素个数 + 新增元素个数,相当于扩容后的列表元素个数
uint32_t newCount = oldCount + addedCount;
// 重新开辟列表内存
setArray((array_t *)realloc(array(), array_t::byteSize(newCount)));
// 设置新列表元素个数
array()->count = newCount;
/**
* 从`array()->lists`所指的内存区域的起始位置拷贝
* `oldCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0])`个字节到
* `array()->lists + addedCount`所指的内存区域。
* 可以避免因为两块内存有重叠区域而被覆盖
*/
memmove(array()->lists + addedCount, array()->lists,
oldCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0]));
/**
* 从`addedLists`所指的内存区域的起始位置拷贝
* `addedCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0])`个字节到
* `array()->lists + addedCount`所指的内存区域。
* 无法避免因为两块内存有重叠区域导致的内存被覆盖问题
* 使用时必须确保两块内存没有重叠部分
* 效率上比`memmove`要高一些
*/
memcpy(array()->lists, addedLists,
addedCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0]));
}
else if (!list && addedCount == 1) {
// 0 lists -> 1 list
// 原来没有元素并且新增元素个数为1
list = addedLists[0];
}
else {
// 1 list -> many lists
// 原来有1个元素并且新增元素个数为复数
List* oldList = list;
uint32_t oldCount = oldList ? 1 : 0;
uint32_t newCount = oldCount + addedCount;
setArray((array_t *)malloc(array_t::byteSize(newCount)));
array()->count = newCount;
if (oldList) array()->lists[addedCount] = oldList;
memcpy(array()->lists, addedLists,
addedCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0]));
}
}
这个函数的作用其实是在原有的数组上做扩容操作,然后把原有的元素向后移,新增的元素插入到最前面。由此可知所谓的分类会覆盖类中的同名方法是一个假象,其实两个方法是同时存在的,只是分类的方法在前面,因为方法查找是按顺序查找的,所以调用的是分类的方法。
3.3.7 发现和处理所有Category
// Discover categories.
// 发现和处理所有Category
for (EACH_HEADER) {
// 外部循环遍历找到当前类,查找类对应的Category数组
category_t **catlist =
_getObjc2CategoryList(hi, &count);
bool hasClassProperties = hi->info()->hasCategoryClassProperties();
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
// 内部循环遍历当前类的所有Category
category_t *cat = catlist[i];
Class cls = remapClass(cat->cls);
if (!cls) {
// Category’s target class is missing (probably weak-linked).
// Disavow any knowledge of this category.
catlist[i] = nil;
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: IGNORING category \?\?\?(%s) %p with "
"missing weak-linked target class",
cat->name, cat);
}
continue;
}
// Process this category.
// First, register the category with its target class.
// Then, rebuild the class’s method lists (etc) if
// the class is realized.
// 首先,通过其所属的类注册Category。如果这个类已经被实现,则重新构造类的方法列表。
bool classExists = NO;
if (cat->instanceMethods || cat->protocols
|| cat->instanceProperties)
{
// 将Category添加到对应Class的value中,value是Class对应的所有category数组
addUnattachedCategoryForClass(cat, cls, hi);
// 将Category的method、protocol、property添加到Class
if (cls->isRealized()) {
remethodizeClass(cls);
classExists = YES;
}
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: found category -%s(%s) %s",
cls->nameForLogging(), cat->name,
classExists ? "on existing class" : "");
}
}
// 这块和上面逻辑一样,区别在于这块是对Meta Class做操作,而上面则是对Class做操作
// 根据下面的逻辑,从代码的角度来说,是可以对原类添加Category的
if (cat->classMethods || cat->protocols
|| (hasClassProperties && cat->_classProperties))
{
addUnattachedCategoryForClass(cat, cls->ISA(), hi);
if (cls->ISA()->isRealized()) {
remethodizeClass(cls->ISA());
}
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: found category +%s(%s)",
cls->nameForLogging(), cat->name);
}
}
}
}
ts.log("IMAGE TIMES: discover categories");
至此,一个非懒加载类的加载过程基本就完成了
4.懒加载类的加载流程
其实大部分开发者都知道懒加载类是在调用的时候才会去初始化的,只不过是没有深入探索过具体流程,这次我们顺便就探索一下。 既然我们知道懒加载类在使用的时候才会初始化,类创建对象又是通过alloc方法来进行,而方法的本质就是消息发送,所以我们就需要去到一个消息发送流程中很重要的函数lookUpImpOrForward,在这个函数内部有这样一段代码:
if (!cls->isRealized()) {
cls = realizeClassMaybeSwiftAndLeaveLocked(cls, runtimeLock);
// runtimeLock may have been dropped but is now locked again
}
这里的判断条件是是否已经实现过,没实现过才符合条件。如果条件判断成立,就会调用realizeClassMaybeSwiftAndLeaveLocked,而realizeClassMaybeSwiftAndLeaveLocked内部又调用了realizeClassMaybeSwiftMaybeRelock:
/***********************************************************************
* realizeClassMaybeSwift (MaybeRelock / AndUnlock / AndLeaveLocked)
* Realize a class that might be a Swift class.
* Returns the real class structure for the class.
* Locking:
* runtimeLock must be held on entry
* runtimeLock may be dropped during execution
* ...AndUnlock function leaves runtimeLock unlocked on exit
* ...AndLeaveLocked re-acquires runtimeLock if it was dropped
* This complication avoids repeated lock transitions in some cases.
**********************************************************************/
static Class
realizeClassMaybeSwiftMaybeRelock(Class cls, mutex_t& lock, bool leaveLocked)
{
lock.assertLocked();
if (!cls->isSwiftStable_ButAllowLegacyForNow()) {
// Non-Swift class. Realize it now with the lock still held.
// fixme wrong in the future for objc subclasses of swift classes
realizeClassWithoutSwift(cls);
if (!leaveLocked) lock.unlock();
} else {
// Swift class. We need to drop locks and call the Swift
// runtime to initialize it.
lock.unlock();
cls = realizeSwiftClass(cls);
assert(cls->isRealized()); // callback must have provoked realization
if (leaveLocked) lock.lock();
}
return cls;
}
从源码中我们可以发现程序最终会调用realizeClassWithoutSwift,而该函数的内容正是我们前面已经分析过的类的加载流程,由此我们可以确定,懒加载类是在第一次被调用的时候才会开始加载到内存的。
五. 总结
这里主要讲了类的加载过程,细探索了类的加载(包括非懒加载类和懒加载类)、分类的加载以及类和分类搭配加载的不同情况,流程已经比较清楚,本人能力有限,如有错误还请指正。