一边看侯捷老师(STL源码分析)课程,一边记录下来,仅是给自己当笔记看的。
1. 认识headers,版本,重要资源
GP(Generic Programming)泛型编程,就是用模板(template)为主要工具来编写程序。STL正是泛型编程最成功的作品。
headers:

版本影响:几乎无影响,不同的编译器vc++6.0/dev-c++5.11 所带的标准版几乎无差别。
重要资源:CPlusPlus.com CppReference.com gcc.gnu.org(里面由标准库详细的函数,使用用法等,可以方便查找如何使用。) 书籍:STL源码剖析 / THE C++ STANDARD LIBRARY
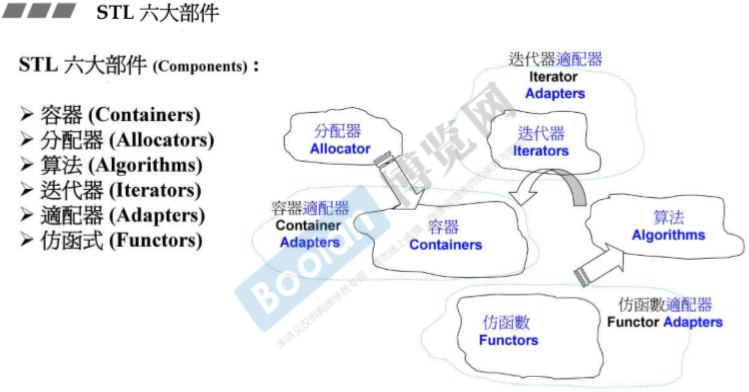
2.STL体系结构基础介绍
输出数组里大于等于40的数量:
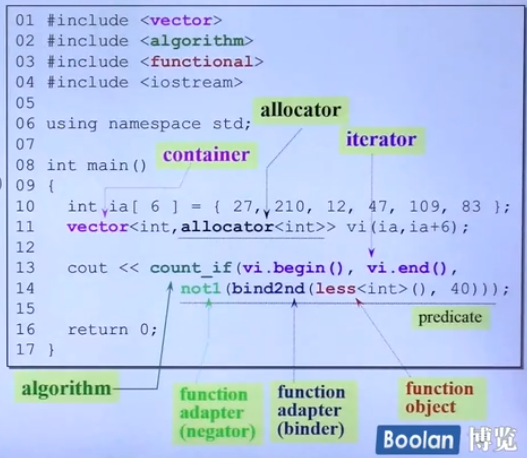
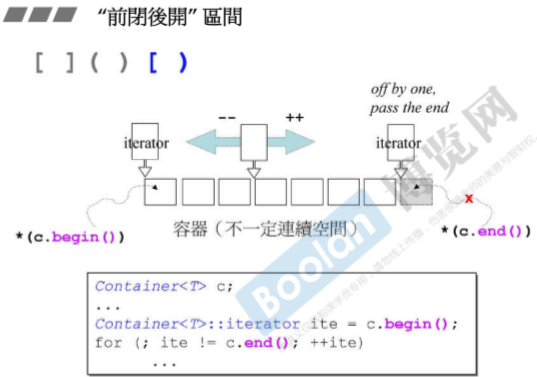
前闭后开原则:所有的容器都遵循前闭后开,begin()指向第一个元素-[,end()指向最后一个元素-)。所以拿最后一个end()返回的泛化指针取引用其实是不存在的,所以遍历容器的话是以下写法:
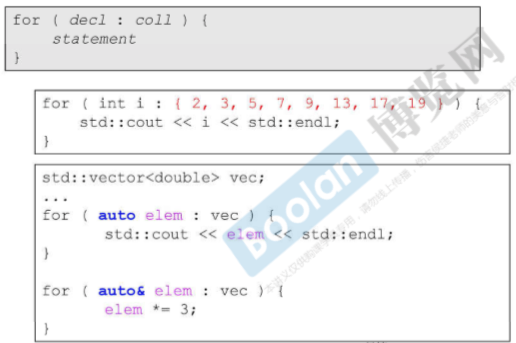

3.容器的结构与分类(一)
序列式容器,关联式容器(key-value 快速查找)- 不定序容器(Hashtable) 红色标注的是c++11加的内容
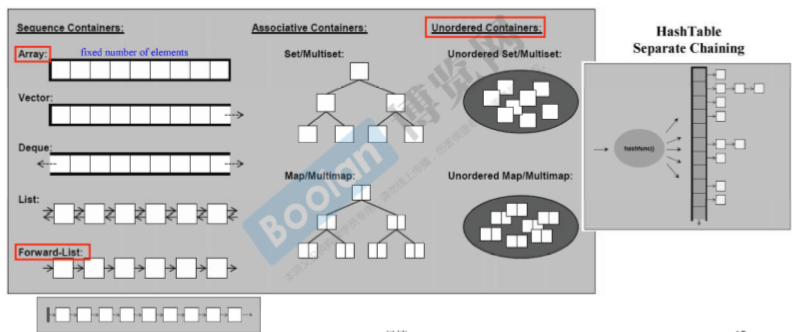
其实标准库并没有规定set/map用什么实现,但由于红黑树的性能很好,所以各家编译器所带的标准库所用的就是红黑树。
测试程序之 辅助函数
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::string;
long get_a_target_long()
{
long target=0;
cout << "target (0~" << RAND_MAX << "): ";
cin >> target;
return target;
}
string get_a_target_string()
{
long target=0;
char buf[10];
cout << "target (0~" << RAND_MAX << "): ";
cin >> target;
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", target);
return string(buf);
}
int compareLongs(const void* a, const void* b)
{
return ( *(long*)a - *(long*)b );
}
int compareStrings(const void* a, const void* b)
{
if ( *(string*)a > *(string*)b )
return 1;
else if ( *(string*)a < *(string*)b )
return -1;
else
return 0;
}
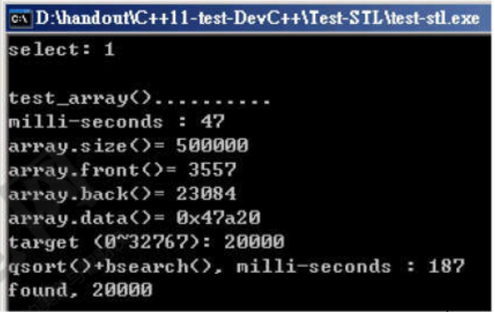
调用以上代码,测试array的性能
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib> //qsort, bsearch, NULL
namespace jj01
{
void test_array()
{
cout << "\ntest_array().......... \n";
array<long,ASIZE> c;
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< ASIZE; ++i) {
c[i] = rand();
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; //
