先了解一些SQL的结构和执行顺序
SQL的结构:
select
*,列,case when(列),聚合函数(列),分析函数(列)
from 表1
inner/left join 表2
on 表1.关联列=表2.关联列
inner/left join 表3
..
where
group by
having
order by
Limit 执行顺序:
From -> where-> group by -> having -> select -> order by -> limit
两大利器
1. case when
2.分析函数(窗口函数)
第一部分:基础
Drop table t_emp;
mysql> create table t_emp
(
deptno int,
empno int,
ename varchar(10),
sal int,
comm int,
flag int
);
insert into t_emp values (10,101,'张一',5000,null,0);
insert into t_emp values (10,102,'张二',8000,null,0);
insert into t_emp values (10,103,'张三',9000,1000,0);
insert into t_emp values (20,201,'李一',11000,null,0);
insert into t_emp values (20,202,'李二',30000,null,0);
insert into t_emp values (20,203,'李三',15000,3000,0);
insert into t_emp values (20,204,'李四',16000,null,1);
insert into t_emp values (30,301,'赵一',50000,5000,0);
mysql> drop table t_dept;
create table t_dept (deptno int,dname varchar(16));
insert into t_dept values (10,'财务部');
insert into t_dept values (20,'IT部');
insert into t_dept values (30,'行政部');
insert into t_dept values (40,'后勤部');
insert into t_dept values (50,'销售部');
1.查询(select)
select deptno as new,empno,ename,sal from t_emp
2.过滤(where)
select deptno,empno,ename,sal from t_emp
where
--ename='张一'
--sal=5000
--sal > 5000 and sal < 9000
--sal >= 5000 and sal <= 9000
--sal between 5000 and 9000 作用同上
--(sal = 5000 or sal = 9000)
--sal in (5000,9000) 作用同上
--deptno in (select deptno from t_dept) 稍后细讲解
--ename like '_二'
--ename like '张%'
order by deptno
上面的过滤条件
3.逻辑判断(case when)
格式:
Case when 字段 then 结果 else 其它结果 end
select deptno,empno,ename,sal,
case
when sal< 10000 then '低'
when sal>= 10000 and sal<=20000 then '中' else '高' end as level_n
from t_emp
order by sal
若字段满足第一个when的判断会输出第一个then的结果,则该判断就将停止,不会继续判断;
4.排序(order by)
select deptno,empno,ename,sal
from t_emp
order by sal desc等同于
select deptno,empno,ename,sal from t_emp order by 4 desc
‘如果要这种排序呢?
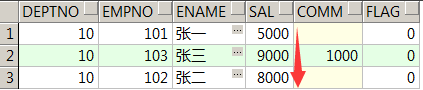
select deptno,empno,ename,sal
from t_emp
where deptno=10
order by
case when sal=5000 then 1
when sal=9000 then 2 else 3 end
5.分组(group by)
select deptno,count(empno) from t_emp
group by deptno
order by deptno
将30号部门人员已被归到10号部门,请统计每个部门的人数
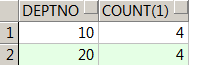
select
case when deptno=30 then 10 else deptno end new_deptno,count(1)
from t_emp t
group by case when deptno=30 then 10 else deptno end
order by 1
6.分组后过滤(having)
select deptno,sum(sal) from t_emp
group by deptno
having sum(sal) > 30000
7.常见聚合函数及空值处理
select
deptno,
sum(sal),count(sal),avg(sal),max(sal),min(sal),count(comm)
from t_emp
group by deptno
