摘要
本文从 V8 源码的角度分析为什么 Javascript 语言中的函数是一等公民。首先会介绍一等公民的概念,然后对比一下 C 语言函数和 Javascript 函数的底层表示,以便理解为什么说 Javascript 函数是一等公民。
什么是编程语言中的一等公民
In computer science, a programming language is said to have first-class functions if it treats functions as first-class citizens. This means the language supports passing functions as arguments to other functions, returning them as the values from other functions, and assigning them to variables or storing them in data structures.
以上内容来自维基百科,也就是说,在编程语言中,一等公民可以作为函数参数,可以作为函数返回值,也可以赋值给变量。
C 语言函数的底层表示
以下代码,可复制粘贴在 tool.lu/coderunner/ 运行。
#include <stdio.h>
int times10 (int small) {
return small * 10;
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
int small = 1;
int large = times10(small);
printf("result is %d\n", large);
return 0;
}代码逻辑非常简单,定义了 times10 函数,函数的功能是将入参乘 10 后返回。main 函数调用 times10 函数,代码运行结果在 Xcode 中如下:
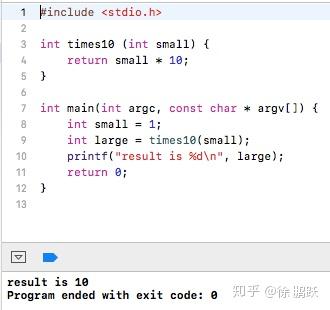
times10 函数对应的 X64 汇编如下:
0x100000f30 <+0>: pushq %rbp
0x100000f31 <+1>: movq %rsp, %rbp ; 前两行是套路,保存栈寄存器
0x100000f34 <+4>: movl %edi, -0x4(%rbp) ; edi 寄存器存的是入参
0x100000f37 <+7>: imull $0xa, -0x4(%rbp), %eax ; 乘 10 后的结果存入 eax
0x100000f3b <+11>: popq %rbp ; 最后两行也是套路,恢复栈寄存器
0x100000f3c <+12>: retqC 语言是编译型语言,编译器会将 C 语言的函数体编译成机器码,反汇编后就是上面看到的汇编语言函数。
main 函数对应的 X64 汇编如下:
0x100000f40 <+0>: pushq %rbp
0x100000f41 <+1>: movq %rsp, %rbp
0x100000f44 <+4>: subq $0x20, %rsp
0x100000f48 <+8>: movl $0x0, -0x4(%rbp)
0x100000f4f <+15>: movl %edi, -0x8(%rbp)
0x100000f52 <+18>: movq %rsi, -0x10(%rbp)
0x100000f56 <+22>: movl $0x1, -0x14(%rbp)
0x100000f5d <+29>: movl -0x14(%rbp), %edi
0x100000f60 <+32>: callq 0x100000f30 ; 调用 times10
0x100000f65 <+37>: leaq 0x3a(%rip), %rdi
0x100000f6c <+44>: movl %eax, -0x18(%rbp)
0x100000f6f <+47>: movl -0x18(%rbp), %esi
0x100000f72 <+50>: movb $0x0, %al
0x100000f74 <+52>: callq 0x100000f86 ; 调用 printf
0x100000f79 <+57>: xorl %esi, %esi
0x100000f7b <+59>: movl %eax, -0x1c(%rbp)
0x100000f7e <+62>: movl %esi, %eax
0x100000f80 <+64>: addq $0x20, %rsp
0x100000f84 <+68>: popq %rbp
0x100000f85 <+69>: retq在地址为 0x100000f60 的这行汇编里
0x100000f60 <+32>: callq 0x100000f30 ; 调用 times10main 函数调用 times10 函数,从生成的汇编来看,编译完成后 times10 这个函数名称对应的是地址,也就是说 C 语言的函数名在编译后将不复存在,它对应的是地址。 看到这里,可以看出 C 语言函数和 JavaScript 函数的区别,由于 C 语言函数体对应机器码,函数名称对应地址,所以 C 语言不支持为函数添加属性。
对照编程语言一等公民的定义,虽然 C 语言的函数不能直接做为参数传递,也不能直接做为结果返回,但通过函数指针,可以完成这一切。所以 C 语言的函数“勉强”是一等公民,笔者的第一份工作是 C 语言程序员,C 语言程序员比较关注底层实现,基本不会讨论也不会在意 C 语言函数到底是不是一等公民。写这段文字的目的是为了对比 JavaScript 语言函数的底层表示,见下文。
JavaScript 语言函数的底层表示
V8 会将 JavaScript 函数编译成 C++ 类 JSFunction 的实例,JSFunction 声明代码如下:
// JSFunction describes JavaScript functions.
class JSFunction : public JSObject {
public:
// [prototype_or_initial_map]:
DECL_ACCESSORS(prototype_or_initial_map, Object)
// [shared]: The information about the function that
// can be shared by instances.
