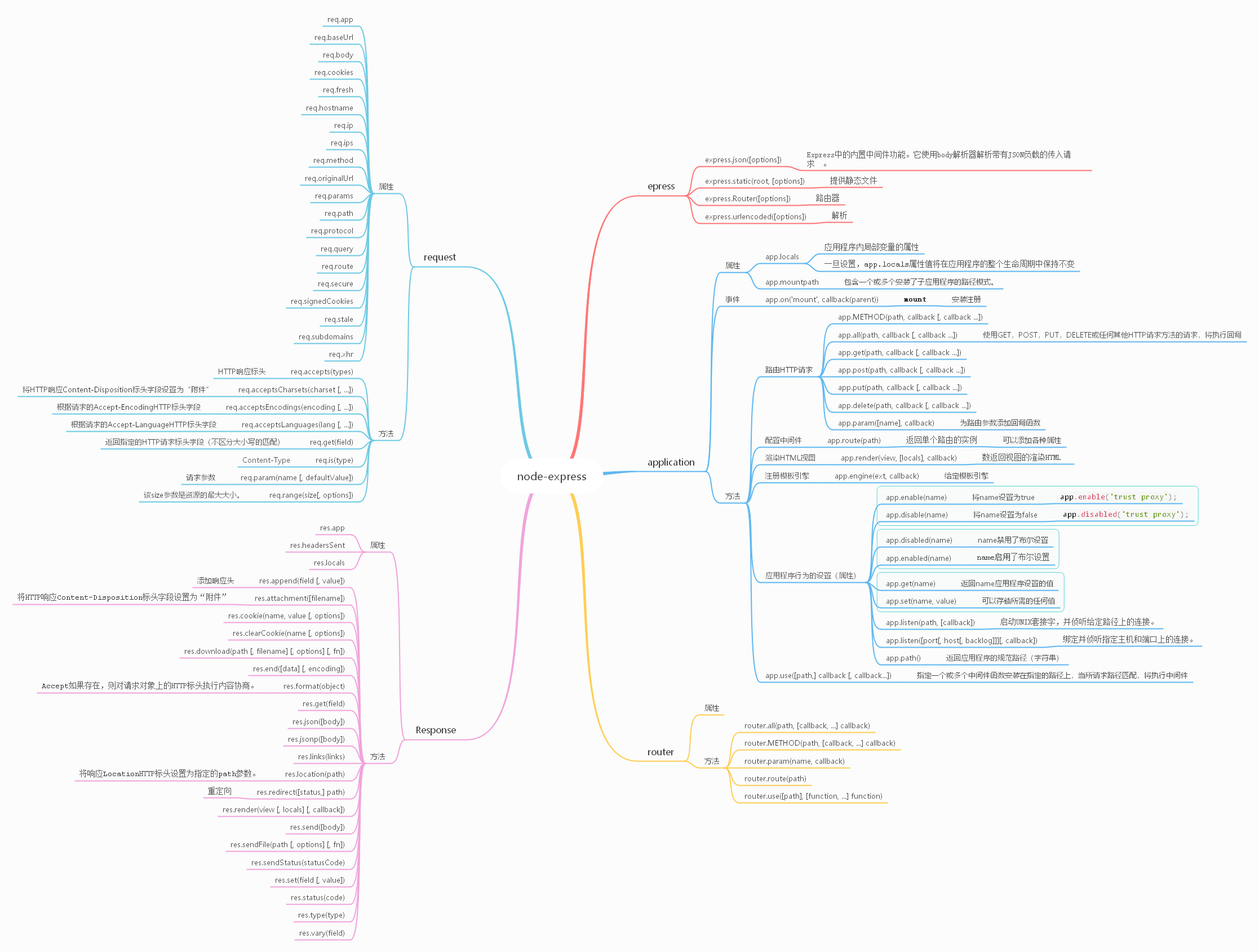
Nodejs: express、koa、eggjs、nextjs
express 学习路线
安装
npm install express --save
hello World
- 创建项目文件夹
- npm init 初始化项目package.json
- npm i express --save 安装express包
- 创建app.js
- 编辑app.js
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
app.get('/', (req, res) => res.send('Hello World!'))
app.listen(3000, () => console.log('Example app listening on port 3000!'))