Order by 1
select
deptno,
count(sal),count(comm),count(coalesce(comm,0)),
count(case when comm is not null then comm else 0 end)
from t_emp
group by deptno
order by 1;
补充:空值对某些聚合有影响,需要进行空值处理
hive:coalesce(comm,0) mysql:ifnull(comm,0) oracle:nvl(comm,0)8.临时表(with as)
with
tmp1 as
(select * from t_emp where deptno=10),
tmp2 as
(select * from t_emp where deptno=20)
select * from tmp1
9.合并(union/union all)
--union all
with
tmp1 as
(select * from t_emp where deptno=10),
tmp2 as
(select * from t_emp where deptno in (10,20))
select * from tmp1
union all
select * from tmp2--union
with
tmp1 as
(select * from t_emp where deptno=10),
tmp2 as
(select * from t_emp where deptno in (10,20))
select * from tmp1
union
select * from tmp2
无论union还是union all,需要合并的结果集必须列个数以及列的数据类型是一致的;10.去重(distinct)
with
tmp as
(select * from t_emp where deptno=10
union all
select * from t_emp where deptno in (10,20))
select distinct * from tmp
order by 1
多表关联
1.内连接
2.外连接(左连接/右连接)
3.笛卡尔积
with
w1 as
(select 1 num
union all
select 2 num
union all
select 3 num),
w2 as
(select 2 num
union all
select 3 num
union all
select 4 num
union all
select 2 num
)select * from w1
inner join w2
--Left join w2
--right join w2
on w1.num=w2.num
order by 1
1.内连接
--写法一(推荐)
select * from t_emp e
inner join t_dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno
order by 1--写法二
select * from t_emp e, t_dept d
where e.deptno=d.deptno
2.外连接(左连接/右连接)
select * from t_emp e
left join t_dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno
order by 1
Right join右边的表为主表
select * from t_emp e
right join t_dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno
order by 1
等同于
select * from t_dept d
left join t_emp eo n e.deptno=d.deptno
order by 1
工作中常常会考虑选择哪张表作为主表?看实际情况而定
比如要统计现有员工的最全个人信息,emp作为主表
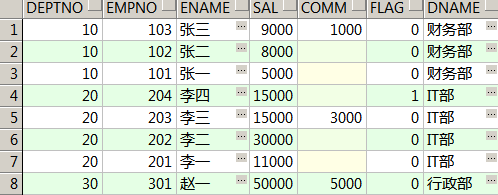
select e.*,d.dname
from t_emp e
left join t_dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno
order by 1;
比如要统计现有每个部门的人数
with
tmp as
(
select d.deptno,empno from t_dept d
left join t_emp e
on e.deptno=d.deptno
)
select deptno,count(empno) from tmp group by deptno
order by deptno
3.笛卡尔积
select * from t_dept d,t_emp e
补充:
通常出现笛卡尔积是忘记写关联条件了,是个错误的sql,但比如计算两个表关联的所有可能时,会使用到笛卡尔积
比如
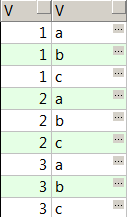
drop table t1;
drop table t2;
create table t1 (v string);
insert into t1 values (1);
insert into t1 values (2);
insert into t1 values (3);
create table t2 (v string);
insert into t2 values ('a');
insert into t2 values ('b');
insert into t2 values ('c');
select * from t1,t2
order by 1,2得到所有可能的组合
on和where在不同的连接方式中作用是一样的吗?
