根据vuex的源码,实现一个vuex,一文带你写一个自己的vuex。
手写一个vuex
我们将实现vuex的主要以下功能:
- state :唯一的数据源
- getter :可以认为是store的计算属性,getter的返回值会根据它的依赖缓存起来,依赖值发生改变才会重新计算
- mutation :更改Vuex的store中的状态的唯一方法就是提交mutation
- action :action提交的是一个mutation,用来改变store的状态
- module :将一个store分割成多个模块,每个模块都有自己的状态
- 工具函数:mapGetters,mapStates,mapMutations,mapActions
Vuex基础用法
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。Vuex官方
让我们现在初始化一个项目
vue create vuex-test cd vuex-test yarn serve
store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment() {
this.count++
}
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
}
})
让我们实现一个基础的vuex
myvuex.js
let Vue; // vue实例
const install = (_vue) => {
Vue = _vue;
console.log('install');
}
export default {
install
}
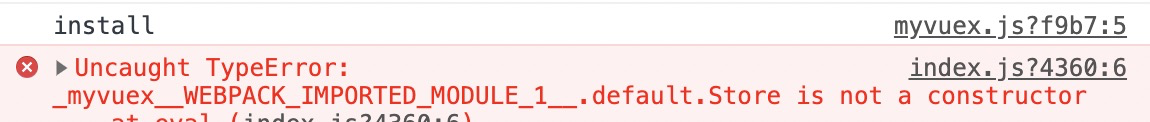
我们在项目中用于自己的vuex看是否好使。 这里我们可以看到打印出来的install,同时还有一个关于store的报错。 先来解释一下install方法,vue在使用插件的时候会调用提供的install方法,同时将当前的vue实例传进去。
给每个组件增加$store属性
let Vue; // vue实例
class Store {
}
const install = (_vue) => {
Vue = _vue;
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
if(this.$options ? this.$options.store) {
this.$store = this.$options.store;
} esle {
this.$store = this.$parent && this.$parent.store;
}
}
})
}
export default {
install,
Store
}
这一步我们将拿到的store给每个组件增加$store属性。我们知道store只有一个,所以我们只需要返回根组件的store即可
state是响应式的
this.stateData = new Vue({
data() {
return {state: options.state}
}
})
get state() {
return this.stateData.state
}
vue中会遍历data将数据变成响应式的,当数据一变视图就跟着改变。我们利用这个特性来做state的响应式。
实现getters
let Vue; // vue实例
class Store {
constructor(options = {}) {
this.state = options.state;
let getters = options.getters;
this.getters = {}
Object.keys(getters).forEach(getterName => {
Object.defineProperty(this.getters, getterName, {
get: () => {
return getters[getterName](this.state)
}
})
})
}
}
const install = (_vue) => {
Vue = _vue;
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
if(this.$options && this.$options.store) {
this.$store = this.$options.store;
} esle {
this.$store = this.$parent && this.$parent.store;
}
}
})
}
export default {
install,
Store
}
实现mutations
接着上面的代码写
let mutations = options.mutations;
this.mutations = {}
Object.keys(mutations).forEach(mutationName => {
this.mutations[mutationName] = (payload) => {
mutations[mutationName](this.state, payload)
}
})
// es7保证this 指向实例
commit = (mutationName, payload) => {
this.mutations[mutationName](payload)
}
现在我们直接调用this.$store.commit('countAdd', 10), 便能实现commit的效果了。
实现dispatchs
actions 异步提交获取完成之后,提交mutation来改状态。
// 在store中定义的
mutations: {
actionsAdd: (state, payload) => {
this.state += payload
}
},
actions:
asyncAdd({commit},payload) {
setTimeout(()=>{
commit('actionsAdd', payload);
}, 1000)
}
}
// 实现dispatchs
let actions = optinos.actions;
this.actions = {}
Object.keys(actions).forEach(actionName => {
this.actions[actionName] = (payload) => {
actions[actionName](this, payload)
}
})
dispatch = (actionName,payload) => {
this.actions[actionName](payload)
}
我们可以看到commit和dispatch的实现是一样的,没有特别的差别,在源码里面有enableStrictMode这个函数来判断是否是通过mutation来更改状态的,如果不是将会抛出警告 'do not mutate vuex store state outside mutation handlers'。 到现在我们的store基本可以使用了,除了modules。
实现modules
vuex数据格式化
// store
modules:{
a: {
state: {a: 1}
},
b: {
state: {b: 1}
}
}
//我们需要将数据格式化成我们需要的数据结构,
// 这样我们在遍历数据的时候可以很好的递归处理,
// vuex中数据结构大致如下:
// 同时用ModuleCollection函数来进行数据格式化。
let root = {
_raw: optinos,
_chidlren: {
a: {
_raw: {},
_chidlren: {},
state: {a:1}
},
b: {
_raw: {},
_chidlren: {},
state: {b:1}
}
},
state: options.state
}
let _modules = new ModuleCollection(options)
class ModuleCollection {
constructor(options) {
this.register([], options);
}
register(path, rootModule) {
let module = {
_rawModule: rootModule,
_chidlren: {},
state: rootModule.state
