1. 两数之和
HashMap,一次遍历
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的那 两个 整数,并返回他们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,你不能重复利用这个数组中同样的元素。
示例:
给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
因为 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9
所以返回 [0, 1] class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (map.containsKey(nums[i])) {
return new int[]{map.get(nums[i]), i};
} else {
map.put(target - nums[i], i);
}
}
return new int[]{-1, -1};
}
}2. 两数相加
链表,增加空头节点
给出两个 非空 的链表用来表示两个非负的整数。其中,它们各自的位数是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且它们的每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。 如果,我们将这两个数相加起来,则会返回一个新的链表来表示它们的和。 您可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例:
输入:(2 -> 4 -> 3)+ (5 -> 6 -> 4)
输出:7 -> 0 -> 8
原因:342 + 465 = 807/** * Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
int next = 0;
ListNode res = new ListNode(0);
ListNode curr = res;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null || next != 0) {
int tmp = (l1 != null ? l1.val : 0) + (l2 != null ? l2.val : 0) + next;
if (tmp < 10) {
curr.next = new ListNode(tmp);
next = 0;
} else {
curr.next = new ListNode(tmp % 10);
next = tmp / 10;
}
l1 = l1 != null ? l1.next : null;
l2 = l2 != null ? l2.next : null;
curr = curr.next;
}
return res.next;
}
}3. 无重复字符的最长字串
HashMap+滑动窗口法,有限map可用数组代替
给定一个字符串,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
示例:
输入: "abcabcbb"
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "abc",所以其长度为 3。 class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int[] map = new int[128];
int maxLen = 0;
int left = 0;
for (int right = 0; right < s.length(); right++) {
left = Math.max(left, map[s.charAt(right)]);
maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, right - left + 1);
map[s.charAt(right)] = right + 1;
}
return maxLen;
}
}4. 寻找两个有序数组的中位数
设置i,j分别切割两数组,二分法定i
给定两个大小为 m 和 n 的有序数组 nums1 和 nums2。 请你找出这两个有序数组的中位数,并且要求算法的时间复杂度为 O(log(m + n))。
你可以假设 nums1 和 nums2 不会同时为空。
示例:
nums1 = [1, 3] nums2 = [2] 则中位数是 2.0 class Solution {
public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int m = nums1.length;
int n = nums2.length;
if (m > n) return findMedianSortedArrays(nums2, nums1);
int left = 0, right = m, half = (m + n + 1) / 2;
while (left <= right) {
int i = (left + right) / 2;
int j = half - i;
if (i < right && nums1[i] < nums2[j - 1]) {
left = i + 1;
} else if (i > left && nums1[i - 1] > nums2[j]) {
right = i - 1;
} else {
double maxLeft = 0;
if (i == 0) maxLeft = nums2[j - 1];
else if (j == 0) maxLeft = nums1[i - 1];
else maxLeft = Math.max(nums1[i - 1], nums2[j - 1]);
if ((m + n) % 2 == 1) return maxLeft;
double minRight = 0;
if (i == m) minRight = nums2[j];
else if (j == n) minRight = nums1[i];
else minRight = Math.min(nums1[i], nums2[j]);
return (minRight + maxLeft) / 2.0;
}
}
return 0.0;
}
}5. 最长回文子串
中心扩展法,有2n-1个中心
给定一个字符串 s,找到 s 中最长的回文子串。你可以假设 s 的最大长度为 1000。
示例:
输入: "babad"
输出: "bab"
注意: "aba" 也是一个有效答案。 class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() < 1) return "";
int start = 0, end = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
int len1 = expandCentral(s, i, i);
int len2 = expandCentral(s, i, i + 1);
int len = Math.max(len1, len2);
if (len > end - start + 1) {
start = i - (len - 1) / 2;
end = i + len / 2;
}
}
return s.substring(start, end + 1);
}
private int expandCentral(String s, int left, int right) {
while (left >= 0 && right < s.length() && s.charAt(left) == s.charAt(right)) {
left--;
right++;
}
return right - left - 1;
}
}10. 正则表达式匹配
动态规划,dp[i][j]是s的前i个元素与p的前j个元素的匹配情况,注意“*”的分类讨论
