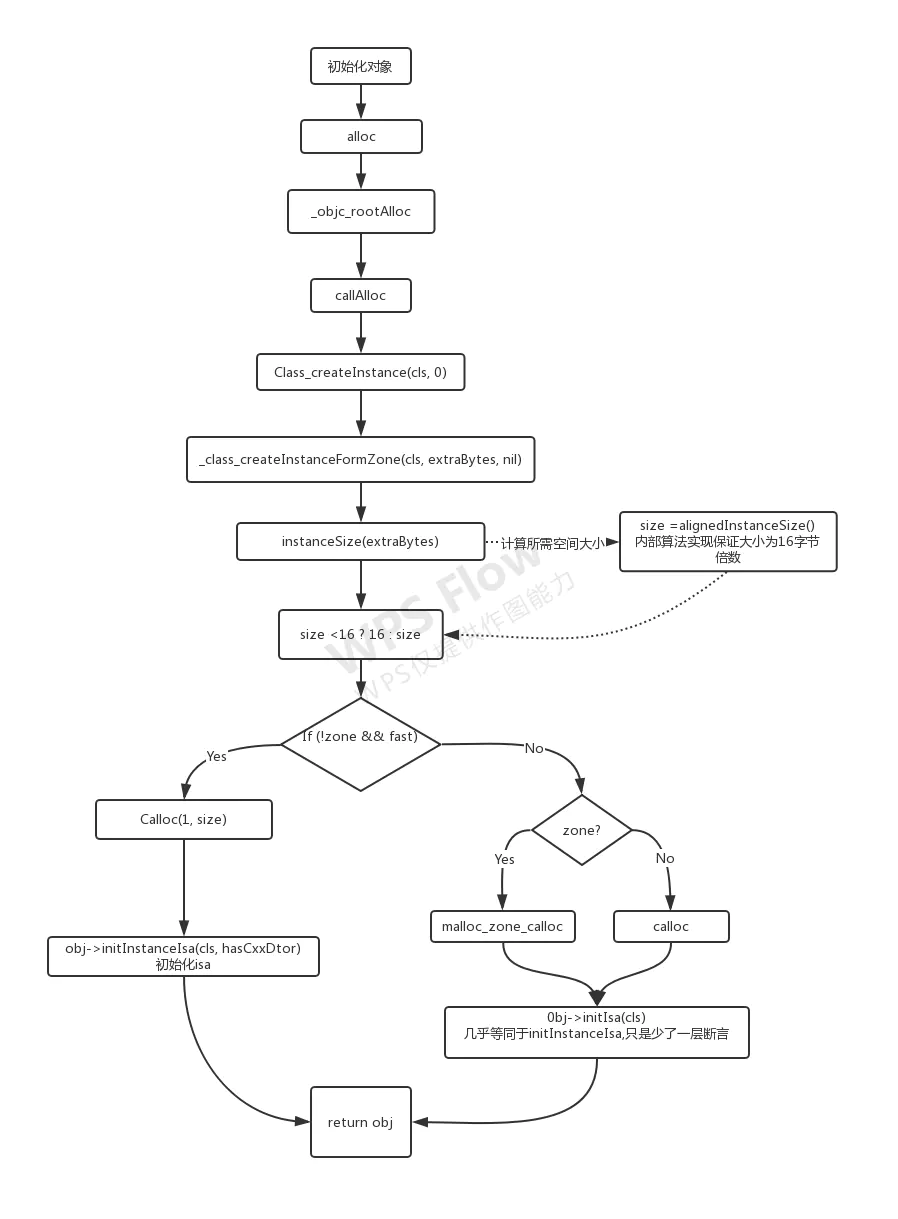
初探alloc
在开发中, 初始化几乎是必须会经过的一个流程.那在iOS开发中, 一个对象的初始化究竟干了一些什么.
探索源码所在位置
探索一个方法的底层实现,那么首先就是需要找到这个方法具体实现的位置.
1: 下断点 : control + in - objc_alloc
2: 下符号断点 : libobjc.A.dylib + [NSObject alloc]:
3: 汇编 libobjc.A.dylib 、objc_alloc:
源码配置
objc4-750源码
Xcode11
MacOS 10.15
源码跟踪
1. 创建一个空类,初始化该类,打上断点
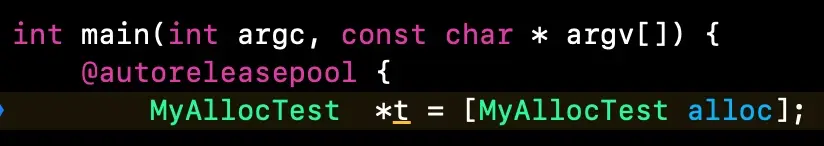
2. 真机运行,跟随alloc进入源码
+ (id)alloc {
return _objc_rootAlloc(self);
}
alloc返回了一个_objc_rootAlloc(self)方法,继续跟进
3. 进入rootAlloc方法
// Base class implementation of +alloc. cls is not nil.
