优秀的一些博客网站
这是知乎上的一个链接,我相信这里面的内容能更好的引导大家学习springBoot
Redis相关
SpringBoot中自定义RedisTemplate-谢谢同学,这里面Redis做缓存版本很老,方法都失效了
打破沉默CSDN-SpringBoot集成Redis和配置Redis做缓存
什么是Redis

SpringBoot与Redis整合--一般配置以及简单使用
- 引入pom
<!--引入spring data redis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
- Redis配置类
/**
* @author a small asshole
* @version 1.0
* @description redis配置类
* @date in 13:52 2020/1/16
* @since 1.0
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory){
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate = new StringRedisTemplate(redisConnectionFactory);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
objectMapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
//objectMapper.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL); 这个方法在jackson Since 2.10版本中移除掉了
objectMapper.activateDefaultTyping(BasicPolymorphicTypeValidator.builder().build(),ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(objectMapper);
/**
* 设置template set value时使用的序列化方式
*/
stringRedisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
/**必须执行这个函数,初始化RedisTemplate*/
stringRedisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return stringRedisTemplate;
}
}
上面是对RedisTemplate做的一些定制化操作(定义Redis存储value的序列化方式等),下面图片是我在编码时不理解的地方的答案,虽然 还不是很清楚,但是看看还是能增长见识的,希望知其然而知其所以然。 一般情况下,我个人认为,使用SpringBoot提供的自动配置的RedisTemplate也就足够了,随意定制化不是必须的,看需要。

- redis测试类
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class RedisTestController {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
/**
*正常使用
*/
@Test
public void setValueToRedis(){
User user = new User();
user.setUserId(123);
user.setName("jim");
String userJosnStr = JSONObject.toJSONString(user);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("system-user",userJosnStr);
}
@Test
public void getValue(){
System.out.println(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("system-user"));
}
}
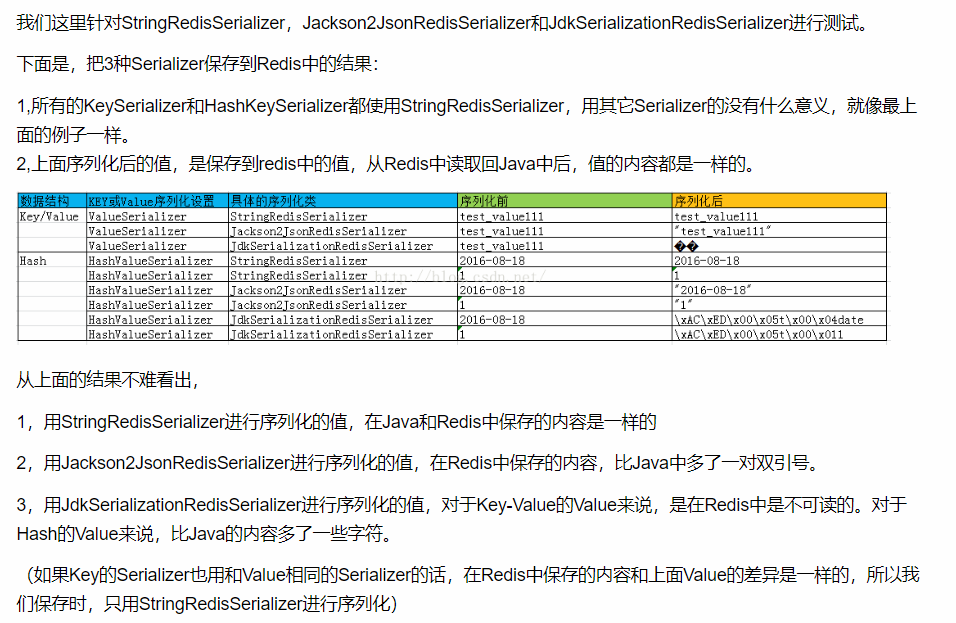
SpringBoot使用Redis作为缓存
Spring Cache是Spring框架提供的对缓存使用的抽象类,支持多种缓存,比如Redis、EHCache等,集成很方便。同时提供了多种注解来简化缓存的使用,可对方法进行缓存。 设置RedisConfig
- 在Redis配置类上加上 @EnableCaching注解表明开启缓存
- 配置类配置缓存管理器
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManagerBuilder(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(60)); // 设置缓存有效期一分钟
return RedisCacheManager
.builder(RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(connectionFactory))
.cacheDefaults(redisCacheConfiguration).build();
}
- 在需要使用缓存的地方加上 @Cacheable(value = "commodity",key = "#id"),这会自动把当前被标注的方法的返回值存入Redis中作为缓存,如果这个注解是标记在类上的,该类中的所有方法的返回值都会存入Redis作为缓存。 下面的代码,我在get查询时设置了一个缓存,然后在对这个数据进行update时直接把这个缓存删除,下次再get时就会查询数据库同时设置一个新的缓存。
@RestController
public class RedisCacheController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@PostMapping("/add")
public boolean addUser(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("jim");
return userService.addUser(user);
}
@GetMapping("/get")
@Cacheable(value = "commodity",key = "#id")
public User getUser(Integer id){
return userService.getUser(id);
}
@PutMapping("/update")
@CacheEvict(value = "commodity",key = "#user.userId")
public boolean updateUser(@RequestBody User user){
return userService.updateUser(user);
}
}
验证:第一次查询时会访问数据库,后面的查询在缓存未失效时都是拿去缓存中的数据。
@Cacheable的一些使用理解:
这是注解下中value属性的注释,大致看下可以知道,value表示cache的name
/** * Names of the caches in which method invocation results are stored. *
Names may be used to determine the target cache (or caches), matching * the qualifier value or bean name of a specific bean definition. * @since 4.2 * @see #value * @see CacheConfig#cacheNames */ @AliasFor("value") String[] cacheNames() default {};
另外一个属性key,就是当前缓存对象对应的key值。研究下注释大致可以知道,key这个属性是致辞spring表达式的,默认情况下是“”,这意味着当前被标注的方法的参数都讲自动作为cache对象的key存在,除非自定义了key的生成方式。
/** * Spring Expression Language (SpEL) expression for computing the key dynamically. *
Default is {@code ""}, meaning all method parameters are considered as a key, * unless a custom {@link #keyGenerator} has been configured. *
The SpEL expression evaluates against a dedicated context that provides the * following meta-data: *
*
*/ String key() default "";- {@code #root.method}, {@code #root.target}, and {@code #root.caches} for * references to the {@link java.lang.reflect.Method method}, target object, and * affected cache(s) respectively.
*- Shortcuts for the method name ({@code #root.methodName}) and target class * ({@code #root.targetClass}) are also available. *
- Method arguments can be accessed by index. For instance the second argument * can be accessed via {@code #root.args[1]}, {@code #p1} or {@code #a1}. Arguments * can also be accessed by name if that information is available.
*
所以最后存入redis中是就形成这样的整个键value:key,就像文件夹套文件夹,cacaheName文件夹里面有key的文件夹,每个不同名字的key文件夹里面都是自己的cache对象
面试相关:
思考题:像我这样在配置cacheManager的时候就设置缓存的失效时间会带来什么问题吗?
我们考虑一种场景,大量并发情况下,大量缓存设置了一样的失效时间,比如60s失效,同一时刻,大量缓存失效,导致所有的连接都直接访问数据库去了,导致数据库一瞬间挂掉了。这就是缓存雪崩。解决这个问题,有一个比较通用的做法,就是给缓存设置过期时间的时加上一个随机数,避免大量缓存都设置同样的过去时间。
一些Redis相关的面试题