cout << "array.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "array.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "array.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
cout << "array.data()= " << c.data() << endl;
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
::qsort(c.data(), ASIZE, sizeof(long), compareLongs);//排序
long* pItem = (long*)::bsearch(&target, (c.data()), ASIZE, sizeof(long), compareLongs);
cout << "qsort()+bsearch(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; //
if (pItem != NULL)
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
}
执行结果:

#include <vector>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <algorithm> //sort()
namespace jj02
{
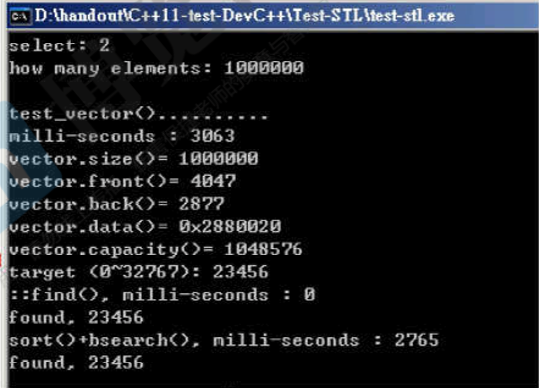
void test_vector(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_vector().......... \n";
vector<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_back(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
//曾經最高 i=58389486 then std::bad_alloc
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "vector.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //1073747823
cout << "vector.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "vector.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "vector.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
cout << "vector.data()= " << c.data() << endl;
cout << "vector.capacity()= " << c.capacity() << endl << endl;
string target = get_a_target_string();
//比较find和先sort后bsearch(二分查找)两种查找方式的速度
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target);
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl << endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
sort(c.begin(), c.end());
cout << "sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
timeStart = clock();
string* pItem = (string*)::bsearch(&target, (c.data()),
