回顾
首先回顾一下未学习Spring之前的Mybatis配置.
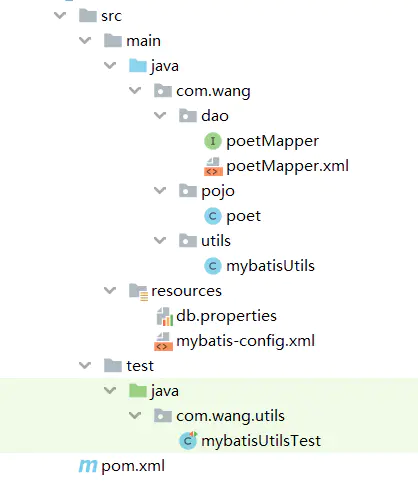
- 首先我们创建了 mybatis-config.xml文件用来配置数据库连接的相关信息,以及注册了相关的Mapper映射文件.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<properties resource="db.properties"/>
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.wang.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/wang/dao/poetMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
然后编写了一个工具类,用于获得sqlSession连接.
public class mybatisUtils {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
static {
String res = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(res);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
}
public static SqlSession getSession() {
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
}
最后测试
public class mybatisUtilsTest {
//注意此处的 @Test 注解,不可少。
@Test
public void test() {
//下边两行就是我们创建的工厂类的使用,从工厂类中获得一个session。
SqlSession sqlSession = mybatisUtils.getSession();
poetMapper poetMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(com.wang.dao.poetMapper.class);
List<poet> poets = poetMapper.getList();
for (poet poet : poets) {
System.out.println(poet);
}
}
}
在Spring中,自然要将一部分托管给Spring容器.
Spring整合Mybatis
虽然 Spring 可以将mybatis整合,但是答题的思路是不会变的.
首先创建一个数据源,再创建一个SQLSession工厂,最后获取sqlSession.
类似传统方式的Spring模式实现
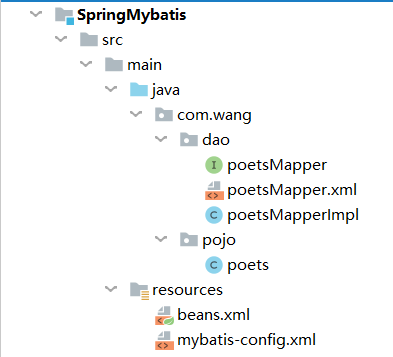
- 创建数据源
Spring框架中,有一个org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource bean,我们只需要显式的将数据注入其中即可.
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="username" value="XXX"/>
<property name="password" value="XXX"/>
<property name="url" value="XXX"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="XXX"/>
</bean>
- 创建sqlSession工厂
同上,Spring也有一个内置的org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean,我们将第一步获得的数据源以引用的方式注入即可. 在这一步,仅有 "datasource"属性是必须注入的,其余无要求.
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"/>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="com/wang/dao/poetsMapper.xml"/>
</bean>
- 获取session
Spring真是万能啊,感叹一下,这一步它又替我们解决了.
<bean id="sqlSession" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate">
<constructor-arg name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
上边这三个步骤在整合时100%会使用到,且不会有太大的变化.下边需要我们编写一些自己的东西
- 实现一个接口
public class poetsMapperImpl implements poetsMapper {
private SqlSessionTemplate sqlSession;
public void setSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate sqlSession) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
}
@Override
public List<poets> getPoets() {
return sqlSession.getMapper(poetsMapper.class).getPoets();
}
}
与之前不同的是,在实现接口的同时,我们在类的内部增加了一个属性SqlSessionTemplate sqlSession ,并且增加了相应的set方法.这是为了将SQLSession工厂生产的sqlSession注入到类中.当然,使用构造器注入的方式也是可行的.
最后我们需要将这个类注册到Spring容器中.
<bean id="poetsMapper" class="com.wang.dao.poetsMapperImpl">
<property name="sqlSession" ref="sqlSession"/>
</bean>
- 测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext cpx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
poetsMapper poetsMapper = cpx.getBean("poetsMapper", poetsMapper.class);
List<poets> poets = poetsMapper.getPoets();
for (com.wang.pojo.poets poet : poets) {
System.out.println(poet);
}
- 完成

继承SqlSessionDaoSupport类实现
和上边方法相比,这种方法更为简单,但是本质是一样的.
只需要在实现接口的时候继承 SqlSessionDaoSupport 类,然后再注入依赖即可,
public class poetsMapperImpl extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements poetsMapper {
@Override
public List<poets> getPoets() {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(poetsMapper.class).getPoets();
}
}
sqlSessionTemplate和sqlSessionFactory两个属性任意注入一个即可,两个都注入也不会报错.
<bean id="poetsMapper" class="com.wang.dao.poetsMapperImpl">
<property name="sqlSessionTemplate" ref="sqlSession"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>