给你一个字符串 s 和一个字符规律 p,请你来实现一个支持 '.' 和 '*' 的正则表达式匹配。
'.' 匹配任意单个字符
'*' 匹配零个或多个前面的那一个元素所谓匹配,是要涵盖 整个 字符串 s的,而不是部分字符串。
说明:
s 可能为空,且只包含从 a-z 的小写字母。
p 可能为空,且只包含从 a-z 的小写字母,以及字符 . 和 *。示例:
输入: s = "aa" p = "a"
输出: false
解释: "a" 无法匹配 "aa" 整个字符串。class Solution {
public boolean isMatch(String s, String p) {
int m = s.length(), n = p.length();
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[m + 1][n + 1];
dp[0][0] = true;
for (int j = 2; j <= n; j++) {
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 2] && p.charAt(j - 1) == '*';
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (s.charAt(i - 1) == p.charAt(j - 1) || p.charAt(j - 1) == '.') {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
} else if (p.charAt(j - 1) == '*') {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 2] ||
dp[i - 1][j] && (s.charAt(i - 1) == p.charAt(j - 2) || p.charAt(j - 2) == '.');
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
}11. 盛水最多的容器
双指针,从两侧往中间,哪边矮就移哪边
给定 n 个非负整数 a1,a2,...,an,每个数代表坐标中的一个点 (i, ai) 。在坐标内画 n 条垂直线,垂直线 i 的两个端点分别为 (i, ai) 和 (i, 0)。找出其中的两条线,使得它们与 x 轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
说明:你不能倾斜容器,且 n 的值至少为 2。
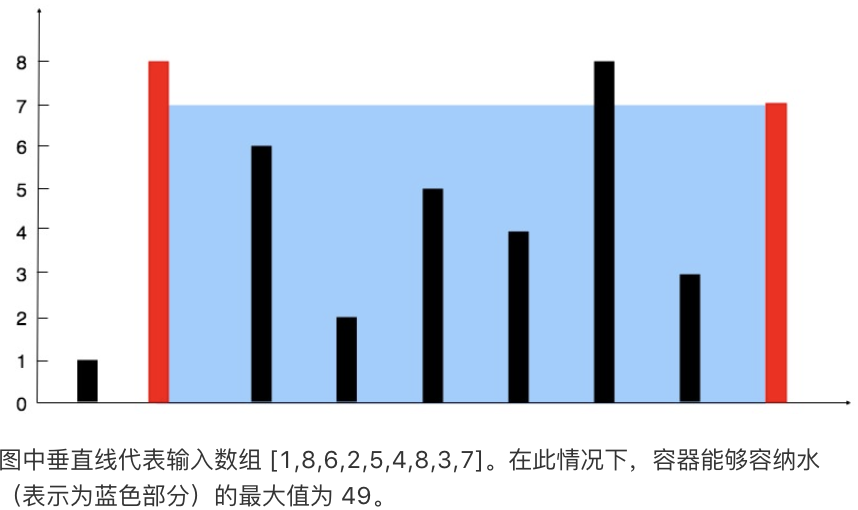
示例:
输入: [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
输出: 49class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int maxarea = 0;
int left = 0, len = height.length - 1, right = len;
while (left <= right) {
if (height[left] < height[right]) {
maxarea = Math.max(maxarea, height[left++] * len);
} else {
maxarea = Math.max(maxarea, height[right--] * len);
}
len--;
}
return maxarea;
}
}15. 三数之和
排序,从头遍历为第一个数a(a>0时跳出),双指针在后半部分从两边往中间找剩余两数,注意跳过重复值
给定一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?找出所有满足条件且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例:
给定数组 nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4],
满足要求的三元组集合为: [ [-1, 0, 1], [-1, -1, 2] ] class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
int len = nums.length;
if (nums == null || len < 3) return res;
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (nums[i] > 0) break;
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) continue;
int L = i + 1;
int R = len - 1;
while (L < R) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[L] + nums[R];
if (sum == 0) {
res.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[L], nums[R]));
while (L < R && nums[L] == nums[L + 1]) L++;
while (L < R && nums[R] == nums[R - 1]) R--;
L++;
R--;
} else if (sum > 0) {
R--;
} else {
L++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}17. 电话号码的字母组合
回溯,树形分支
给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。
给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。

示例:
输入:"23"
输出:["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"].class Solution {
private String[] lettermap = {"abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
private List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
if (digits == null || digits.length() == 0) return res;
helper(digits, 0, new StringBuilder());
return res;
}
private void helper(String digits, int index, StringBuilder pre) {
if (pre.length() == digits.length()) {
res.add(pre.toString());
return;
}
String letter = lettermap[digits.charAt(index) - '0' - 2];
for (int i = 0; i < letter.length(); i++) {
helper(digits, index + 1, pre.append(letter.charAt(i)));
pre.deleteCharAt(index);
}
}
}19. 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
双指针,先后差n出发,注意删除第一个节点和只有一个节点的情况
给定一个链表,删除链表的倒数第n个节点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例:
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 n = 2.