insert into t_ emp values (10,101,'张一',5000,null,0);
insert into t_ emp values (10,102,'张二',8000,null,0);
insert into t_ emp values (10,103,'张三',9000,1000,0);
insert into t_ emp values (20,201,'李一',11000,null,0);
insert into t_ emp values (20,202,'李二',30000,null,0);
insert into t_ emp values (20,203,'李三',15000,3000,0);
insert into t_ emp values (20,204,'李四',16000,null,1);
insert into t_ emp values (30,301,'赵一',50000,5000,0);
drop table t_dept_1;
create table t_dept_1 (deptno int,dname string,flag int);
insert into t_dept_1 values (10,'财务部',0);
insert into t_dept_1 values (20,'IT部',1);
insert into t_dept_1 values (20,'技术部',0);
insert into t_dept_1 values (30,'行政部',0);
insert into t_dept_1 values (40,'后勤部',0);
insert into t_dept_1 values (50,'销售部',0);
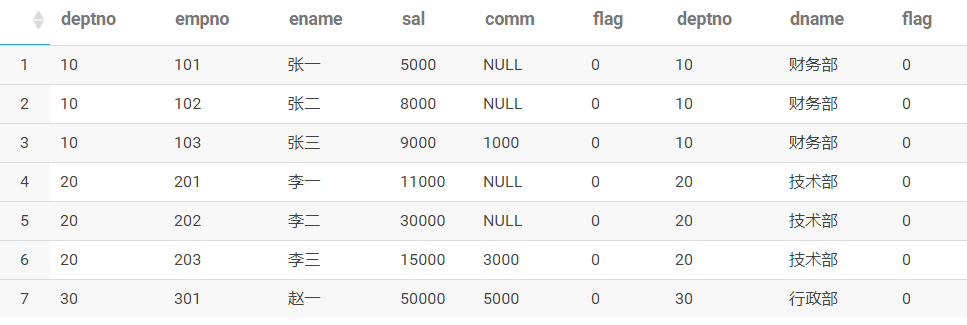
以下两个sql
的执行的结果是一样的吗?
select *
from t_emp e
inner join t_dept_1 d on e.deptno=d.deptno and e.flag=0 and d.flag=0
order by 1,2select *
from t_emp e
left join t_dept_1 d on e.deptno=d.deptno and e.flag=0 and d.flag=0
order by 1,2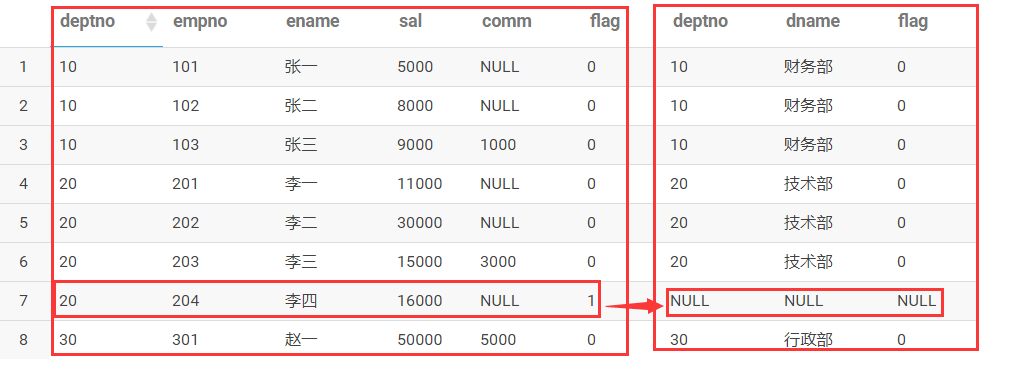
总结:
当内连接时,因为都是主表,on
和
where
都可以起到过滤的作用。
当外连接时,
因为区分了主表和子表,
on后面的子表的字段可以起到过滤作用,而主表的字段,不能起到过滤掉,起到能影响到关联的作用。
select * from t_emp e
left join t_dept_1 d
on e.deptno=d.deptno and d.flag=0 --子表字段
where e.flag=0--主表的字段
order by 1,2子查询及等价改写
--in/exists
select deptno from t_dept d
where deptno in (select deptno from t_emp)
select deptno from t_dept d
where exists (select 0 from t_emp e where e.deptno=d.deptno )
select distinct d.deptno from t_dept d
inner join t_emp e
on e.deptno=d.deptno--not in/not exists
select deptno from t_dept d
where deptno not in (select deptno from t_emp)
select deptno from t_dept d
where not exists (select deptno from t_emp e where e.deptno=d.deptno)
select d.deptno from t_dept d
left join t_emp e
on e.deptno=d.deptno
where e.deptno is null总结:
In/exists 可以改写为内连接
Not in/not exists 可以改写为外连接
Or的等价改写
select * from t_emp
where sal=5000 or sal=9000
等价改写为
select * from t_emp where sal=5000
union all
select * from t_emp where sal=9000