DECL_ACCESSORS(shared, SharedFunctionInfo)
static const int kLengthDescriptorIndex = 0;
static const int kNameDescriptorIndex = 1;
// Home object descriptor index when function has a [[HomeObject]] slot.
static const int kMaybeHomeObjectDescriptorIndex = 2;
// [context]: The context for this function.
inline Context context();
inline bool has_context() const;
inline void set_context(Object context);
inline JSGlobalProxy global_proxy();
inline NativeContext native_context();
inline int length();
static Handle<Object> GetName(Isolate* isolate, Handle<JSFunction> function);
static Handle<NativeContext> GetFunctionRealm(Handle<JSFunction> function);
// [code]: The generated code object for this function. Executed
// when the function is invoked, e.g. foo() or new foo(). See
// [[Call]] and [[Construct]] description in ECMA-262, section
// 8.6.2, page 27.
inline Code code() const;
inline void set_code(Code code);
inline void set_code_no_write_barrier(Code code);
// 源码太长,复制粘贴到此结束
}
从代码的第一行注释:
// JSFunction describes JavaScript functions.可知,JavaScript 函数在 V8 中是 JSFunction 的实例,JSFunction 源码很长,这里举例佐证 JavaScript 函数是 V8 中的一个 C++ 对象。
JavaScript 函数的 toString 方法,可以输出一个函数的实现代码。比如:
a = _ => console.log(_)
a.toString() // 输出 "_ => console.log(_)"
但当对内置对象的方法调用 toString 时,比如:
Math.max.toString() // 输出 "function max() { [native code] }"
并没有输出函数的实现代码,而且输出的字符串中 native code 是从哪里来的呢?这个问题困扰了笔者 3 年,下面,我们一起看下 JavaScript 函数的 toString 方法在 V8 中的实现,源码如下:
// ES6 section 19.2.3.5 Function.prototype.toString ( )
BUILTIN(FunctionPrototypeToString) {
HandleScope scope(isolate);
Handle<Object> receiver = args.receiver();
if (receiver->IsJSBoundFunction()) {
return *JSBoundFunction::ToString(Handle<JSBoundFunction>::cast(receiver));
}
if (receiver->IsJSFunction()) {
return *JSFunction::ToString(Handle<JSFunction>::cast(receiver));
}
// 源码太长,而且本文中的例子在上面的 return 已经返回,故后面省略,对源码感兴趣的朋友请点击上面的源码链接
}
BUILTIN 是 C++ 定义的宏,C++ 预处理阶段后,上面的代码会变成 C++ 类的一个方法。Math.max 是 JSFunction 的实例,receiver->IsJSFunction() 为true,会执行 JSFunction 的 ToString 类方法,源码如下:
// static
Handle<String> JSFunction::ToString(Handle<JSFunction> function) {
Isolate* const isolate = function->GetIsolate();
Handle<SharedFunctionInfo> shared_info(function->shared(), isolate);
// Check if {function} should hide its source code.
if (!shared_info->IsUserJavaScript()) {
return NativeCodeFunctionSourceString(shared_info);
}
// 源码太长,而且本文中的例子在上面的 return 已经返回,故后面省略,对源码感兴趣的朋友请点击上面的源码链接
}
Math.max 是 V8 内置函数,不是由用户定义的,!shared_info->IsUserJavaScript() 结果是 true,执行 NativeCodeFunctionSourceString 函数。源码如下:
Handle<String> NativeCodeFunctionSourceString(
Handle<SharedFunctionInfo> shared_info) {
Isolate* const isolate = shared_info->GetIsolate();
IncrementalStringBuilder builder(isolate);
builder.AppendCString("function ");
builder.AppendString(handle(shared_info->Name(), isolate));
builder.AppendCString("() { [native code] }");
return builder.Finish().ToHandleChecked();
}
我们终于看到了期待的字符串 native code:
builder.AppendCString("() { [native code] }");
梳理一下 JavaScript 函数 toString 方法的调用链路:BUILTIN(FunctionPrototypeToString) -> JSFunction::ToString -> NativeCodeFunctionSourceString。可见 JavaScript 函数对应 V8 JSFunction 的实例,JavaScript 函数的 toString 方法对应 V8 的 JSFunction::ToString 方法。
JavaScript 函数的 name 属性,可以获取函数名称,比如:
a = _ => console.log(_)
a.name // 输出函数名 "a"
JavaScript 函数 name 属性的实现过程中,调用了 JSFunction 的 GetName 方法,源码如下:
// static
Handle<Object> JSFunction::GetName(Isolate* isolate,
Handle<JSFunction> function) {
if (function->shared().name_should_print_as_anonymous()) {
return isolate->factory()->anonymous_string();
}
return handle(function->shared().Name(), isolate);
}
JavaScript 函数的 length 属性,可以获取参数个数,比如:
a = _ => console.log(_)
a.length // 输出 1
JavaScript 函数 length 属性的实现过程中,调用了 JSFunction 的 length 方法,源码如下:
int JSFunction::length() { return shared().length(); }
举例佐证到此为止,可见 JavaScript 函数在 V8 中是 JSFunction 的实例,既然是 C++ 对象,JavaScript 函数当然可以做为参数传递给其它函数,也可以做为函数的返回值。理解了 JavaScript 函数是 C++ 对象,也很容易理解 JavaScript 函数式编程中的一些写法,比如:
const isNumber = _ => !isNaN(_);
function isPrice (price) {
return [Boolean, isNumber].every(fn => {
return fn(price)
})
}
isPrice ('123') // 返回 true
isPrice 校验用户输入的字符串是否是一个价格,Boolean 和 isNumber 这两个 JavaScript 函数都是 V8 中 JSFunction 的实例,那么在 V8 看来,[Boolean, isNumber].every 相当于遍历数组,并且数组中的每一个对象都最 JSFunction。如果把 every 换成 reduce,稍加改造便可实现类似 Vue 过滤器 filter 的功能。
const add3 = num => num + 3;
const mul2 = num => num * 2;
function numberReduce (num) {
return [add3, mul2].reduce((acc, fn) => {
return fn(acc)
}, num)
}
numberReduce(3) // 返回 (3 + 3) * 2 = 12
在 V8 中 JSFunction 继承自 JSObject,如下:
// JSFunction describes JavaScript functions.
class JSFunction : public JSObject {
// 略
}
JSObject 的声明如下:
// The JSObject describes real heap allocated JavaScript objects with
// properties.
// Note that the map of JSObject changes during execution to enable inline
// caching.
class JSObject : public JSReceiver {
public:
static bool IsUnmodifiedApiObject(FullObjectSlot o);
V8_EXPORT_PRIVATE static V8_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT MaybeHandle<JSObject> New(
Handle<JSFunction> constructor, Handle<JSReceiver> new_target,
Handle<AllocationSite> site);
static MaybeHandle<NativeContext> GetFunctionRealm(Handle<JSObject> object);
// 9.1.12 ObjectCreate ( proto [ , internalSlotsList ] )
// Notice: This is NOT 19.1.2.2 Object.create ( O, Properties )
static V8_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT MaybeHandle<JSObject> ObjectCreate(
Isolate* isolate, Handle<Object> prototype);
// 源码太长,略。。。
}
V8 会将 JavaScript 对象编译成 JSObject 的实例,从 JavaScript 层面看来,函数(Function)和对象(Object)的关系是你中有我,我中有你,互相依偎,唇齿相依,如下图:
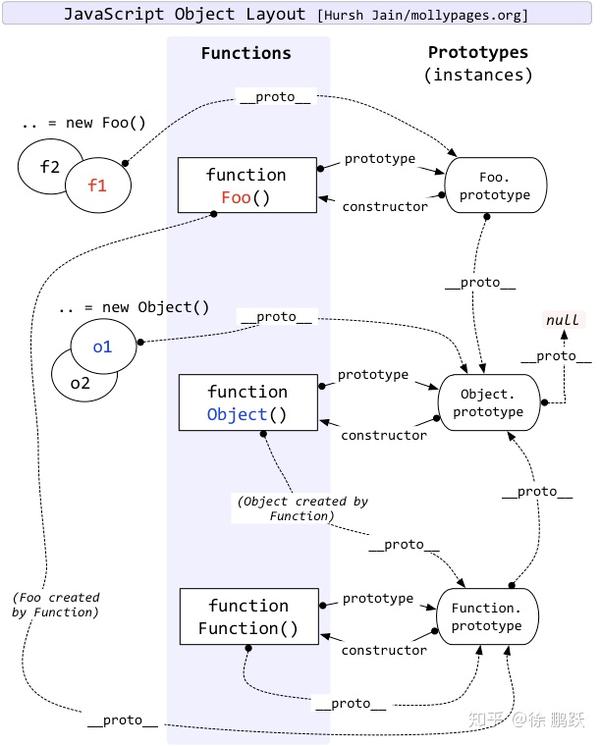
从 V8 源码来看,JavaScript 函数是 JSFunction 的实例,JavaScript 对象是 JSObject 的实例,JSObject 是 JSFunction 的父类,所以 JavaScript 函数具备 JavaScript 对象拥有的绝大部分功能,对象能做的事情,函数也可以做,从这个角度也可以理解 JavaScript 的函数是一等公民。
总结
C 语言编译器把 C 语言函数编译成机器码,V8 把 JavaScript 函数编译成 C++ 对象,C++ 对象是 C++ 世界中当之无愧的一等公民,JavaScript 函数当然也是一等公民。