当删除了倒数第二个节点后,链表变为 1->2->3->5.
说明: 给定的 n 保证是有效的。
进阶:
你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode pre = new ListNode(0);
pre.next = head;
ListNode first = pre, second = pre;
while (n > 0) {
first = first.next;
n--;
}
while (first.next != null) {
first = first.next;
second = second.next;
}
second.next = second.next.next;
return pre.next;
}
}20. 有效的括号
HashMap存左右括号对应关系 & 栈
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
注意空字符串可被认为是有效字符串。
示例1:
输入: "()[]{}"
输出: true示例2:
输入: "(]"
输出: falseclass Solution {
private Map<Character, Character> map = new HashMap<>();
public Solution() {
map.put(')', '(');
map.put('}', '{');
map.put(']', '[');
}
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<Character>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char curr = s.charAt(i);
if (!map.containsKey(curr)) {
stack.push(curr);
} else {
char top = stack.empty() ? '#' : stack.pop();
if (top != map.get(curr))
return false;
}
}
return stack.empty();
}
}21. 合并两个有序链表
简单题
将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例:
输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
输出:1->1->2->3->4->4/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode pre = new ListNode(0);
ListNode res = pre;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
pre.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
pre.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
pre = pre.next;
}
pre.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return res.next;
}
}22. 括号生成
给出n代表生成括号的对数,请你写出一个函数,使其能够生成所有可能的并且有效的括号组合。
例如,给出n=3,生成结果为:
[
"((()))",
"(()())",
"(())()",
"()(())",
"()()()"
]- 动态规划,回溯,考虑n括号与n-1括号的关系,放在中间或右边(时间和空间复杂度:
class Solution {
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (n == 0) {
res.add("");
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (String left : generateParenthesis(i)) {
for (String right : generateParenthesis(n - i -1)) {
res.add('(' + left + ')' + right);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}- 辅助函数,左括号小于等于n,右括号小于等于左括号
class Solution {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
int n;
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
this.n = n;
backtrack(0, 0, "");
return res;
}
private void backtrack(int left, int right, String pre) {
if (pre.length() == n * 2) {
res.add(pre);
return;
}
if (left < n)
backtrack(left + 1, right, pre + '(');
if (right < left)
backtrack(left, right + 1, pre + ')');
}
}23. 合并K个排序链表
拆分为合并2个有序链表(题21),首尾合并至list[0]
合并k个排序链表,返回合并后的排序链表。请分析和描述算法的复杂度。
示例:
输入:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
输出: 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists == null || lists.length == 0) return null;
int len = lists.length;
while (len > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < len / 2; i++) {
lists[i] = merge2Lists(lists[i], lists[len - i - 1]);
}
len = (len + 1) / 2;
}
return lists[0];
}
private ListNode merge2Lists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode pre = new ListNode(0);
ListNode res = pre;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
pre.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
pre.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
pre = pre.next;
}
pre.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return res.next;
}
}31. 下一个排列
实现获取下一个排列的函数,算法需要将给定数字序列重新排列成字典序中下一个更大的排列。
如果不存在下一个更大的排列,则将数字重新排列成最小的排列(即升序排列)。
必须原地修改,只允许使用额外常数空间。