c.size(), sizeof(string), compareStrings);
cout << "bsearch(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != NULL)
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl << endl;
}
c.clear();
test_moveable(vector<MyString>(),vector<MyStrNoMove>(), value);
}
}
执行结果:

#include <list>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <algorithm> //find()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj03
{
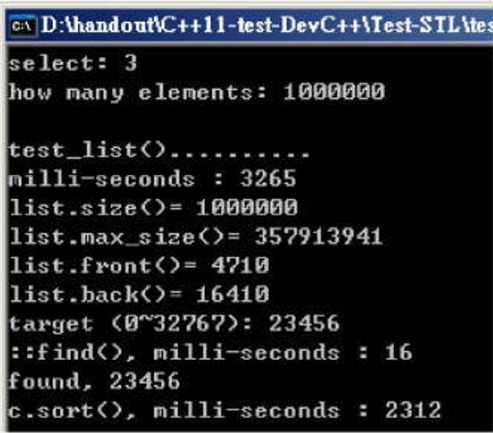
void test_list(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_list().......... \n";
list<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_back(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "list.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "list.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //357913941
cout << "list.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "list.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
string target = get_a_target_string();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target);
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
timeStart = clock();
c.sort();//标准库有sort(),容器自己也有sort(),一般容器内的较快
cout << "c.sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
c.clear();
test_moveable(list<MyString>(),list<MyStrNoMove>(), value);
}
}
执行结果:
#include <forward_list>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj04
{
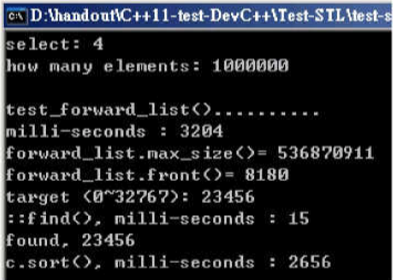
void test_forward_list(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_forward_list().......... \n";
forward_list<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_front(string(buf)); //因为是单向链表,所以只能单向插入
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "forward_list.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //536870911
cout << "forward_list.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