- node app.js 启动服务
两大部分构成 路由和中间件
1. 路由
路由是指应用程序的端点(URI)如何响应客户端请求。特定端点由URI(或路径)和HTTP请求方法(get\post\put\delete)组成。
应用程序“侦听”与指定的路由和方法匹配的请求,并且当它检测到匹配项时,它将调用指定的回调函数。
每个路由可以具有一个或多个处理程序函数,这些函数在匹配该路由时执行。对于多个回调函数,重要的是提供next回调函数的参数,然后next()在函数体内调用以将控制权移交给下一个回调。
app.METHOD(PATH, HANDLER)
app是的实例express。
METHOD是小写的HTTP请求方法。
PATH 是服务器上的路径。
HANDLER 是匹配路线时执行的功能。
1. 方法
- app.get
- app.post
- app.put
- app.delete
- app.all 用于为所有 HTTP请求方法的路径加载中间件功能。
- app.route
代码分析
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.send('GET request to the homepage')
})
- epress 是引入的包
- app 是express的实例,具体操作路由等
- res
2. 路径
路由路径可以是字符串,字符串模式或正则表达式。
字符?,+,*,和()是他们的正则表达式的对应的子集。连字符(-)和点(.)由基于字符串的路径逐字解释。
路由参数被命名为URL段,用于捕获URL中在其位置处指定的值。捕获的值将填充到req.params对象中,并将路径中指定的route参数的名称作为其各自的键。
Route path: /users/:userId/books/:bookId
Request URL: http://localhost:3000/users/34/books/8989
req.params: { "userId": "34", "bookId": "8989" }
3. 回调函数
路由处理程序可以采用函数,函数数组或二者组合的形式,如以下示例所示。
app.get('/example/b', function (req, res, next) {
console.log('the response will be sent by the next function ...')
next()
}, function (req, res) {
res.send('Hello from B!')
})
4. 回调返回res对象
- res.download() 下载一个文件
- res.end() 结束请求
- res.json() 返回json格式数据
- res.jsonp() Send a JSON response with JSONP support.
- res.redirect() Redirect a request.
- res.render() Render a view template.
- res.send() Send a response of various types.
- res.sendFile() Send a file as an octet stream.
- res.sendStatus() Set the response status code and send its string representation as the response body.
2.中间件
-
中间件功能可以执行以下任务:
- 执行任何代码。
- 更改请求和响应对象。
- 结束请求-响应周期。
- 调用堆栈中的下一个中间件函数。
-
Express应用程序可以使用以下类型的中间件:
- 应用层中间件
- 路由器级中间件
- 错误处理中间件
- 内置中间件
- 第三方中间件
应用层中间件
- 只要进入应用程序都访问
var app = express()
app.use(function (req, res, next) {
console.log('Time:', Date.now())
next()
})
- 查找对应的路由才访问,无论任何请求
app.use('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
console.log('Request Type:', req.method)
next()
})
- 路由的回调函数也可以看作是一个中间件
app.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
res.send('USER')
})
- 一系列中间件功能,是工作栈,通过next依次执行
app.use('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
console.log('Request URL:', req.originalUrl)
next()
}, function (req, res, next) {
console.log('Request Type:', req.method)
next()
})
- 从上到下执行,所有后面的中间件被忽略
app.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
console.log('ID:', req.params.id)
next()
}, function (req, res, next) {
res.send('User Info')
})
// handler for the /user/:id path, which prints the user ID
app.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
res.end(req.params.id)
})
- 要从路由器中间件堆栈中跳过其余中间件功能,请调用next('route')将控制权传递给下一条路由。 注意:next('route')仅在使用app.METHOD()或router.METHOD()函数加载的中间件函数中有效。
app.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
// if the user ID is 0, skip to the next route
if (req.params.id === '0') next('route')
// otherwise pass the control to the next middleware function in this stack
else next()
}, function (req, res, next) {
// send a regular response
res.send('regular')
})
// handler for the /user/:id path, which sends a special response
app.get('/user/:id', function (req, res, next) {
res.send('special')
})
路由器级中间件
路由器级中间件与应用程序级中间件的工作方式相同,只不过它绑定到的实例express.Router()。
var router = express.Router() 使用router.use()和router.METHOD()函数加载路由器级中间件。
错误处理中间件 四个参数
app.use(function (err, req, res, next) {
console.error(err.stack)
res.status(500).send('Something broke!')
})
内置中间件
- express.static提供静态资源,例如HTML文件,图像等。
app.use(express.static('public'))使用中间件
- express.json使用JSON负载解析传入的请求。
- express.urlencoded使用URL编码的有效内容解析传入的请求。
第三方中间件
思维导图