以下是一些例子,输入位于左侧列,其相应输出位于右侧列。
1,2,3 → 1,3,2
3,2,1 → 1,2,3
1,1,5 → 1,5,1
- 字典序定义:
(a,b) ≤ (a',b')当且仅当a<a'或(a=a'且b≤b')。 - 推导:我们希望下一个数比当前数大,因此只需要将后面的大数与前面的小数交换;同时希望下一个数增加的幅度尽可能的小,因此需要在尽可能靠右的低位进行交换,且将一个尽可能小的大数与前面的小数交换;大数换到前面后,需要将大数后面的所有数重置为升序,升序排列就是最小的排列。
- 步骤:
- 从后向前查找第一个相邻升序的元素对
(i,j),满足A[i] < A[j]。此时[j,end)必然是降序 - 在
[j,end)从后向前查找第一个满足A[i] < A[k] 的 k。A[i]、A[k]分别就是上文所说的“小数”、“大数” - 将
A[i]与A[k]交换 - 可以断定这时
[j,end)必然是降序,逆置[j,end),使其升序 - 如果在步骤 1 找不到符合的相邻元素对,说明当前
[begin,end)为一个降序顺序,则直接跳到步骤 4
class Solution {
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
int i = nums.length - 2;
while (i >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[i + 1]) {
i--;
}
if (i >= 0) {
int j = nums.length - 1;
while (j >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[j]) {
j--;
}
swap(nums, i, j);
}
reverse(nums, i + 1);
}
public void reverse(int[] nums, int start){
int end = nums.length - 1;
while (start < end) {
swap(nums, start++, end--);
}
}
public void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = tmp;
}
}32. 最长有效括号
- 动态规划,dp[i]包括第i个括号的有效长度,每次遇到‘)’进行判断
- 左右分别遍历,遵循left>=right原则,一旦left==right则认为有效并记录
给定一个只包含 '(' 和 ')' 的字符串,找出最长的包含有效括号的子串的长度。
示例:
输入: "(()"
输出: 2
解释: 最长有效括号子串为 "()"// 动态规划,时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
class Solution {
public int longestValidParentheses(String s) {
int maxres = 0;
int[] dp = new int[s.length()];
for (int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == ')') {
if (s.charAt(i - 1) == '(') {
dp[i] = (i >= 2 ? dp[i - 2] : 0) + 2;
} else if (i - dp[i - 1] >= 1 && s.charAt(i - dp[i - 1] - 1) == '(') {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + (i - dp[i - 1] >= 2 ? dp[i - dp[i - 1] - 2] : 0) + 2;
}
maxres = Math.max(maxres, dp[i]);
}
}
return maxres;
}
}// 左右遍历,时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
class Solution {
public int longestValidParentheses(String s) {
int maxres = 0, left = 0, right = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == '(') {
left++;
} else {
right++;
}
if (left < right) {
left = right = 0;
} else if (left == right) {
maxres = Math.max(maxres, left * 2);
}
}
left = right = 0;
for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (s.charAt(i) == '(') {
left++;
} else {
right++;
}
if (left > right) {
left = right = 0;
} else if (left == right) {
maxres = Math.max(maxres, left * 2);
}
}
return maxres;
}
}33. 搜索旋转排序数组
时间复杂度log必用二分法,分234501(前半有序)和450123(后半有序)两种数组讨论
假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转。
( 例如,数组 [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] )。
搜索一个给定的目标值,如果数组中存在这个目标值,则返回它的索引,否则返回 -1 。
你可以假设数组中不存在重复的元素。
你的算法时间复杂度必须是 O(log n) 级别。
示例:
输入: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
输出: 4// 分234501(前半有序)和450123(后半有序)两种数组讨论
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
int mid;
while (left <= right) {
mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
if (nums[mid] >= nums[left]) { // 前半有序
if (target >= nums[left] && target <= nums[mid])
right = mid - 1;
else
left = mid + 1;
} else { // 后半有序
if (target <= nums[right] && target >= nums[mid])
left = mid + 1;
else
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
二分法分别找两次第一个和最后一个位置,函数可复用
给定一个按照升序排列的整数数组 nums,和一个目标值 target。找出给定目标值在数组中的开始位置和结束位置。
你的算法时间复杂度必须是 O(log n) 级别。
如果数组中不存在目标值,返回 [-1, -1]。
示例:
输入: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 8
输出: [3,4]class Solution {