string target = get_a_target_string();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target);
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
timeStart = clock();
c.sort();
cout << "c.sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
c.clear();
}
}
执行结果:
#include <deque>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj05
{
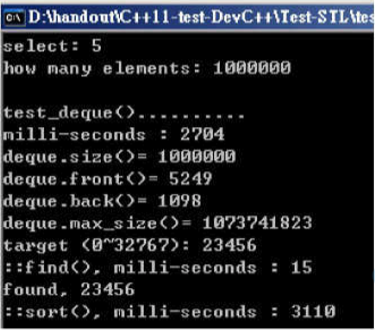
void test_deque(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_deque().......... \n";
deque<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_back(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "deque.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "deque.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "deque.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
cout << "deque.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //1073741821
string target = get_a_target_string();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target);
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
timeStart = clock();
sort(c.begin(), c.end());
cout << "sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
c.clear();
test_moveable(deque<MyString>(),deque<MyStrNoMove>(), value);
}
}
执行结果:
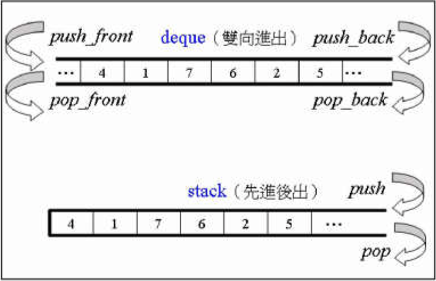
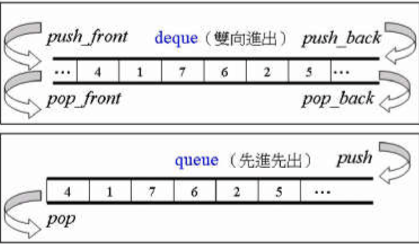
使用容器multiset:(重复的也会放进去)
#include <set>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj06
{
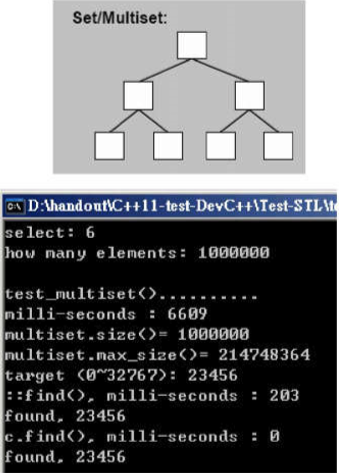
void test_multiset(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_multiset().......... \n";
multiset<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.insert(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "multiset.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "multiset.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //214748364
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); //比 c.find(...) 慢很多
