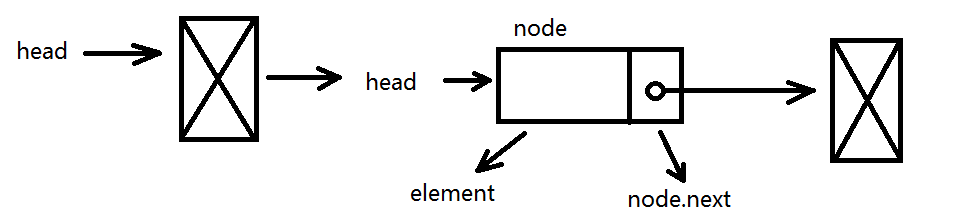
链表特点:链表存储有序的元素集合,但不同于数组,链表中的元素在内存中并不是连续放置的。每个元素由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的引用(指针或链接)组成。
相对于传统的数组,链表的一个好处在于,添加或移除元素的时候不需要移动其他元素。然而,链表需要使用指针,因此实现链表时需要额外注意。数组的另一个细节是可以直接访问任何位置的元素,而想要访问链表中间的一个元素,需要从起点开始迭代链表直到找到所需元素。
创建链表
我们先搭建一个类的骨架
function LinkedList () {
//辅助类 表示要加入链表的项
var Node = function (element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null; //指向链表中下一个节点项的指针
};
var length = 0;
var head = null;
this.append = function (element) {}; //向链表尾部添加一个新的项
this.insert = function (position, element) {}; //向链表特定位置插入一个新的项
this.removeAt = function (position) {}; //从链表特定位置移除一项
this.remove = function (element) {}; //从链表中移除一项
this.indexOf = function (element) {}; //返回元素在链表中的索引,如果没有则返回-1
this.isEmpty = function () {}; //判断链表是否为空
this.size = function () {}; //返回链表包含元素个数
this.getHead = function () {}; //返回链表第一个元素
this.toString = function () {}; //只输出元素的值
this.print = function () {}; //打印元素的值
}
下面,我们来一一实现他们
this.append = function (element) {
var node = new Node(element),
current;
if (head === null) { //链表为空,添加到首部
head = node;
}else {
current = head;
//循环链表,直到找到最后一项
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
//找到最后一项,将其next赋为node,建立连接
current.next = node;
}
length++;
};
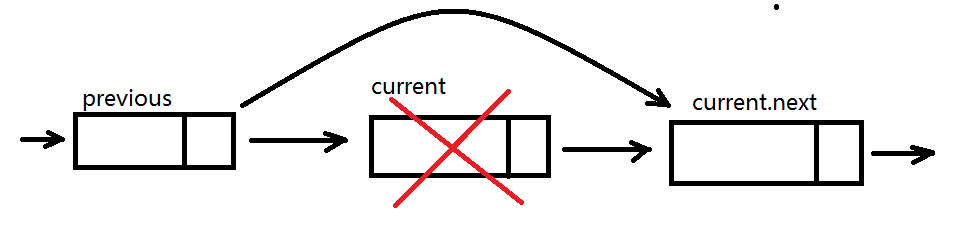
this.removeAt = function (position) {
//检查是否越界
if (position > -1 && position < length) {
var current = head,
previous,
index = 0;
if (position === 0) { //移除第一项
head = current.next;
}else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
//将previous与current的下一项链接起来,跳过current,从而移除它
previous.next = current.next;
}
length--;
return current.element;
}else {
return null;
}
};
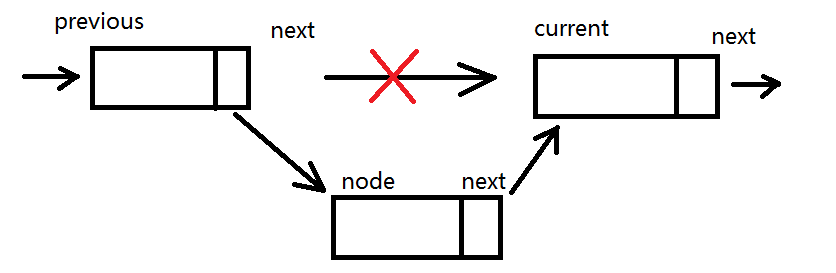
this.insert = function (position, element) {
//检查是否越界
if (position >= 0 && position <= length) {
var node = new Node(element),
current = head,
previous,
index = 0;
if (position === 0) { //在第一个位置添加
node.next = current;
head = node;
}else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
//通过改变指针,将node链接在previous和current之间
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
}
length++;
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
};
//只输出链表中元素
this.toString = function () {
var current = head,
string = "";
while (current) {
string += "," + current.element;
current = current.next;
}
return string.slice(1);
};
this.indexOf = function (element) {
var current = head,
index = 0;
while (current) {
if (current.element === element) {
return index;
}
index++;
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
};
this.remove = function (element) {
var index = this.indexOf(element);
return this.removeAt(index);
};
this.isEmpty = function () {
return length === 0;
};
this.size = function () {
return length;
};
//head是一个私有变量,当需要在类的实现外部循环访问链表时,就可以使用getHead方法获取类的第一个元素
this.getHead = function () {
return head;
};
this.print = function () {
console.log( this.toString() );
};
接下来,我们在上面的基础上做点扩展
双向链表
一个链向下一个元素,另一个链向前一个元素。
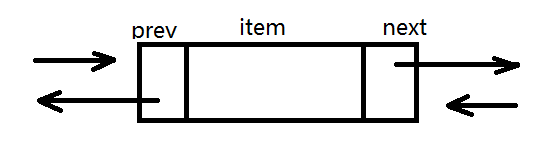
function DoublyLinkedList () {
var Node = function (element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null; //新
};
var length = 0;
var head = null;
var tail = null; //新 对最后一项的引用
//方法
}
this.append = function (element) {
var node = new Node(element),
current;
if (head === null) { //链表为空,添加到首部
head = node;
tail = node; //新
}else {
current = head;
//循环链表,直到找到最后一项
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
//找到最后一项,将其next赋为node,建立连接
current.next = node;
tail = node; //新
}
length++;
};
this.insert = function (position, element) {
//检查是否越界
if (position >= 0 && position <= length) {
var node = new Node(element),
current = head,
previous,
index = 0;
if (position === 0) { //在第一个位置添加
if (!head) { //新
head = node;
tail = node;
}else {
node.next = current;
current.prev = node; //新
head = node;
}
}else if (position === length) { //新 最后一项
//改变指针,再把node赋值给tail
current = tail;
current.next = node;
node.prev = current;
tail = node;
}else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
//通过改变指针,将node链接在previous和current之间
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
current.prev = node; //新
node.prev = previous; //新
}
length++;
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
};
this.removeAt = function (position) {
//检查是否越界
if (position > -1 && position < length) {
var current = head,
previous,
index = 0;
if (position === 0) { //移除第一项
head = current.next;
//新 如果只有一项,更新tail
if (length === 1) {
tail = null;
}else {
head.prev = null;
}
}else if(position === length - 1) { //新 最后一项
current = tail;
tail = current.prev;
tail.next = null;
}else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
//将previous与current的下一项链接起来,跳过current,从而移除它
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = previous; //新
}
length--;
return current.element;
}else {
return null;
}
};
其它的方法和单向链表一样
扩展就到这里,有兴趣的朋友可以试试在此基础上再进行扩展 比如,循环链表:将链表最后一项的next指向head 在升级就是双向循环链表,感觉要被玩坏了~