应用进程是怎么启动的?
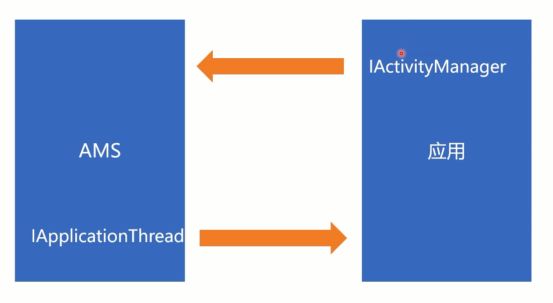
AMS在启动Activity和Service时会检查其所在的应用进程是否存在,不存在就会请求Zygote进程启动需要的应用程序进程。
public class ActivityStack {
......
private final void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {
// Is this activity's application already running?
ProcessRecord app = mService.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName,
r.info.applicationInfo.uid);
......
//app.thread是AMS里面的IApplicationThread
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
//进程已经启动,可以启动组件了。
try {
realStartActivityLocked(r, app, andResume, checkConfig);
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
......
}
}
//启动组件进程
mService.startProcessLocked(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo, true, 0,
"activity", r.intent.getComponent(), false);
}
}
public final class ActivityThread {
......
final ApplicationThread mAppThread = new ApplicationThread();
......
public static void main(String[] args) {
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
private void attach(boolean system) {
......
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
......
}
}
boolean runOnce() throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
String args[];
args = readArgumentList();//参数
if (pid == 0) {
//子进程
handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd, newStderr);
return true;
} else {
//父进程
return handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd, parsedArgs);
}
}
}
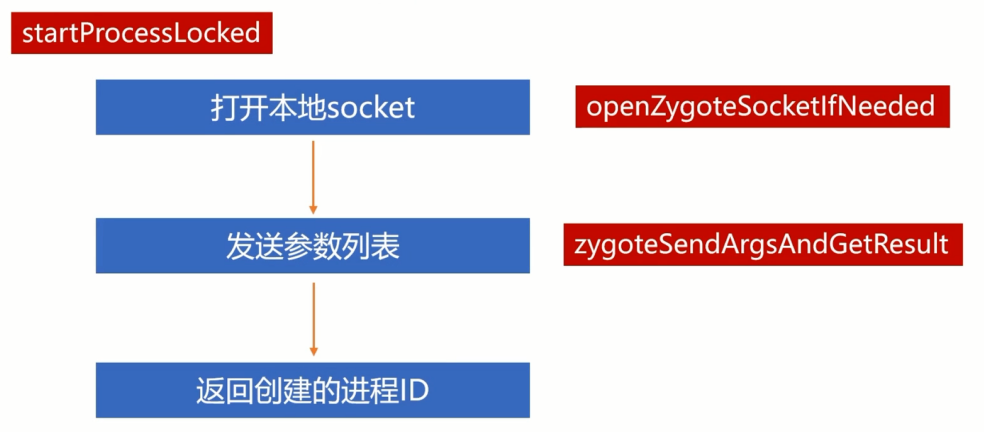
- AMS调用startProcessLocked方法。
- 通过openZygoteSocketIfNeeded打开本地socket。
- 通过zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult发送参数列表。
- zygote如果创建的进程pid=0,代表是子进程,会执行传递过来参数的main方法,如果不为0,则返回pid。
AMS和zygote为什么通过socket通信?
- 因为Binder通信是需要多线程的,代理对象对binder的调用是在binder线程,需要再通过Hander调用主线程来操作。
- 总结起来就是怕父进程binder线程有锁,然后子进程的主线程一直在等其子线程(从父进程拷贝过来的子进程)的资源,但是其实父进程的子进程并没有被拷贝过来,造成死锁,所以fork不允许存在多线程。而非常巧的是Binder通讯偏偏就是多线程,所以干脆父进程(Zgote)这个时候就不使用binder线程。
孵化应用进程这种事为什么不交给SystemServer来做,而专门设计一个Zygote?
- 使用fork()函数得到的子进程是父进程的复制品,子进程完全复制了父进程的资源,包括进程上下文、代码区、数据区、堆区、栈区、内存信息、打开文件的文件描述符、信号处理函数、进程优先级、进程组号、当前工作目录、根目录、资源限制和控制终端等信息,而子进程与父进程的区别有进程号、资源使用情况和计时器等。
- 应用在启动的时候需要做很多准备工作,包括启动虚拟机,加载各类系统资源等等,这些都是非常耗时的,Linux通过写时拷贝技术子进程直接共享zygote进程资源,这个就是zygote存在的价值,这一点呢SystemServer是替代不了的,主要是因为SystemServer里跑了一堆系统服务,这些是不能继承到应用进程的。