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target); //比 std::find(...) 快很多
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
c.clear();
test_moveable(multiset<MyString>(),multiset<MyStrNoMove>(), value);
}
}
执行结果:
#include <map>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj07
{
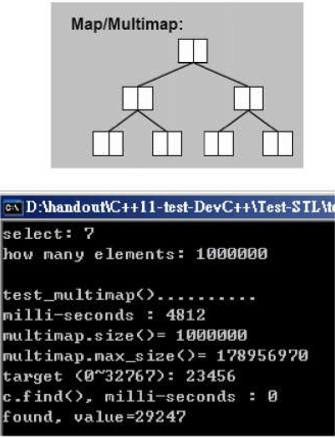
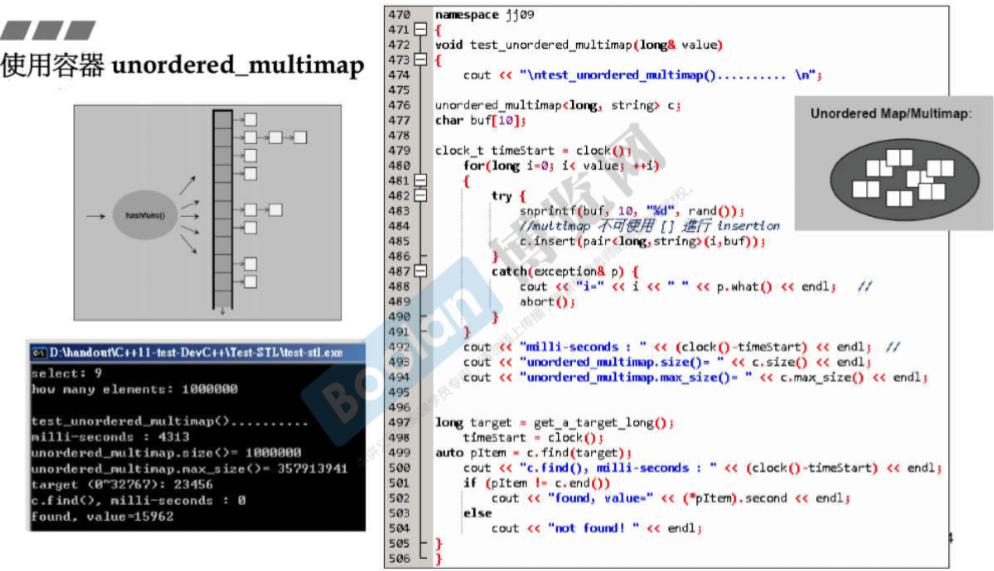
void test_multimap(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_multimap().......... \n";
multimap<long, string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
//multimap 不可使用 [] 做 insertion
c.insert(pair<long,string>(i,buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "multimap.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "multimap.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //178956970
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target);
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, value=" << (*pItem).second << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
c.clear();
}
}
执行结果:
#include <unordered_set>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj08
{
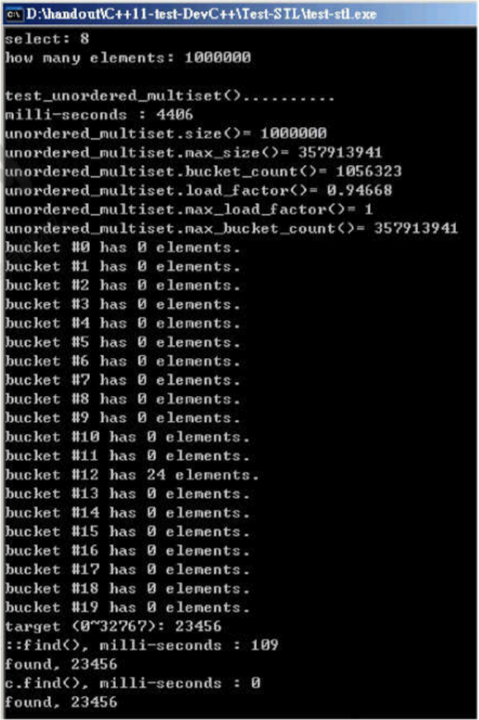
void test_unordered_multiset(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_unordered_multiset().......... \n";
unordered_multiset<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.insert(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //357913941
cout << "unordered_multiset.bucket_count()= " << c.bucket_count() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.load_factor()= " << c.load_factor() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_load_factor()= " << c.max_load_factor() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_bucket_count()= " << c.max_bucket_count() << endl;
for (unsigned i=0; i< 20; ++i) {