public int[] searchRange(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] res = {-1, -1};
int left_index = findIndex(nums, target, true);
if (left_index == nums.length || nums[left_index] != target)
return res;
res[0] = left_index;
res[1] = findIndex(nums, target, false) - 1;
return res;
}
private int findIndex(int[] nums, int target, boolean left) {
int L = 0, R = nums.length;
while (L < R) {
int mid = (L + R) / 2;
if (nums[mid] > target || (left && nums[mid] == target))
R = mid;
else
L = mid + 1;
}
return L;
}
}39. 组合总和
回溯,树,剩余target为负剪枝,顺序考虑元素去重,sort(candidate)提速
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
说明:
- 所有数字(包括
target)都是正整数。 - 解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例:
输入: candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
所求解集为:
[
[7],
[2,2,3]
]class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
private int[] candidates;
int len;
private void recall(int index, int retarget, Stack pre) {
if (retarget == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(pre));
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < len; i++) {
if (retarget - candidates[i] >= 0) {
pre.push(candidates[i]);
recall(i, retarget - candidates[i], pre);
pre.pop();
}
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
this.candidates = candidates;
this.len = candidates.length;
recall(0, target, new Stack<>());
return res;
}
}42. 接雨水
- 两个数组分别记录左右两侧的最高值 -> 一个数组从右记录最大值,后从左遍历并计算
- 维护栈记录,遇到height上升时开始pop计算水量(height上升是因为接水,注意与84柱状图中的最大矩形区分,求矩形是当height下降时开始pop)
给定n个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
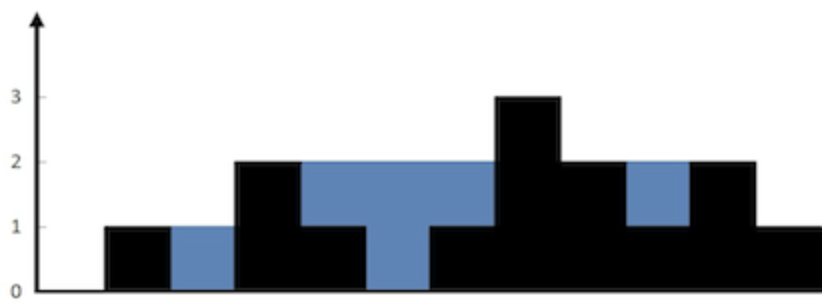
上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。 感谢 Marcos 贡献此图。
示例:
输入: [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
输出: 6// 两次遍历,左右分别记录最高点
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int res = 0, max_left = 0;
if (height == null || height.length == 0) return res;
int len = height.length;
int[] max_right = new int[len];
max_right[len - 1] = height[len - 1];
for (int i = len - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
max_right[i] = Math.max(height[i], max_right[i + 1]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
max_left = Math.max(max_left, height[i]);
res += (Math.min(max_left, max_right[i]) - height[i]);
}
return res;
}
}// 维护栈
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int current = 0, res = 0;
while (current < height.length) {
while (!stack.empty() && height[current] > height[stack.peek()]) {
int h = height[stack.pop()];
if (stack.empty()) break;
int len = current - stack.peek() - 1;
res += (Math.min(height[current], height[stack.peek()]) - h) * len;
}
stack.push(current);
current++;
}
return res;
}
}46. 全排列
回溯,树状交换,从头开始交换
- ArrayList可直接用Array List Stack Set 初始化,但不能用数组直接初始化,可建立空的Array 遍历加入
- new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(nums)) 该方法仅限于数组与Array中元素类型相同的情况,int与Integer间无法转换
给定一个没有重复数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
输入: [1,2,3]
输出:
[
[1,2,3],
[1,3,2],
[2,1,3],
[2,3,1],
[3,1,2],
[3,2,1]
] class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
int len;
private void backtrack(int start, ArrayList<Integer> pre) {
if (start == len - 1) {
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(pre));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < len; i++) {
Collections.swap(pre, start, i);
backtrack(start + 1, pre);