}
// 这是根模块
if(path.length === 0) {
this.root = module
} else {
/**
* 如果a:{modules: {c:state: 1}}在深一层我们需要将c挂在
* a._chidlren属性上,此时path=[a]时,parent = this.root,
* 当path=[a, c]时,parent = this._chidlren[a]。
* 这样就能保证深层的嵌套。
*/
let parent = path.slice(0, -1).reduce((root, current) => {
return root._chidlren[current]
}, this.root)
parent._chidlren[path[path.lenght -1]] = module
}
// 递归调用register将子模块注入
if(rootModule.modules) {
let modules = rootModule.modules
Object.keys(modules).forEach(moduleName => {
this.register(path.concat(moduleName), modules[moduleName])
})
}
}
}
数据合并
我们需要将各个模块的getter,mutation,action都放在一起,所以现在我们就需要用的我们格式化好的_modules数据。
// class store
this.getters = {}
this.mutaitons = {}
this.actions = {}
this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options)
installModule(this, [], this.state, this._modules.root)
function installModule(store,rootState,path,rootModule) {
/**
* 处理state,访问this.$store.state.a.a
* 将state归并在一起
*/
if(path.length > 0) {
let state = path.slice(0, -1).reduce((root, current) => {
return rootState[current]
}, rootState)
// vue不能直接在对象上添加不存在的数据,这样就不是响应式的
Vue.set(rootState,rootState[path[path.lenght -1]], state)
}
let getters = rootState._modules.getters
if(getters) {
Objects.keys(getters).forEach((getterName) => {
Object.defineProperty(getters, getterName, {
get: () => {
return getters[getterName](rootModule.state)
}
})
})
}
/**
* 同时这里需要将commit改掉
* commit = (mutationName, payload) => {
* this.mutations[mutationName].forEach((fn) => {
* fn(payload)
* })
* }
*/
let mutations = rootState._modules.mutations
if(mutations) {
Objects.keys(mutations).forEach((mutationName) => {
let mutationNameArr = store.mutations[mutationName] || []
mutationNameArr.push((payload) => {
mutations[mutationName](rootModule.state, payload)
})
store.mutations[mutationNameArr] = mutationNameArr
})
}
/**
* 同时这里需要将dispatch同上
*/
let actions = rootState._modules.actions
if(actions) {
Objects.keys(actions).forEach((actionName) => {
let actionName = mutations[actionName] || []
actionNameArr.push((payload) => {
actions[actionName](store, payload)
})
})
}
/**
* 我们递归注册子模块
*/
let children = rootModule._children
Object.keys(children).forEach((state) => {
installModule(store, rootState, path.concat(state), children[state])
})
}
好了基本上,我们就实现的大致的vuex的功能。下面我们来实现mapState,mapActions,mapMutations,mapGetters
mapState
/**
* 格式化我们的数据结构,
* ['a', 'b'] => [{key: 'a', val: 'a'},{key: 'b', val: 'b'}]
* {'a': ()=>{} 'b': 11} => [{key: 'a', val: ()=>{}},{key: 'b', val: 11}]
*/
function normalizeMap(target) {
return Array.isArray(target)
? target.map(key => ({key, val: key})
: Object.keys(target).map(key => ({key, val: target[key])
}
export function mapState(states) {
const result = {}
normalizeMap(states).forEach((state) => {
result[state.key] = () => {
return typeof state.val === 'function'
? val.call(this, this.$store.state, this.$store.getters)
: this.state[val]
}
})
}
mapGetters
export function mapGetters(getters) {
const result = {}
normalizeMap(states).forEach((getters) => {
result[getters.key] = () => {
if ((getters.val in this.$store.getters)) {
return this.$store.getters[getters.val]
}
}
return result
})
}
mapActions
export function mapActions (actions) {
const res = {}
normalizeMap(actions).forEach(({ key, val }) => {
res[key] = function mappedAction (...args) {
return this.$store.dispatch.apply(this.$store, [val].concat(args))
}
})
return res
}
mapMutations
export function mapMutations (mutations) {
const res = {}
normalizeMap(mutations).forEach(({ key, val }) => {
res[key] = function mappedMutation (...args) {
return this.$store.commit.apply(this.$store, [val].concat(args))
}
})
return res
}
好了,基本上我们实现了所有vuex的基础方法。欢迎大家批评指正。