cout << "bucket #" << i << " has " << c.bucket_size(i) << " elements.\n";
}
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); //比 c.find(...) 慢很多
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target); //比 std::find(...) 快很多
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
c.clear();
test_moveable(unordered_multiset<MyString>(),unordered_multiset<MyStrNoMove>(), value);
}
}
#include <set>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj13
{
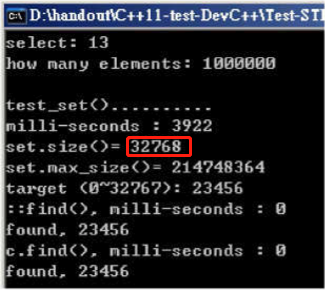
void test_set(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_set().......... \n";
set<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.insert(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "set.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "set.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //214748364
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); //比 c.find(...) 慢很多
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target); //比 std::find(...) 快很多
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
}
}
#include <map>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj14
{
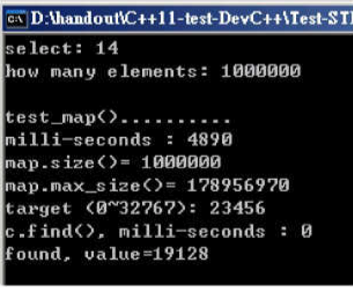
void test_map(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_map().......... \n";
map<long, string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c[i] = string(buf);
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "map.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "map.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //178956970
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target);
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, value=" << (*pItem).second << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
c.clear();
}
}
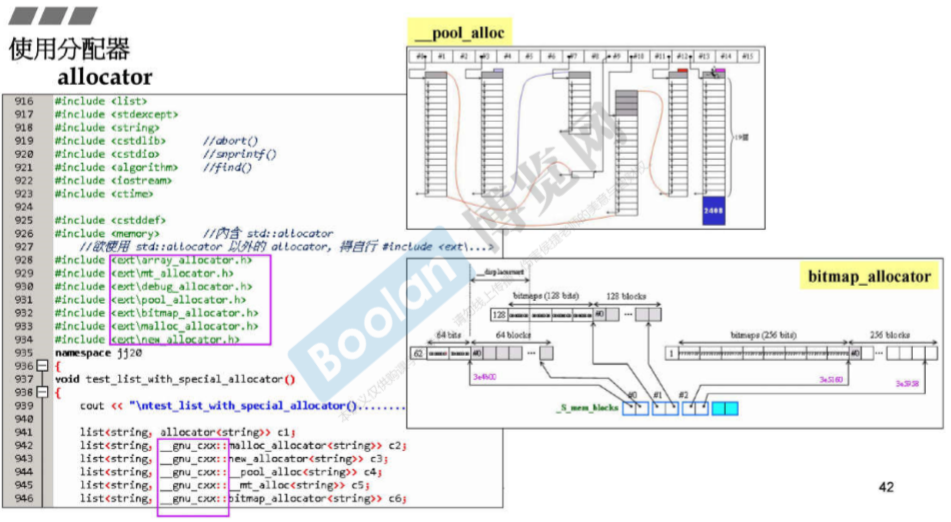
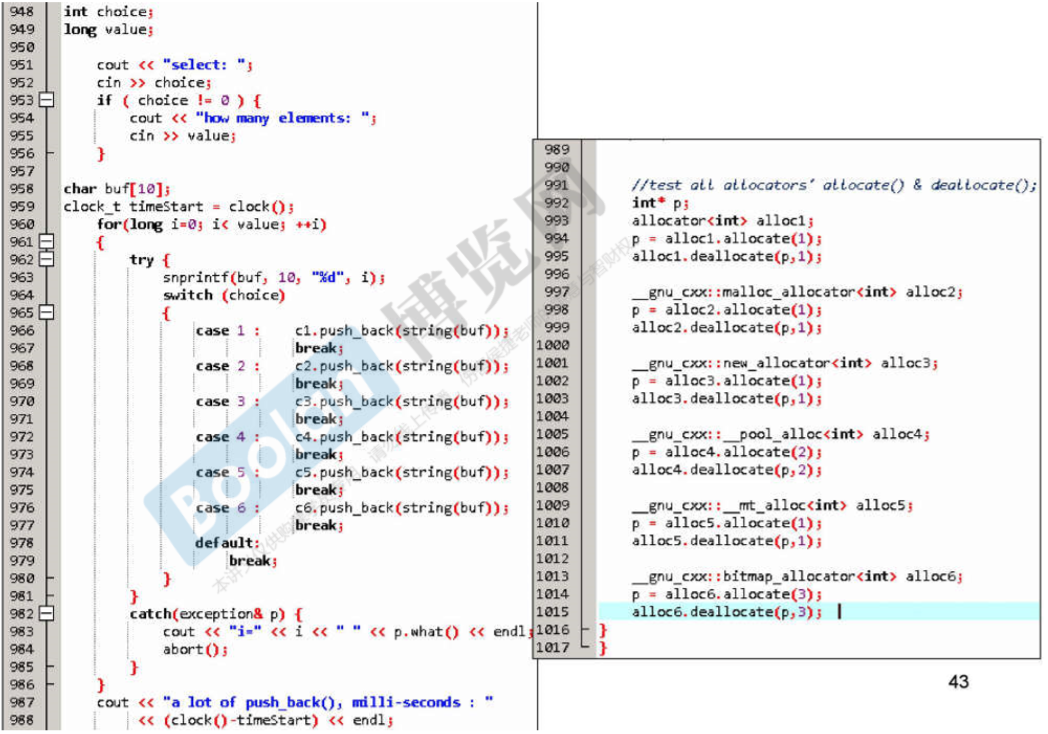
4.使用分配器