Collections.swap(pre, start, i);
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
len = nums.length;
ArrayList<Integer> pre = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int num : nums) {
pre.add(num);
}
backtrack(0, pre);
return res;
}
}48. 旋转图像
切分为四块,遍历第一块的所有元素,每次旋转4个元素,注意找到row和col间的关系
给定一个 n × n 的二维矩阵表示一个图像。
将图像顺时针旋转 90 度。
说明:
你必须在原地旋转图像,这意味着你需要直接修改输入的二维矩阵。请不要使用另一个矩阵来旋转图像。
示例:
给定 matrix =
[
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9]
],
原地旋转输入矩阵,使其变为:
[
[7,4,1],
[8,5,2],
[9,6,3]
] class Solution {
public void rotate(int[][] matrix) {
int n = matrix.length;
for (int i = 0; i < (n + 1) / 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n / 2; j++) {
int row = i, col = j;
int[] target = new int[4];
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
target[k] = matrix[row][col];
int x = row;
row = col;
col = n - 1 - x;
}
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
matrix[row][col] = target[(k + 3) % 4];
int x = row;
row = col;
col = n - 1 - x;
}
}
}
}
}49. 字母异位词分组
- 将String变为char[]并用sort排序,Map<String, List>存储,最后返回用map.values()初始化的List
- 将每个str的各字母数量作为key合并
- str.toCharArray(); String.valueOf(char[]);
给定一个字符串数组,将字母异位词组合在一起。字母异位词指字母相同,但排列不同的字符串。
输入: ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"],
输出:
[
["ate","eat","tea"],
["nat","tan"],
["bat"]
] 说明:
- 所有输入均为小写字母。
- 不考虑答案输出的顺序。
// sort(char[])
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
if (strs == null || strs.length == 0)
return new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, List> ans = new HashMap<String, List>();
for (String str : strs) {
char[] ca = str.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(ca);
String key = String.valueOf(ca);
if (!ans.containsKey(key))
ans.put(key, new ArrayList<>());
ans.get(key).add(str);
}
return new ArrayList(ans.values());
}
}// 字母数量为key
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
if (strs == null || strs.length == 0)
return new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, List> ans = new HashMap<String, List>();
int[] count = new int[26];
for (String str : strs) {
Arrays.fill(count, 0);
for (char c : str.toCharArray()) count[c - 'a']++;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
sb.append(count[i]);
String key = sb.toString();
if (!ans.containsKey(key))
ans.put(key, new ArrayList<>());
ans.get(key).add(str);
}
return new ArrayList(ans.values());
}
}53. 最大子序和
- 动态规划
- 分治法:最大子序列是否包括最中间的元素(在左边/在右边/从中间往左右延伸)选最大
给定一个整数数组 nums ,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
示例:
输入: [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4],
输出: 6
解释: 连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6。进阶:
如果你已经实现复杂度为 O(n) 的解法,尝试使用更为精妙的分治法求解。
// 动态规划
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int res = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i - 1] > 0)
nums[i] += nums[i - 1];
res = Math.max(res, nums[i]);
}
return res;
}
}55. 跳跃游戏
- 动态规划,时间复杂度O(n^2),空间复杂度O(n)
- 贪心算法,从后往前确定最后能到到达的位置,
nums[i] + i >= lastIndex即可到达i
给定一个非负整数数组,你最初位于数组的第一个位置。
数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。
判断你是否能够到达最后一个位置。
示例:
输入: [2,3,1,1,4]
输出: true
解释: 我们可以先跳 1 步,从位置 0 到达 位置 1, 然后再从位置 1 跳 3 步到达最后一个位置。class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
int lastIndex = nums.length - 1;
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (nums[i] + i >= lastIndex)
lastIndex = i;
}
return lastIndex == 0;
}
}