// Calls [cls allocWithZone:nil].
id
_objc_rootAlloc(Class cls)
{
return callAlloc(cls, false/*checkNil*/, true/*allocWithZone*/);
}
rootAlloc返回一个callAlloc方法. 另外可以根据官方注释了解到cls不可为空等其他信息
4. 进入callAlloc方法
// Call [cls alloc] or [cls allocWithZone:nil], with appropriate
// shortcutting optimizations.
static ALWAYS_INLINE id
callAlloc(Class cls, bool checkNil, bool allocWithZone=false)
{
//首先,进入callAlloc之后, 官方第一步进行的就是排除传入class是否为nil
if (slowpath(checkNil && !cls)) return nil;
#if __OBJC2__
if (fastpath(!cls->ISA()->hasCustomAWZ())) {
// No alloc/allocWithZone implementation. Go straight to the allocator.
// fixme store hasCustomAWZ in the non-meta class and
// add it to canAllocFast's summary
//此处返回固定false. 见附图一
if (fastpath(cls->canAllocFast())) {
// No ctors, raw isa, etc. Go straight to the metal.
bool dtor = cls->hasCxxDtor();
id obj = (id)calloc(1, cls->bits.fastInstanceSize());
if (slowpath(!obj)) return callBadAllocHandler(cls);
obj->initInstanceIsa(cls, dtor);
return obj;
}
else {
// Has ctor or raw isa or something. Use the slower path.
//可根据返回的obj是我们初始化返回的对象得知, 具体实现是在class_createInstance中
id obj = class_createInstance(cls, 0);
if (slowpath(!obj)) return callBadAllocHandler(cls);
return obj;
}
}
#endif
// No shortcuts available.
if (allocWithZone) return [cls allocWithZone:nil];
return [cls alloc];
}
5. 进入class_createInstance方法
id
class_createInstance(Class cls, size_t extraBytes)
{
return _class_createInstanceFromZone(cls, extraBytes, nil);
}
6. 进入_class_createInstanceFromZone方法
/***********************************************************************
* class_createInstance
* fixme
* Locking: none
**********************************************************************/
static __attribute__((always_inline))
id
_class_createInstanceFromZone(Class cls, size_t extraBytes, void *zone,
bool cxxConstruct = true,
size_t *outAllocatedSize = nil)
{
//同样的防止空
if (!cls) return nil;
assert(cls->isRealized());
// Read class's info bits all at once for performance
bool hasCxxCtor = cls->hasCxxCtor();
bool hasCxxDtor = cls->hasCxxDtor();
bool fast = cls->canAllocNonpointer();
//根据函数名可猜测为创建这个类所分配的大小空间(跳往6.1节)
size_t size = cls->instanceSize(extraBytes);
if (outAllocatedSize) *outAllocatedSize = size;
//由第4节跳往此方法得知,第三个参数为nil, 即zone=nil, fast值根据canAllocNonpointer进入后可得知与生成isa相关,暂不做分析
id obj;
if (!zone && fast) {
obj = (id)calloc(1, size);
if (!obj) return nil;
obj->initInstanceIsa(cls, hasCxxDtor);
}
else {
//根据不同状体,调用不同的初始化方法
if (zone) {
obj = (id)malloc_zone_calloc ((malloc_zone_t *)zone, 1, size);
} else {
obj = (id)calloc(1, size);
}
if (!obj) return nil;
// Use raw pointer isa on the assumption that they might be
// doing something weird with the zone or RR.
//初始化Isa,几乎等同于initInstanceIsa, 比之少了一些断言
obj->initIsa(cls);
}
//c++等相关判断,暂不做分析
if (cxxConstruct && hasCxxCtor) {
obj = _objc_constructOrFree(obj, cls);
}
//返回对象
return obj;
}
6.1 进入instanceSize方法
size_t instanceSize(size_t extraBytes) {
//计算所需大小
size_t size = alignedInstanceSize() + extraBytes;
// CF requires all objects be at least 16 bytes.
//得知一个初始化对象最小为16个字节
if (size < 16) size = 16;
return size;
}
// Class's ivar size rounded up to a pointer-size boundary.
uint32_t alignedInstanceSize() {
return word_align(unalignedInstanceSize());
}
static inline size_t word_align(size_t x) {
//WORD_MASK 在64位下为7
//进行字节对齐保证大小为8的倍数
return (x + WORD_MASK) & ~WORD_MASK;
}
附图:
附一: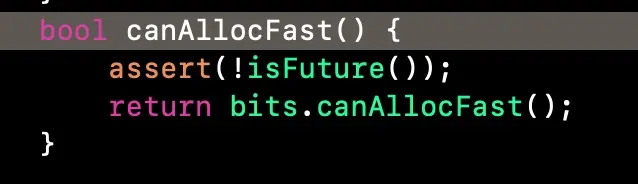
附二:alloc流程分析图